- Memmingen
-
Memmingen The Renaissance town hall of Memmingen. 
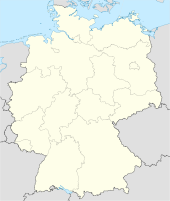
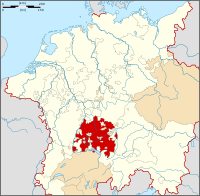
Coordinates 47°59′16″N 10°10′52″E / 47.98778°N 10.18111°ECoordinates: 47°59′16″N 10°10′52″E / 47.98778°N 10.18111°E Administration Country Germany State Bavaria Admin. region Swabia District Urban district Mayor Ivo Holzinger (SPD) Basic statistics Area 70.17 km2 (27.09 sq mi) Elevation 601 m (1972 ft) Population 41,025 (31 December 2010)[1] - Density 585 /km2 (1,514 /sq mi) Other information Time zone CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) Licence plate MM Postal code 87700 Area code 08331 Website www.memmingen.de Memmingen is a town in the Bavarian administrative region of Swabia in Germany. It is the central economic, educational and administrative centre in the Danube-Iller region. To the west the town is flanked by the Iller, the river that marks the Baden-Württemberg border. To the north, east and south the town is surrounded by the district of Unterallgäu (Lower Allgäu).
With about 42,000 inhabitants, Memmingen is the 5th biggest town in the administrative region of Swabia. The origins of the town go back to the Roman Empire. The old town, with its many courtyards, castles and patricians' houses, palaces and fortifications is one of the best preserved in southern Germany. With good transport links by road, rail and air, it is the transport hub for Upper and Central Swabia, and the Allgäu.
Due to its proximity to the Allgäu region, Memmingen is often called the Gateway to the Allgäu (Tor zum Allgäu). The town motto is Memmingen – Stadt mit Perspektiven ("Memmingen - a town with perspectives"). In recent times it has been frequently referred to as Memmingen – Stadt der Menschenrechte (Memmingen - the town of human rights). This alludes to the Twelve Articles, considered to be the first written set of human rights in Europe, which were penned in Memmingen in 1525. Every four years there is the Wallensteinfestspiel, with about 4,500 participants, the biggest historical reenactment in Europe. It commemorates the invasion of Wallenstein and his troops in 1630.
Contents
History
It is believed that on the site of present day Memmingen in Roman times there was a small military town, probably called Cassiliacum. In the 5th century an Alemanic settlement was established and in the 7th century there was here a palace belonging to the king of the Franks.
Memmingen was linked to Bohemia, Austria and Munich by the salt road to Lindau. Another important route through Memmingen was the Italian road from Northern Germany to Switzerland and Italy. Both roads helped Memmingen gain importance as a trading centre. In the Middle Ages, the place was known as Mammingin; in 1158 the Welfian Duke Welf VI founded the town of Memmingen. In 1286 it became an Imperial City, responsible only to the Kaiser.
Christoph Schappeler, the preacher at St. Martin's in Memmingen during the early 16th century, was an important figure during the Protestant Reformation and the German Peasants' War. His support for peasant rights helped to draw peasants to Memmingen. The city first followed the Tetrapolitan Confession, and then the Augsburg Confession.
The Twelve Articles: The Just and Fundamental Articles of All the Peasantry and Tenants of Spiritual and Temporal Powers by Whom They Think Themselves Oppressed was written (probably by Schappeler and Sebastian Lotzer) in early 1525. This was a religious petition borrowing from Luther's ideas to appeal for peasant rights. Within two months of its publication in Memmingen, 25,000 copies of the tract were in circulation around Europe. These are the first known set of human rights documents in the world.
In the 1630s Memmingen was at centre stage during the Thirty Years' War, and the Imperial generalissimo Wallenstein was quartered in the town when he was dramatically dismissed from service. From 1632 Memmingen was briefly garrisoned by the Swedish army, and became a base of operations for Swedish troops in Swabia.
Following the reorganization of Germany in 1802, Memmingen became part of Bavaria. The 19th century saw the slow economic deterioration of the town, which was halted only with the building of a railway following the course of the River Iller.
Since World War II Memmingen has been a developing town, with a rate of economic growth above the average for Bavaria.
Culture and main attractions
Every year Memmingen celebrates the Fischertag (Fisherman's day), recreating medieval traditions. Every four years Memmingen re-enacts the events around the visit of Wallenstein in 1630. The next Wallenstein Festival will occur during the summer of 2012.
Theatre
The theatre has a long tradition in Memmingen. By the Middle Ages some chroniclers were already recording different theatre performances. In 1937 the Landestheater Schwaben (State Theatre of Swabia) or LTS was founded in the city. In 1945, after World War II, the LTS was one of the first theatres in West Germany to begin putting on performances again. The performances take place in the Rooms of the City Theatre, the theatre at the Schweizerberg (cabaret stage), in the Kaminwerk cultural centre or in rooms at the boroughs of Memmingen. The Schweizerberg Theatre will be closed at the end of 2010. It will move to new premises in the Elsbethen area, behind the City Theatre, where a new cabaret stage, rehearsing rooms, workshops, depots, management rooms, the foyer and some guest rooms will be built.[2] Another theatre was founded by Helmut Wolfseher and members of the Alternative Kleinkunst e.V. (Alternative Cabaret Society), Parterretheater im Künerhaus (PIK). This theatre is specifically for amateur actors and young talented musicians. The Kaminwerk also puts on major plays by amateur actors. The municipal hall is for Volksschauspieler or other artists. There have also been several world premières in Memmingen. For example the Metal Operas by David DeFeis who has reached pan-German popularity with reports in Der Spiegel or national newspapers like the Süddeutsche Zeitung.
The following works featuring Memmingen have been produced:
- Stage play Memmingen from Bettina Fless (1989)
- Book Mohr of Memmingen from Utz Benkel
- Song Memmingen by Blackmore’s Night, see aso Shadow of the Moon
Stage plays and operas that have had world premières in Memmingen are:
- 1995: The Jewbank
- Metal-Operas by David DeFeis:
- 2005: Mohr of Memmingen
- 2007: Green Organes
- 2008: Katharina and Till (10 January 2009)
Museums
The biggest museum in Memmingen is the Town Museum at the Hermannsbau.[3] The town's history is described in its historical rooms. There is also a section covering the history of the Jewish people, who lived in Memmingen until 1939. Part of a Torah from the destroyed synagogue is on display there. The Freudenthal/Altvater Homeland Museum for refugees who have settled in Memmingen is also part of the town museum. It is one of 43 homeland museums recognised by the Ministry of the Interior. A foundation, founded and administered by the town, takes responsibility for the museum. The Antonier- and Strigelmuseum at the Antonierkloster have displayes of the wood carvings and paintings from the Strigel artist's family and the work of the Hospital Brothers of St. Anthony.[4] The museum was opened in 1996. With donations from the Memminger Wohnungsbaugenossenschaft (MeWo) the MeWo-Kunsthalle (art hall) was opened in 2005 in the rooms of the old station postal depot. The museum has paintings from the Memmingen artists Max Unold and Josef Madlener as well as a rolling exhibition of other artists.[5] Such an art gallery is unique in Middle and Upper Swabia. The former Kreuzherren monastery is used for rolling exhibitions.[6]
Music
The organ concerts in the St.-Martins-Church are famous in the region. Chamber music would be performed in the former Kreuzherren monastery and also in some other buildings in Memmingen.
There are several Pubs, Restaurants, Wine taverns and Cafés and also some discothèques in an around the City. The cultural centre Kaminwerk (Chimney factory) is for concerts, theater, program cinema, readings and special parties.
Buildings
Memmingen has considerable tourist interest, mainly because large areas of the medieval old town survived both World War II and the tasteless post-war reconstruction which has ruined many other German cities. There are ten city gates and towers and about two kilometres of the city wall. The old town contains many interesting houses of patricians, some in the baroque style. They are picturesque Streets with the Stadtbach (town river) beside. The medieval market place, surrounded by the town hall, which is built in renaissance style, the Großzunft(Guildhouse) and the painted Steuerhaus (tax house). Also famous is St. Martin's church, built in gothic style with its over 500 year-old Choir and the 1996 restored Hospital Brothers of St. Anthony monastery (Antonierkloster), the oldest, best conserved and biggest of these kind. The probably oldest church in town Unser Frauen (Church of Our Lady) or also called Frauenkirche with significant frescos of the 15. and 16. century. Also the Seven Roof House, the baroque Kreuzherren monastery, the renovated whorehouse of the city, the Salzstadel (salt barn), the Kramerzunft (shopkeepers guild, also called the Twelve-Article-House are sights in Memmingen. Not so well known is the Bismarck tower in the west of Memmingen. Beside the tower is the 2007 build new soccer stadium.[7]
Parks
Green areas were created all along the city wall. The old ditches where filled up and replaced with green areas or parks with partially over 150-year-old trees. The name of the parks are (starting clockwise at the Ulmer Gate): Hubergarten, Zollergarten, Ratzengraben/Zollergraben, Kohlschanze, Reichshain, Kaisergraben, Hohe Wacht, Westertorplatz, Grimmelschanze. Nearby every residential area has its own smaller parks. There is also the city park in the New World, the old Landesgartenschau place. Also the old and the forest cemetery, which are both used as parks.
Cemeteries
There were four cemeteries in Memmingen in the Middle Ages. They were around the St. Martin's Church and the Church of Our Lady, also at the Kreuzherren monastery and the Scottish monastery.[8] They were abandoned in 1530. The replacement was the Old cemetery at the former Scottish monastery. This cemetery was abandoned in 1930. The closing of the Old Cemetery has involved a new Cemetery. It was founded in the east of Memmingen as a Forest Cemetery. More cemeteries are in the districts Amendingen, Steinheim, Buxach, Volkratshofen, Ferthofen and Dickenreishausen. In the east of the city is also a Jewish cemetery.
Geography
Memmingen is located at the western border of Bavaria at the river Iller, 50 km south of Ulm, and 100 km west of Munich. The landscape or region beginning with Memmingen is called Unterallgäu and forms a part of the region Mittelschwaben who is next to Oberschwaben and Allgäu. Memmingens named also Gate to the Allgäu. It is reached by the A7 and the A96 motorways and connected to the railroads Munich-Lindau and Ulm-Oberstdorf.
Politics
Although the Lord Mayor has been from the Social Democratic Party of Germany since 1966, the biggest party in the city council is traditionally the Christian Social Union.
The city politics is mostly dominated by a coalition of bigger parties ("coalition of the reasoned") from CSU, SPD, Christlicher Rathausblock Memmingen (Christian Town Hall Party Memmingen) and the Free Voters. The smaller parties of Ecological Democratic Party, Alliance '90/The Greens and the Free Democratic Party are building the opposition.
There was a hefty dispute between the parties in 2005, concerning financial participation in the Memmingen Airport. The Ecological Democratic Party and the Greens initiated a referendum to inhibit financial support for the airport, but this vote met with no success.
At the top of the city government is the Lord Mayor, who is elected directly by the people. The next vote will be 2010. He is the representative of the town and the leader of municipality. As second representatives, tho majors are elected from the members of the city council. Historically the CSU, as biggest party, appoints the second major. The third major is appointed by the third biggest party. The second biggest party, the SPD, traditionally declines to appoint the third major, because they already appoint the Lord Mayor.
Memmingen is building, alongside the double centre Ulm/Neu-Ulm, the second economical centre in Upper Swabia. It thus leads the central supply function for the adjoining cities and districts.
City Council
The last local elections were on March 2, 2008, with following results:[9]
CSU SPD CRB ¹ FV Greens ödp FDP Sum Seats 13 9 4 5 3 4 2 40 Percent 32,2 % 22,0 % 10,8 % 11,8 % 6,7 % 10,5 % 5,9 % ¹ Christlicher Rathausblock Memmingen ("Christian Townhall-Party")
Lord Mayors
- 1884–1909: Karl Scherer
- 1910–1931: Fritz Braun
- 1932–1945: Heinrich Berndl, NSDAP
- 1945–1948: Georg Fey, CSU
- 1948–1952: Lorenz Riedmiller, SPD
- 1952–1966: Heinrich Berndl, without party
- 1966–1968: Rudolf Machnig, SPD
- 1968–1980: Johannes Bauer, SPD
- 1980–today: Ivo Holzinger, SPD
City Finances
Memmingen is, with its low level of debt, from €512 per capita, is one of the cities in Germany with the lowest level of debt[10] (Germany-wide more than €1,300). The city had 2007 a management budget (Verwaltungshaushalt) of €94,925,160 and an asset budget (Vermögenshaushalt) of €19,490,860. The income from trade taxes amounted to about €40 million, the income tax assignment to about €20 million. The local rates were last changed in 2003. The city has many charitable foundations, with roots partly going back to the Middle Ages (such as the Unterhospitalstiftung).
Coat of Arms and Flag
Blazon: Split from gold and silver, in front a half, reinforced in red, black eagle. Backward a red pawcross
The city's colours, handed down since 1488, are Black, Red, White. The flag is a banner flag with cross bar.
Amendingen and Eisenburg have their own historical coats of arms.
International relations
Memmingen is twinned with:
 Glendale, Arizona, USA, since 1976
Glendale, Arizona, USA, since 1976 Province of Teramo, Italy, since 1981
Province of Teramo, Italy, since 1981 Teramo, Italy, since 1981
Teramo, Italy, since 1981 Auch, France, since 1990
Auch, France, since 1990 Eisleben, Germany, since 1990
Eisleben, Germany, since 1990 Kiryat Shmona, Israel, since 2009
Kiryat Shmona, Israel, since 2009 Karataş, Turkey, since 2009
Karataş, Turkey, since 2009 Litzelsdorf, Austria, since 2009
Litzelsdorf, Austria, since 2009 Chernihiv, Ukraine, since 2009
Chernihiv, Ukraine, since 2009
Memmingen has a partnership with:
 Colmar, France
Colmar, France
Trade and Economy
Most of its enterprises are SMEs. Of importance are:
- Metzeler [1]
- Berger High-Tech-Zerspanung
- Magnet-Schultz
- Hans Kolb Wellpappe
- Pfeifer Seil- und Hebetechnik
- Memminger Brauerei
- Gefro Reformversand
- Alpine Hydraulik
- Dachser Logistics
- Rohde & Schwarz
- Goldhofer
Famous people
- Holger Badstuber, Footballer for Bayern Munich.[11]
- Mario Götze, footballer for Borussia Dortmund
- Timo Gebhart, footballer for VfB Stuttgart
References
- ^ "Fortschreibung des Bevölkerungsstandes" (in German). Bayerisches Landesamt für Statistik und Datenverarbeitung. 31 December 2010. https://www.statistikdaten.bayern.de/genesis/online?language=de&sequenz=tabelleErgebnis&selectionname=12411-009r&sachmerkmal=QUASTI&sachschluessel=SQUART04&startjahr=2010&endjahr=2010.
- ^ New Buildings at the Elsbethen area
- ^ The memminger museums
- ^ official museums website
- ^ Official site of the art hall
- ^ Official site of the Kreuzherren monastery
- ^ Meminger soccer stadium
- ^ Author:Joachim Jahn and others, Title:Die Geschichte der Stadt Memmingen – Von den Anfängen bis zum Ende der Reichsstadtzeit (Band 1), Publisher:Theiss Verlag, Location:Memmingen, Year:1997, ISBN:3-8062-1315-1, Page:98
- ^ Election Result
- ^ Memmingen Newspaper, 2008-03-12, Page 27
- ^ "Holger Badstuber". Bayern Munich. http://www.fcbayern.t-home.de/en/teams/profis/19900.php. Retrieved 30 May 2011.
External links
- Official website (English)
- memmingen-online.de (German)
 Swabian League (1488–1534) of the
Swabian League (1488–1534) of the  Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman EmpireImperial Cities Aalen · Augsburg · Biberach · Bopfingen · Dinkelsbühl · Donauwörth · Esslingen · Giengen · Heilbronn · Isny · Kaufbeuren · Kempten · Leutkirch · Lindau · Memmingen · Nördlingen · Pfullendorf · Ravensburg · Reutlingen · Schwäbisch Gmünd · Schwäbisch Hall · Überlingen · Ulm · Wangen · Weil · Wimpfen
Nobility Territories Württemberg · Brandenburg-Ansbach · Baden · Bavaria · Bayreuth · Electoral Palatinate · Hesse · Mainz · TrierFree Imperial Cities of the Holy Roman Empire As of 1792 Aachen · Aalen · Augsburg · Biberach · Bopfingen · BremenH · Buchau · Buchhorn · CologneH · Dinkelsbühl · DortmundH · Eßlingen · Frankfurt · Friedberg · Gengenbach · Giengen · GoslarH · HamburgH · Heilbronn · Isny · Kaufbeuren · Kempten · Kessenich · Leutkirch · Lindau · LübeckH · Memmingen · Mühlhausen · MülhausenD, S · Nordhausen · Nördlingen · Nuremberg · Offenburg · Pfullendorf · Ravensburg · Regensburg · Reutlingen · Rothenburg · RottweilS · Schwäbisch Gmünd · Schwäbisch Hall · Schweinfurt · Speyer · Überlingen · Ulm · Wangen · Weil · Weißenburg in Bayern · Wetzlar · Wimpfen · Windsheim · Worms · Zell
Free Imperial Cities as at 1648 Cities that lost Imperial immediacy or gained independence before 1792 BaselS · BernS · Besançon · Brakel · Cambrai · Diessenhofen · Donauwörth · Duisburg · Düren · Gelnhausen · HagenauD · Herford · KaysersbergD · KolmarD · Konstanz · LandauD · Lemgo · LucerneS · Mainz · Metz · MunsterD · ObernaiD · Pfeddersheim · Rheinfelden · RosheimD · St. GallenS · Sarrebourg · SchaffhausenS · Schmalkalden · SchlettstadtD · SoestH · SolothurnS · Straßburg · Toul · TurckheimD · Verden · Verdun · Warburg · Weißenburg in ElsaßD · ZürichSD: Member of the Décapole. H: Member of the Hanseatic League. S: Member or associate of the Swiss Confederacy. Urban and rural districts in the Free State of Bavaria in Germany
Urban and rural districts in the Free State of Bavaria in Germany 
Urban
districtsAmberg · Ansbach · Aschaffenburg · Augsburg · Bamberg · Bayreuth · Coburg · Erlangen · Fürth · Hof · Ingolstadt · Kaufbeuren · Kempten · Landshut · Memmingen · München (Munich) · Nürnberg (Nuremberg) · Passau · Regensburg · Rosenheim · Schwabach · Schweinfurt · Straubing · Weiden · WürzburgRural
districtsAichach-Friedberg · Altötting · Amberg-Sulzbach · Ansbach · Aschaffenburg · Augsburg · Bad Kissingen · Bad Tölz-Wolfratshausen · Bamberg · Bayreuth · Berchtesgadener Land · Cham · Coburg · Dachau · Deggendorf · Dillingen · Dingolfing-Landau · Donau-Ries · Ebersberg · Eichstätt · Erding · Erlangen-Höchstadt · Forchheim · Freising · Freyung-Grafenau · Fürstenfeldbruck · Fürth · Garmisch-Partenkirchen · Günzburg · Haßberge · Hof · Kelheim · Kitzingen · Kronach · Kulmbach · Landsberg · Landshut · Lichtenfels · Lindau · Main-Spessart · Miesbach · Miltenberg · Mühldorf · München (Munich) · Neuburg-Schrobenhausen · Neumarkt · Neustadt (Aisch)-Bad Windsheim · Neustadt (Waldnaab) · Neu-Ulm · Nürnberger Land · Oberallgäu · Ostallgäu · Passau · Pfaffenhofen · Regen · Regensburg · Rhön-Grabfeld · Rosenheim · Roth · Rottal-Inn · Schwandorf · Schweinfurt · Starnberg · Straubing-Bogen · Tirschenreuth · Traunstein · Unterallgäu · Weilheim-Schongau · Weißenburg-Gunzenhausen · Wunsiedel · WürzburgCategories:- Towns in Bavaria
- Imperial free cities
- Memmingen
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.