- Esslingen am Neckar
-
Esslingen 
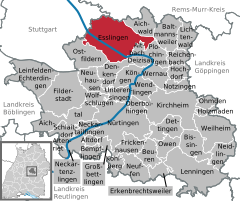
Coordinates 48°44′0″N 9°19′0″E / 48.733333°N 9.316667°ECoordinates: 48°44′0″N 9°19′0″E / 48.733333°N 9.316667°E Administration Country Germany State Baden-Württemberg Admin. region Stuttgart District Esslingen Mayor Jürgen Zieger (SPD) Basic statistics Area 46.43 km2 (17.93 sq mi) Elevation 241 m (791 ft) Population 91,869 (31 December 2010)[1] - Density 1,979 /km2 (5,125 /sq mi) Other information Time zone CET/CEST (UTC+1/+2) Licence plate ES Postal codes 73701–73734 Area code 0711 Website www.esslingen.de Esslingen am Neckar is a city in the Stuttgart Region of Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany, capital of the District of Esslingen as well as the largest city in the district.
It is located on the Neckar River, about 14 km southeast of Stuttgart city centre. The surrounding regions are also mostly developed around the city of Esslingen.
Contents
History
Prehistoric times
Through archealogical findings there is evidence of permanent settlement in what is now the city of Esslingen since the Neolithic Stone Age. Traces of human settlement found at the site of the city church date back to 1000 B.C.
Roman times
In the 1st century AD the Esslingen region became a part of the Roman Empire. During this period there existed a Roman warehouse in the area of Oberesslingen. The next major Roman settlements and garrisons were Cannstatt and Köngen.
Middle Ages
Esslingen was first mentioned in 777 as Ezelinga in the last will of Abbot Fulrad from Saint-Denis (near Paris), the chaplain of Pippin and Charlemagne. He bequeathed the church sixth cell upon the river Neckar to his monastery Saint-Denis. He also brought the bones of Saint Vitalis to Esslingen, which made it a target for pilgrimage and led to its growth.
Around 800 Esslingen became a market town, its market rights being certified in 866. In 949–953 it was a possession of Liudolf, Duke of Swabia. Esslingen received city rights in 1229 under Emperor Frederick II. During the same period the still extant Neckar bridge was constructed, which made Esslingen a major centre for trade on the route between Italy, Switzerland, and Northern Germany. Taxes provided by the bridge and market led to further growth of the town as did the export of the highly regarded wines from the region.
The time between the 13th century and 16th century saw many conflicts between the Free Imperial City and the Counts of Württemberg (later Duchy of Württemberg). About half the population lost their lives in the Thirty Years War between 1618 and 1648 through famine or epidemics. Esslingen lost its independence as an Imperial city in 1803, becoming part of the Duchy of Württemberg.
19th century to date
The beginning of 19th century was characterised by industrialisation. Glove manufacturing, food processing, textiles, and metal working were early industries in Esslingen. On 20 November 1845 the first train ran from Cannstatt to Esslingen station.
Esslingen was occupied by U.S. soldiers in April 1945, toward the end of World War II. During the war the city suffered very little damage thus most of the medivial appearance of its city centre has been preserved.
After the Second World War, about 47,000 people (mostly refugees and displaced persons from the Eastern Germany) moved to Esslingen. There were settlements in Oberesslingen and Zollberg, in order to overcome the shortage of housing.
In 1973 Nürtingen district was merged with Esslingen am Neckar making Esslingen the seat of a much enlarged district.
Hochschule Esslingen
Esslingen is home to a University of Applied Science. The Esslingen University of Applied Sciences (German: Hochschule Esslingen) is known for its mechanical engineering and automotive engineering courses. The graduate school of Hochschule Esslingen offers three Masters courses, taught completely in English.
1. ME in Automotive Systems
2. ME in Design and Development in Automotive and Mechanical Engineering
3. MBA in International Industrial Management
Twin cities
 Eger, Hungary
Eger, Hungary Maladzyechna, Belarus
Maladzyechna, Belarus Neath Port Talbot, United Kingdom
Neath Port Talbot, United Kingdom Norrköping, Sweden
Norrköping, Sweden Piotrków Trybunalski, Poland
Piotrków Trybunalski, Poland Schiedam, Netherlands
Schiedam, Netherlands Sheboygan, Wisconsin, USA
Sheboygan, Wisconsin, USA Udine, Italy
Udine, Italy Velenje, Slovenia
Velenje, Slovenia Vienne, France
Vienne, France Coimbatore, India
Coimbatore, India
References
- ^ "Bevölkerung und Erwerbstätigkeit" (in German). Statistisches Landesamt Baden-Württemberg. 31 December 2009. http://www.statistik-bw.de/Veroeffentl/Statistische_Berichte/3126_10001.pdf.
External links
- Official website (German)
- City Portal (German)
- Esslingen University of Applied Sciences (German) (English)
- description of the Esslingen round walk with many pictures (German)
 Swabian League (1488–1534) of the
Swabian League (1488–1534) of the  Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman EmpireImperial Cities Aalen · Augsburg · Biberach · Bopfingen · Dinkelsbühl · Donauwörth · Esslingen · Giengen · Heilbronn · Isny · Kaufbeuren · Kempten · Leutkirch · Lindau · Memmingen · Nördlingen · Pfullendorf · Ravensburg · Reutlingen · Schwäbisch Gmünd · Schwäbisch Hall · Überlingen · Ulm · Wangen · Weil · Wimpfen
Nobility Territories Württemberg · Brandenburg-Ansbach · Baden · Bavaria · Bayreuth · Electoral Palatinate · Hesse · Mainz · TrierFree Imperial Cities of the Holy Roman Empire As of 1792 Aachen · Aalen · Augsburg · Biberach · Bopfingen · BremenH · Buchau · Buchhorn · CologneH · Dinkelsbühl · DortmundH · Eßlingen · Frankfurt · Friedberg · Gengenbach · Giengen · GoslarH · HamburgH · Heilbronn · Isny · Kaufbeuren · Kempten · Kessenich · Leutkirch · Lindau · LübeckH · Memmingen · Mühlhausen · MülhausenD, S · Nordhausen · Nördlingen · Nuremberg · Offenburg · Pfullendorf · Ravensburg · Regensburg · Reutlingen · Rothenburg · RottweilS · Schwäbisch Gmünd · Schwäbisch Hall · Schweinfurt · Speyer · Überlingen · Ulm · Wangen · Weil · Weißenburg in Bayern · Wetzlar · Wimpfen · Windsheim · Worms · Zell
Free Imperial Cities as at 1648 Cities that lost Imperial immediacy or gained independence before 1792 BaselS · BernS · Besançon · Brakel · Cambrai · Diessenhofen · Donauwörth · Duisburg · Düren · Gelnhausen · HagenauD · Herford · KaysersbergD · KolmarD · Konstanz · LandauD · Lemgo · LucerneS · Mainz · Metz · MunsterD · ObernaiD · Pfeddersheim · Rheinfelden · RosheimD · St. GallenS · Sarrebourg · SchaffhausenS · Schmalkalden · SchlettstadtD · SoestH · SolothurnS · Straßburg · Toul · TurckheimD · Verden · Verdun · Warburg · Weißenburg in ElsaßD · ZürichSD: Member of the Décapole. H: Member of the Hanseatic League. S: Member or associate of the Swiss Confederacy.Aichtal | Aichwald | Altbach | Altdorf | Altenriet | Baltmannsweiler | Bempflingen | Beuren | Bissingen (Teck) | Deizisau | Denkendorf | Dettingen (Teck) | Erkenbrechtsweiler | Esslingen am Neckar | Filderstadt | Frickenhausen | Großbettlingen | Hochdorf | Holzmaden | Kirchheim (Teck) | Kohlberg | Köngen | Leinfelden-Echterdingen | Lenningen | Lichtenwald | Neckartailfingen | Neckartenzlingen | Neidlingen | Neuffen | Neuhausen (Fildern) | Notzingen | Nürtingen | Oberboihingen | Ohmden | Ostfildern | Owen | Plochingen | Reichenbach an der Fils | Schlaitdorf | Unterensingen | Weilheim | Wendlingen | Wernau | Wolfschlugen Categories:
Categories:- Municipalities in Baden-Württemberg
- Towns in Baden-Württemberg
- States of the Holy Roman Empire
- Imperial free cities
- Esslingen district
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.