- Norfolk Southern Railway (1942–1982)
-
Norfolk Southern Railway 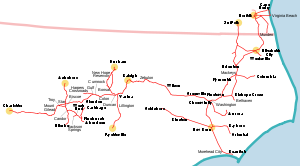
"All-time" system map, showing all lines in the Norfolk Southern system prior to 1974Reporting mark NS Locale Norfolk, VA to Charlotte, NC Dates of operation 1881–1974 Successor Southern Railway (now Norfolk Southern Railway) Track gauge 4 ft 8 1⁄2 in (1,435 mm) (standard gauge) Headquarters Norfolk, VA (moved to Raleigh, NC on September 29, 1961) The Norfolk Southern Railway (reporting mark NS) was the final name of a railroad running from Norfolk, Virginia southwest and west to Charlotte, North Carolina. It was acquired by the Southern Railway in 1974, which was merged with the Norfolk and Western Railway in 1990 to form the current entity of the Norfolk Southern Railway.
Contents
History
The Elizabeth City and Norfolk Railroad was established January 20, 1870, and in 1881 the line opened, running south from Berkley, Virginia, across the Eastern Branch of the Elizabeth River from Norfolk, via Elizabeth City to Edenton, North Carolina. On February 1, 1883 the name was changed to the Norfolk Southern Railroad, reflecting the company's ambitions to build further. It entered receivership for the first time in 1889, and was purchased April 29 and reorganized May 1891 as the Norfolk and Southern Railroad. By that time it had acquired trackage rights over the Norfolk and Western Railroad over the Elizabeth River into Norfolk. With the reorganization also came the acquisition of the Albemarle and Pantego Railroad in North Carolina from the John L. Roper Lumber Company, extending the line from Mackeys on the other side of the Albemarle Sound from Edenton south to Belhaven on the Pungo River, a branch of the Pamlico River.
On November 1, 1899, the N&S bought the Norfolk, Virginia Beach and Southern Railroad, running east from Norfolk to Virginia Beach on the Atlantic Ocean. An extension which ran parallel to the oceanfront took the line north from Virginia Beach to Cape Henry in 1902, but only two years later the N&S bought the competing Chesapeake Transit Company which had a line from Norfolk to Cape Henry via the Lynnhaven Inlet area and hence to Virginia Beach, and abandoned its duplicative trackage between Cape Henry and Virginia Beach. The passenger rail service to the Oceanfront area was a key factor in the growth of the Town of Virginia Beach as a resort in the late 19ths and early 20th century, which was only much later eclipsed by the construction of the paved Virginia Beach Boulevard roadway between the Oceanfront area and Norfolk in 1922.
Also in 1902, the N&S acquired the Roanoke Railroad and Lumber Company's Washington and Plymouth Railroad, running from Plymouth, North Carolina, south to Washington, built a line from Mackeys to Plymouth, and began a car ferry operation across the Albemarle Sound between Edenton and Mackeys (replaced by a bridge in 1910). The W&P had been built by the lumber company in 1889 to 3 foot (914 mm) narrow gauge, became a common carrier in 1901, and was re-gauged by the N&S in 1904.
The Raleigh and Eastern North Carolina Railroad was organized in 1903 and renamed the Raleigh and Pamlico Sound Railroad in 1905. In 1906 it built a line from the end of the N&S at Washington south to Bridgeton, as well as a completely separated line from Raleigh east to Zebulon.
On November 24, 1906, the Norfolk and Southern Railway was formed as a consolidation of the Norfolk and Southern Railroad with the Raleigh and Pamlico Sound Railroad and several other companies:
- Virginia and Carolina Coast Railroad: built 1885 to 1902 from Suffolk, Virginia south to Edenton and from Beckford Junction (on the Suffolk-Edenton section) to Elizabeth City; originally built as the Suffolk and Carolina Railway and renamed in 1906).
- Pamlico, Oriental and Western Railway: built 1906 from New Bern (across the Neuse River from Bridgeton) east to Bayboro, including a bridge over the Neuse River that became part of the main line.
- Atlantic and North Carolina Railroad (leased September 1, 1904): built 1858 from Goldsboro southeast to Morehead City, intersecting the main line at New Bern.
- Beaufort and Western Railroad: built 1905 from Morehead City east to Beaufort.
The company again entered receivership in 1908, and in 1910 reorganized as the Norfolk Southern Railroad. That same year it built a long branch from Chocowinity (also known as Marsden) on the main line south of Washington west to the isolated section to Raleigh at Zebulon (that became the main line to Charlotte via Raleigh, while the old line to New Bern became a branch). Several shorter branches also opened that year - from Bayboro south to Oriental, from Pinetown on the main line east to Bishops Cross on the line to Belhaven, and from Mackeys east to Columbia (as well as a trestle across the Albemarle Sound between Mackeys and Edenton).
The Egypt Railroad was chartered June 14, 1890, and opened October 15, 1891, running a short distance from Colon on the Seaboard Air Line Railroad main line west to Cumnock. It was leased to the Raleigh and Western Railway, another short line continuing west from Cumnock to Harpers Crossroads, on September 6, 1893. The company entered receivership in 1907 and operations west of Cumnock were suspended in 1908. The Egypt Railroad was reorganized April 1, 1910, as the Sanford and Troy Railroad.
The Durham and Charlotte Railroad was chartered March 2, 1893 and planned to connect the two cities named with the railroad. On July 15, 1896, it bought the Glendon and Gulf Railroad, running from Gulf (west of Cumnock) southwest to Glendon. After reaching Elise (Robbins) in 1899, the Durham and Charlotte Railroad was building towards Star. The company endured several years of litigation over the right-of-way with a Wright Tramway, which was built in 1896. The tramway was removed in 1901 and the Durham and Charlotte Railroad was then built to Star by 1902. Some time after 1900 it bought the former Raleigh and Western Railway right-of-way and rebuilt the line from Cumnock to Gulf, and built an extension from Star southwest to Troy.
In November 1911, the NS formed the Raleigh, Charlotte and Southern Railway (RC&S) as a consolidation of several smaller companies; the RC&S was merged into the NS in fall 1912. The RC&S was made up of the Sanford and Troy Railroad, Durham and Charlotte Railroad, and the following lines:
- Raleigh and Southport Railway: Raleigh south to Fayetteville.
- Aberdeen and Asheboro Railroad: Aberdeen northwest to Asheboro, with a branch from Biscoe west via Troy to Mount Gilead, and several other short branches.
At the time, only the Raleigh and Southport Railway connected to the other NS lines. In 1914 the NS built a line from Varina on the former R&S southwest to Colon and from Mount Gilead west to Charlotte, giving it a continuous line, using the former S&T, D&C and branch of the A&A from Colon to Mount Gilead.
On May 27, 1920, the NS leased the Durham and South Carolina Railroad, giving it access to Durham. The D&SC ran from Durham south to Bonsal on the Seaboard Air Line Railroad, and was extended to Duncan on the NS around the time the NS leased it.
Another receivership came in 1932, and in 1935 it defaulted on its lease of the Atlantic and North Carolina Railroad, which was reincorporated November 16 of that year. Many branch lines were abandoned or sold during that period, such as the local lines in Suffolk, Virginia, which were sold to the Virginian Railway in 1940. On January 21, 1942, the company was reorganized for the last time as the Norfolk Southern Railway.
On January 1, 1974, the Southern Railway bought the Norfolk Southern Railway and merged it into the Carolina and Northwestern Railway, but kept the Norfolk Southern Railway name. In 1982 the Carolina and Northwestern name was brought back to free up the Norfolk Southern name for the planned merger of the Southern Railway with the Norfolk and Western Railway. The new Norfolk Southern Railway was formed in 1982; (Or, as some say tongue in cheek, the Southern tucked the Norfolk Southern name in its briefcase, stopped in Roanoke to pick up a friend, and then went on to Washington, D.C.). While the name had once represented simply the Virginia and North Carolina based railroad which ran south from Norfolk to Charlotte, it was now a combination of the names of the two merged Class I railroads.
Norfolk Southern still owns the main line from Gulf (near Cumnock) northeast to Raleigh. The part from Gulf west to Charlotte (as well as the branch to Aberdeen) is now the Aberdeen, Carolina and Western Railway, the part from Edenton north to Norfolk is now the Chesapeake and Albemarle Railroad, and the Belhaven-Pinetown branch as well as the Plymouth-Raleigh segment is now operated by the Carolina Coastal Railway. The line between Plymouth and Edenton has been removed[1], with the famous Albemarle Sound Trestle having been demolished in the late 1980s.
Company officers
Presidents of Norfolk Southern:
- William E. Philips President, EC&N RR (1881-1882)
- William E. Philips President, NS RR (1883-1889)
- Watson B. Dickerman Receiver, NS RR (1889-1891)
- Watson B. Dickerman President, N&S RR (1891-1899)
- John Carstensen President, N&S RR (1900-1904)
- A.H. Flint President, N&S RR (1904-1905)
- Marsden J. Perry President, N&S RR (1905-1906)
- Frank S. Gannon President, N&S RR (1906-1908)
- Thomas Fitzgerald Receiver, N&S Ry (1908)
- Harry K. Walcott Receiver, N&S Ry (1908-1910)
- Hugh M. Kerr Receiver, N&S Ry (1908-1910)
- E.T. Lamb President, NS RR (1910-1912)
- Charles H. Hix President, NS RR (1912-1914)
- Joseph Young President, NS RR (1914-1918)
- R.H. Swartwout President, NS RR (1918-1919)
- George R. Loyall President, NS RR (1920-1932)
- G.R. Loyall & L.H. Windholz Receivers, NS RR (1932-1933)
- M.H. Hawkins & L.H. Windholz Receivers, NS RR (1933-1942)
- L.A. Beck President, NS Ry (1942-1947)
- J.T. Kingsley President, NS Ry (1947-1953)
- Patrick B. McGinnis served as Chairman of the Board during this time with Washington D.C. promoter, Joseph T. Kingsley. He later went on to Central of Georgia Railway for a while, then to the New York, New Haven and Hartford Railroad and later President of the Boston and Maine Railroad.
- G.M. Self President, NS Ry (1953-1954)
- J.R. Prichard President, NS Ry (1954-1956)
- Henry Oetjen President, NS Ry (1956- ?)
External links
- Norfolk & Southern Railway Historical Society
- History of the Shay Locomotives involved in the area of the Norfolk Southern Railway
- A Brief History of the Norfolk Southern (includes abandonment years)
- Railroad History Database
References
- ^ Bobby R. “Bob” Spruill: Norfolk & Southern Railroad at Mackeys Ferry Accessed 23 Nov 2009
Class I railroads of North America Current Former
(1956–present)AA · ACL · AC&Y · AGS · A&SAB · AT&N · AT&SF · AUT · A&WP · B&AR · B&LE · B&M · BN · B&O · CAR&NW · CB&Q · C&EI · CG · CGW · C&IM · CNJ · CNO&TP · C&NW · C&O · CPME · CR · CRI&P · CRR · C&S · CSPM&O · CV · C&W · C&WC · D&H · DL&W · DM&IR · D&RGW · DSS&A · DT&I · D&TSL · DW&P · EJ&E · EL · ERIE · FEC · FW&D · GA · GB&W · G&F · GM&O · GN · GS&F · GTW · IC · ICG · ITC · KO&G · L&A · L&HR · LI · L&M · L&N · L&NE · LS&I · LV · MEC · MGA · MI · MILW · MIS · MKT · MN&S · MON · MP · M&STL · NC&STL · NH · NKP · NO&NE · NP · NS · N&W · NWP · NYC · NYCN · NYO&W · NYS&W · PC · P&LE · P&N · PRR · PRSL · P&WV · RDG · RF&P · RUT · QA&P · S&A · SAL · SBD · SCL · SD&AE · SI · SIRT · SLSF · SLSFTX · SN · SOU · SP · SP&S · SSW · TC · TFM · TM · T&NO · T&P · TP&W · VGN · WA · WAB · WC · WM · WP(pre–1956) A · AB&A · AB&C · AC · A&D · AE · A&NM · A&STL · A&V · BA&P · BC&A · B&G · BRI · BR&P · B&S · BSL&W · C&A · CA&C · C&C · CC&CS · CCC&STL · CD&C · C&E · C&G · CH&D · C&I · CINN · CI&S · CI&W · CL&N · CM · CM&PS · CNE · CNNE · CNOR · C&OIN · CP&STL · CPVT · CRI&G · CR&NW · CRP · CS · CTH&SE · CV&M · CVRR · DGH&M · D&IR · D&M · DM&N · DNW&P · D&SL · EI&TH · EP&SW · E&TH · F&CC · FJ&G · FS&W · FW&RG · GC · GC&SF · GH&SA · GM&N · GR&I · G&SI · HE&WT · H&TC · HV · ICRY · IGN · ISRR · KCM&O · KCM&OTX · K&M · LA&SL · LA&T · LE&W · LH&STL · LR&N · LR&NTX · LS&MS · LW · MTR · M&A · MC · MD&V · M&I · MKTTX · MLR · ML&T · M&NA · M&O · MO&G · MSC · MSP&SSM · MV · NAL · NCRY · NJ&NY · NN · NOGN · NOM&C · NOT&M · NYP&N · OCAA · OE · OR&L · OSL · OWRN · PB&W · PCC&STL · PCO · PE · P&E · PERK · PM · P&NT · PRDG · P&S · P&SF · PS&N · QO&KC · SA&AP · SAU&G · SB&NY · SD&A · SFP&P · S&IE · SIND · SJ&GI · SKTX · SLB&M · SLIM&S · SOUMS · SSWTX · SUN · T&BV · T&FS · T&N · T&OC · TSTL&W · U&D · UTAH · VAND · VS&P · V&SW · WF&NW · WF&S · WJ&S · W&LE · WPT · WSN · WV · Y&MVTimeline 1910–1929 · 1930–1976 · 1977–presentCategories:- Predecessors of the Southern Railway (U.S.)
- Defunct Virginia railroads
- Defunct North Carolina railroads
- Former Class I railroads in the United States
- Railway companies established in 1942
- Railway companies disestablished in 1982
- Defunct South Carolina railroads
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.


