- Moons of Mars
-
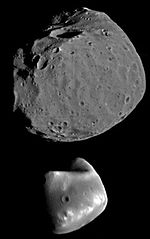
Mars has two small moons, Phobos and Deimos, which are thought to be captured asteroids. Both satellites were discovered in 1877 by Asaph Hall, and are named after the characters Phobos (panic/fear) and Deimos (terror/dread) who, in Greek mythology, accompanied their father Ares, god of war, into battle. Ares was known as Mars to the Romans.
Contents
History
The discovery of the two moons of Mars, Phobos and Deimos, occurred in 1877 when American astronomer Asaph Hall identified them after a long search, although their existence had been a source of speculation before.
Early speculations
The possibility of Martian moons had been speculated long before Hall's discovery. The astronomer Johannes Kepler (1571–1630) even predicted their number correctly, although with faulty logic: he wrote that since Jupiter had four known moons and Earth had one, it was only natural that Mars should have two.[1]
Perhaps inspired by Kepler (and quoting Kepler's third law), Jonathan Swift's satire Gulliver's Travels (1726) refers to two moons in Part 3, Chapter 3 (the "Voyage to Laputa"), in which the astronomers of Laputa are described as having discovered two satellites of Mars orbiting at distances of 3 and 5 Martian diameters, and periods of 10 and 21.5 hours, respectively. The actual orbital distances and periods of Phobos and Deimos of 1.4 and 3.5 Martian diameters, and 7.6 and 30.3 hours, respectively.[1] The orbital periods are roughly similar to those guessed by Swift, but the radii were too big by about a factor of two. Voltaire's 1750 short story Micromégas, about an alien visitor to Earth, also refers to two moons of Mars. Voltaire was presumably influenced by Swift.[2] In recognition of these 'predictions', two craters on Deimos are named Swift and Voltaire.
Discovery
Hall discovered Deimos on August 12, 1877 at about 07:48 UTC and Phobos on August 18, 1877, at the US Naval Observatory in Washington, D.C., at about 09:14 GMT (contemporary sources, using the pre-1925 astronomical convention that began the day at noon, give the time of discovery as August 11, 14:40 and August 17 16:06 Washington mean time respectively).[3][4][5] At the time, he was deliberately searching for Martian moons. Hall had previously seen what appeared to be a Martian moon on August 10, but due to bad weather, he could not definitively identify them until later.
Hall recorded his discovery of Phobos in his notebook as follows:[6]
- I repeated the examination in the early part of the night of [August] 11th, and again found nothing, but trying again some hours later I found a faint object on the following side and a little north of the planet. I had barely time to secure an observation of its position when fog from the River stopped the work. This was at half past two o'clock on the night of the 11th. Cloudy weather intervened for several days.
- On 15 August the weather looking more promising, I slept at the Observatory. The sky cleared off with a thunderstorm at 11 o'clock and the search was resumed. The atmosphere however was in a very bad condition and Mars was so blazing and unsteady that nothing could be seen of the object, which we now know was at that time so near the planet as to be invisible.
- On August 16 the object was found again on the following side of the planet, and the observations of that night showed that it was moving with the planet, and if a satellite, was near one of its elongations. Until this time I had said nothing to anyone at the Observatory of my search for a satellite of Mars, but on leaving the observatory after these observations of the 16th, at about three o'clock in the morning, I told my assistant, George Anderson, to whom I had shown the object, that I thought I had discovered a satellite of Mars. I told him also to keep quiet as I did not wish anything said until the matter was beyond doubt. He said nothing, but the thing was too good to keep and I let it out myself. On 17 August between one and two o'clock, while I was reducing my observations, Professor Newcomb came into my room to eat his lunch and I showed him my measures of the faint object near Mars which proved that it was moving with the planet.
- On August 17 while waiting and watching for the outer moon, the inner one was discovered. The observations of the 17th and 18th put beyond doubt the character of these objects and the discovery was publicly announced by Admiral Rodgers.
The names, originally spelled Phobus and Deimus, respectively, were suggested by Henry Madan (1838–1901), Science Master of Eton, from Book XV of the Iliad, where Ares summons Fear and Fright.[7]
Mars moon hoax
In 1959, Walter Scott Houston perpetrated a celebrated April Fool's hoax in the April edition of the Great Plains Observer, claiming that "Dr. Arthur Hayall of the University of the Sierras reports that the moons of Mars are actually artificial satellites". Both Dr. Hayall and the University of the Sierras were fictitious. The hoax gained worldwide attention when Houston's claim was repeated, apparently in earnest, by a Soviet scientist, Iosif Shklovsky.[8]
Recent surveys
Searches have been conducted for additional satellites. Most recently, Scott S. Sheppard and David C. Jewitt surveyed the Hill sphere of Mars for irregular satellites. [The] search covered nearly the entire Hill sphere, but scattered light from Mars excluded the inner few arcminutes where the satellites Phobos and Deimos reside. No new satellites were found to an apparent limiting red magnitude of 23.5, which corresponds to radii of about 0.09 km using an albedo of 0.07.[9]
Characteristics
 Night sky of Mars showing Deimos (left) and Phobos (right) in front of Sagittarius, as seen by Mars Exploration Rover Spirit on August 26, 2005
Night sky of Mars showing Deimos (left) and Phobos (right) in front of Sagittarius, as seen by Mars Exploration Rover Spirit on August 26, 2005
If viewed from the surface of Mars near its equator, full Phobos looks about one third as big as the Earth's full moon from Earth. It has an angular diameter of between 8' (rising) and 12' (overhead). It would look smaller when the observer is further away from the Martian equator, and is completely invisible (always beyond the horizon) from Mars' polar ice caps. Deimos looks more like a bright star or planet for an observer on Mars, only slightly bigger than Venus looks from Earth; it has an angular diameter of about 2'. The Sun's angular diameter as seen from Mars, by contrast, is about 21'. Thus there are no total solar eclipses on Mars, as the moons are far too small to completely cover the Sun. On the other hand, total lunar eclipses of Phobos are very common, happening almost every night.[10] See also Transit of Phobos from Mars and Transit of Deimos from Mars for eclipse-like events.
The motions of Phobos and Deimos would appear very different from that of our own Moon. Speedy Phobos rises in the west, sets in the east, and rises again in just eleven hours, while Deimos, being only just outside synchronous orbit, rises as expected in the east but very slowly. Despite its 30 hour orbit, it takes 2.7 days to set in the west as it slowly falls behind the rotation of Mars, and has long again to rise.
Both moons are tidally locked, always presenting the same face towards Mars. Since Phobos orbits Mars faster than the planet itself rotates, tidal forces are slowly but steadily decreasing its orbital radius. At some point in the future, when it approaches Mars closely enough (see Roche limit), Phobos will be broken up by these tidal forces.[11] Several strings of craters on the Martian surface, inclined further from the equator the older they are, suggest that there may have been other small moons that suffered the fate expected of Phobos, and also that the Martian crust as a whole shifted between these events.[12] Deimos, on the other hand, is far enough away that its orbit is being slowly boosted instead,[13] as in the case of our own Moon.
Orbital details
Name and pronunciation Image Diameter (km) Mass (kg) Semi-major
axis (km)Orbital
period (h)Average moonrise
period (h, d)Mars I Phobos /ˈfoʊbəs/
FOE-bəs22.2 km (27×21.6×18.8) 1.08×1016 9 377 km 7.66 11.12 h (0.463 d) Mars II Deimos /ˈdaɪməs/
DYE-məs12.6 km (10×12×16) 2×1015 23 460 km 30.35 131 h (5.44 d) The relative sizes of and distance between Mars, Phobos, and Deimos, to scale. Origin
The origin of the Martian moons is still controversial.[14] Phobos and Deimos both have much in common with carbonaceous C-type asteroids, with spectra, albedo, and density very similar to those of C- or D-type asteroids.[15] Based on their similarity, one hypothesis is that both moons may be captured main-belt asteroids.[16][17] Both moons have very circular orbits which lie almost exactly in Mars's equatorial plane, and hence a capture origin requires a mechanism for circularizing the initially highly eccentric orbit, and adjusting its inclination into the equatorial plane, most probably by a combination of atmospheric drag and tidal forces,[18] although it is not clear that sufficient time is available for this to occur for Deimos.[14] Capture also requires dissipation of energy. The current Mars atmosphere is too thin to capture a Phobos-sized object by atmospheric braking.[14] Geoffrey Landis has pointed out that the capture could have occurred if the original body was a binary asteroid that separated under tidal forces.[17]
Phobos could be a second-generation Solar System object that coalesced in orbit after Mars formed, rather than forming concurrently out of the same birth cloud as Mars.[19]
Another hypothesis is that Mars was once surrounded by many Phobos- and Deimos-sized bodies, perhaps ejected into orbit around it by a collision with a large planetesimal.[20] The high porosity of the interior of Phobos (based on the density of 1.88 g/cm3, voids are estimated to comprise 25 to 35 percent of Phobos' volume) is inconsistent with an asteroidal origin.[21] Observations of Phobos in the thermal infrared suggest a composition containing mainly phyllosilicates, which are well known from the surface of Mars. The spectra are distinct from those of all classes of chondrite meteorites, again pointing away from an asteroidal origin.[22] Both sets of findings support an origin of Phobos from material ejected by an impact on Mars that reaccreted in Martian orbit,[23] similar to the prevailing theory for the origin of Earth's moon.
References
- ^ a b MathPages - Galileo's Anagrams and the Moons of Mars[unreliable source?]
- ^ William Sheehan, The Planet Mars: A History of Observation and Discovery
- ^ "Notes: The Satellites of Mars". The Observatory, Vol. 1, No. 6. September 20, 1877. pp. 181–185. http://adsabs.harvard.edu//full/seri/Obs../0001//0000181.000.html. Retrieved September 12, 2006.
- ^ Hall, A. (October 17, 1877, signed September 21, 1877). "Observations of the Satellites of Mars". Astronomische Nachrichten, Vol. 91, No. 2161. pp. 11/12–13/14. http://adsabs.harvard.edu//full/seri/AN.../0091//0000013.000.html. Retrieved September 12, 2006.
- ^ Morley, T. A.; A Catalogue of Ground-Based Astrometric Observations of the Martian Satellites, 1877-1982, Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series (ISSN 0365-0138), Vol. 77, No. 2 (February 1989), pp. 209–226 (Table II, p. 220: first observation of Phobos on 1877-08-18.38498)
- ^ "The Discovery of the Satellites of Mars". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Vol. 38, No. 4. February 8, 1878. pp. 205–209. http://adsabs.harvard.edu//full/seri/MNRAS/0038//0000205.000.html. Retrieved September 12, 2006.
- ^ Hall, A. (March 14, 1878, signed February 7, 1878). "Names of the Satellites of Mars". Astronomische Nachrichten, Vol. 92, No. 2187. pp. 47–48. http://adsabs.harvard.edu//full/seri/AN.../0092//0000031.000.html. Retrieved September 12, 2006.
- ^ Jefferson City Post-Tribune May 4, 1959
- ^ Astron. J., 128, 2542-2546 (2004)
- ^ Moon Shadows: "Somewhere near the martian equator, Phobos eclipses the sun nearly every day."
- ^ In 100 million years or so Phobos will likely be shattered by stress caused by the relentless tidal forces, the debris forming a decaying ring around Mars.
- ^ New Map Provides More Evidence Mars Once Like Earth: "… the new map shows evidence of features, transform faults, that are a "tell-tale" of plate tectonics on Earth."
- ^ Sahife 6: "Deimos orbits far enough away from Mars that it is being slowly pushed farther and farther away from the planet."
- ^ a b c Burns, J. A. "Contradictory Clues as to the Origin of the Martian Moons," in Mars, H. H. Kieffer et al., eds., U. Arizona Press, Tucson, 1992
- ^ "New Views of Martian Moons". http://www.physorg.com/news115483748.html.
- ^ "Close Inspection for Phobos". http://sci.esa.int/science-e/www/object/index.cfm?fobjectid=31031. "One idea is that Phobos and Deimos, Mars's other moon, are captured asteroids."
- ^ a b Landis, G. A. "Origin of Martian Moons from Binary Asteroid Dissociation," American Association for the Advancement of Science Annual Meeting; Boston, MA, 2001; abstract.
- ^ Martin Pätzold and Olivier Witasse (March 4, 2010). "Phobos Flyby Success". ESA. http://www.esa.int/esaSC/SEMIPX6K56G_index_0.html. Retrieved March 4, 2010.
- ^ Craddock, R. A.; (1994); The Origin of Phobos and Deimos, Abstracts of the 25th Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, held in Houston, TX, March 14–18, 1994, p. 293
- ^ Andert, T. P.; Rosenblatt, P.; Pätzold, M.; Häusler, B.; Dehant, V.; Tyler, G. L.; Marty, J. C. (2010-05-07). "Precise mass determination and the nature of Phobos". Geophysical Research Letters (American Geophysical Union) 37 (L09202). Bibcode 2010GeoRL..3709202A. doi:10.1029/2009GL041829. http://www.agu.org/pubs/crossref/2010/2009GL041829.shtml. Retrieved 2010-10-01.
- ^ Giuranna, M.; Roush, T. L.; Duxbury, T.; Hogan, R. C.; Geminale, A.; Formisano, V. (2010). "Compositional Interpretation of PFS/MEx and TES/MGS Thermal Infrared Spectra of Phobos". European Planetary Science Congress Abstracts, Vol. 5. http://meetingorganizer.copernicus.org/EPSC2010/EPSC2010-211.pdf. Retrieved 2010-10-01.
- ^ "Mars Moon Phobos Likely Forged by Catastrophic Blast". Space.com web site. 2010-09-27. http://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/martian-moon-forged-by-catastrophic-blast-100927.html. Retrieved 2010-10-01.
- Further reading
External links
Mars Areography General- Observation history
- Albedo features (Solis Lacus)
- Atmosphere
- Canals (list)
- Climate
- Color
- Water
- Glaciers
- Life
- North Polar Basin
- Chaos terrain
- Noachian
- Soil
Regions- Alba Mons
- Albor Tholus
- Arsia Mons
- Ascraeus Mons
- Biblis Tholus
- Elysium Mons
- Hecates Tholus
- Olympus Mons
- Pavonis Mons
- Syrtis Major Planum
- Tharsis
- Tharsis Montes
- North Polar Basin
- Hellas Planitia
- Argyre Planitia
- Schiaparelli
- Gusev
- Eberswalde
- Bonneville
- Eagle
- Endeavour
- Endurance
- Erebus
- Victoria
- Gale
- Galle
- Ibragimov
- Santa Maria
- Valles
- Chasmata
- Outflow channel
- Valles Marineris
Moons Specific- Phobos
- (Features
- Stickney crater
- Monolith)
- Deimos
- (Features)
CommonExploration Past and
CurrentFutureAstronomy EclipsesAsteroidsMeteorites Other topics - Darian calendar
- Timekeeping on Mars
- Flag of Mars
- In Fiction
- Martian
- Mars Society
- (FMARS
- MDRS)
- Mars Institute
- (Haughton–Mars Project)
- Mythology
- Ocean Hypothesis
Natural satellites of the Solar System Planetary satellites - Terrestrial
- Martian
- Jovian
- Saturnian
- Uranian
- Neptunian

Other satellite systems Largest satellites - Inner satellites
- Trojans
- Irregulars
- List
- Timeline of discovery
- Naming
The Solar System  Categories:
Categories:- Moons of Mars
- Lists of moons
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.