- North Polar Basin (Mars)
-
Not to be confused with Vastitas Borealis.
North Polar Basin 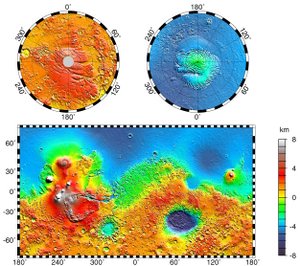
The North Polar Basin is the large blue low-lying area at the northern end of this topographical map of Mars. Its elliptical shape is partially obscured by volcanic eruptions (red, center left).Coordinates 67°N 208°E / 67°N 208°ECoordinates: 67°N 208°E / 67°N 208°E The North Polar Basin, or Borealis basin, is a large basin in the northern hemisphere of Mars that covers 40% of the planet. Chryse Planitia, the landing site of the Viking 1 lander, is a bay which opens into this basin.
One possible explanation for the basin's low, flat and relatively crater-free topography is that the basin was formed by a single large impact. Two simulations of a possible impact sketched a profile for the collision: low velocity (6 – 10 km/s), oblique angle and diameter 1,600 - 2,700 km.[1][2] Topographical data from the Mars Global Surveyor are consistent with the models and also suggest that the elliptical crater has axes of length 10,600 km and 8,500 km, centered on 67°N, 208°E, though this has been partially obscured by later volcanic eruptions that created the Tharsis bulge along its rim. There is evidence for a secondary rim as well.[3][4] This would make the North Polar Basin by far the largest impact crater in the Solar System, approximately four times the diameter of the next largest craters, the South Pole – Aitken basin on Earth's Moon and Hellas Planitia on the southern hemisphere of Mars.[5]
References
- Martel, L.M.V. (June, 2001), "Outflow Channels May Make a Case for a Bygone Ocean on Mars", Planetary Science Research Discoveries. http://www.psrd.hawaii.edu/June01/MarsChryse.html. (retrieved 17 August 2005)
- ^ Marinova et al. (2008). "Mega-impact formation of the Mars hemispheric dichotomy". Nature 453 (7199): 1216–1219. Bibcode 2008Natur.453.1216M. doi:10.1038/nature07070. PMID 18580945.
- ^ Nimmo et al. (2008). "Implications of an impact origin for the Martian hemispheric dichotomy". Nature 453 (7199): 1220–1223. Bibcode 2008Natur.453.1220N. doi:10.1038/nature07025. PMID 18580946.
- ^ Andrews-Hanna et al. (2008). "The Borealis basin and the origin of the Martian crustal dichotomy". Nature 453 (7199): 1212–1215. Bibcode 2008Natur.453.1212A. doi:10.1038/nature07011. PMID 18580944.
- ^ "Huge Impact Created Mars' Split Personality". Space.com. http://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/080625-mars-impact.html. Retrieved 2008-07-01.
- ^ Chandler, David (2008-06-25). "Solar system's biggest impact scar discovered: MIT scientists solve riddle of Mars' two-faced nature". MIT News. http://web.mit.edu/newsoffice/2008/mars-basin-0625.html. Retrieved 2010-04-15.
See also
- Vastitas Borealis
- Mars Ocean Hypothesis (Oceanus Borealis)
- Utopia Planitia
- Planum Boreum
- North Polar Basin (Earth)
Mars Areography General- Observation history
- Albedo features (Solis Lacus)
- Atmosphere
- Canals (list)
- Climate
- Color
- Water
- Glaciers
- Life
- North Polar Basin
- Chaos terrain
- Noachian
- Soil
Regions- Alba Mons
- Albor Tholus
- Arsia Mons
- Ascraeus Mons
- Biblis Tholus
- Elysium Mons
- Hecates Tholus
- Olympus Mons
- Pavonis Mons
- Syrtis Major Planum
- Tharsis
- Tharsis Montes
- North Polar Basin
- Hellas Planitia
- Argyre Planitia
- Schiaparelli
- Gusev
- Eberswalde
- Bonneville
- Eagle
- Endeavour
- Endurance
- Erebus
- Victoria
- Gale
- Galle
- Ibragimov
- Santa Maria
- Valles
- Chasmata
- Outflow channel
- Valles Marineris
Moons Specific- Phobos
- (Features
- Stickney crater
- Monolith)
- Deimos
- (Features)
CommonExploration Past and
CurrentFutureAstronomy EclipsesAsteroidsMeteorites Other topics - Darian calendar
- Timekeeping on Mars
- Flag of Mars
- In Fiction
- Martian
- Mars Society
- (FMARS
- MDRS)
- Mars Institute
- (Haughton–Mars Project)
- Mythology
- Ocean Hypothesis
Categories:- Mare Boreum quadrangle
- Surface features of Mars
- Mars stubs
- Astrogeology stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

