- Metabolic acidosis
-
Metabolic acidosis Classification and external resources 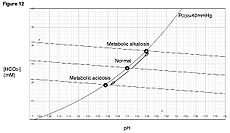
Davenport diagramICD-10 E87.2 ICD-9 276.2 DiseasesDB 92 MedlinePlus 000335 eMedicine emerg/312 med/1458 ped/15 In medicine, metabolic acidosis is a condition that occurs when the body produces too much acid or when the kidneys are not removing enough acid from the body. If unchecked, metabolic acidosis leads to acidemia, i.e., blood pH is low (less than 7.35) due to increased production of hydrogen by the body or the inability of the body to form bicarbonate (HCO3-) in the kidney. Its causes are diverse, and its consequences can be serious, including coma and death. Together with respiratory acidosis, it is one of the two general causes of acidemia.
Contents
Terminology
- Acidosis refers to a low pH in tissue.
- Acidemia refers to a low pH in the blood.
In most cases, acidosis occurs first for reasons explained below. Free hydrogen ions then diffuse into the blood, lowering the pH. Arterial blood gas analysis detects acidemia (pH lower than 7.35). When acidemia is present, acidosis is presumed.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms are aspecific, and diagnosis can be difficult unless the patient presents with clear indications for arterial blood gas sampling. Symptoms may include chest pain, palpitations, headache, altered mental status such as severe anxiety due to hypoxia, decreased visual acuity, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, altered appetite (either loss of or increased) and weight loss (longer term), muscle weakness and bone pains. Those in metabolic acidosis may exhibit deep, rapid breathing called Kussmaul respirations which is classically associated with diabetic ketoacidosis. Rapid deep breaths increase the amount of carbon dioxide exhaled, thus lowering the serum carbon dioxide levels, resulting in some degree of compensation. Over compensation via respiratory alkalosis to form an alkalemia does not occur.
Extreme acidemia leads to neurological and cardiac complications:
- Neurological: lethargy, stupor, coma, seizures.
- Cardiac: arrhythmias (ventricular tachycardia), decreased response to epinephrine; both lead to hypotension (low blood pressure).
Physical examination occasionally reveals signs of disease, but is otherwise normal. Cranial nerve abnormalities are reported in ethylene glycol poisoning, and retinal edema can be a sign of methanol (methyl alcohol) intoxication. Longstanding chronic metabolic acidosis leads to osteoporosis and can cause fractures.
Diagnosis
Arterial blood gas sampling is essential for the diagnosis. If the pH is low (under 7.35) and the bicarbonate levels are decreased (<24 mmol/l), metabolic acidemia is present, and metabolic acidosis is presumed. Due to respiratory compensation (hyperventilation), carbon dioxide is decreased and conversely oxygen is increased. An ECG can be useful to anticipate cardiac complications.
Other tests that are relevant in this context are electrolytes (including chloride), glucose, renal function and a full blood count. Urinalysis can reveal acidity (salicylate poisoning) or alkalinity (renal tubular acidosis type I). In addition, it can show ketones in ketoacidosis.
To distinguish between the main types of metabolic acidosis, a clinical tool called the anion gap is considered very useful. It is calculated by subtracting the chloride and bicarbonate levels from the sodium.
Anion gap = ( [Na+] ) - ( [Cl-]+[HCO3-] )
As sodium is the main extracellular cation, and chloride and bicarbonate are the main anions, the result should reflect the remaining anions. Normally, this concentration is about 8-16 mmol/l (12±4). An elevated anion gap (i.e. > 16 mmol/l) can indicate particular types of metabolic acidosis, particularly certain poisons, lactate acidosis and ketoacidosis.
As the differential diagnosis is made, certain other tests may be necessary, including toxicological screening and imaging of the kidneys. It is also important to differentiate between acidosis-induced hyperventilation and asthma; otherwise, treatment could lead to inappropriate bronchodilation.[1]
Causes
Metabolic acidosis occurs when the body produces too much acid, or when the kidneys are not removing enough acid from the body. There are several types of metabolic acidosis. The main causes are best grouped by their influence on the anion gap.
It bears noting that the anion gap can be spuriously normal in sampling errors of the sodium level, e.g. in extreme hypertriglyceridemia. The anion gap can be increased due to relatively low levels of cations other than sodium and potassium (e.g. calcium or magnesium).
Increased anion gap
Main article: High anion gap metabolic acidosisCauses include:
- lactic acidosis
- ketoacidosis
- chronic renal failure (accumulation of sulfates, phosphates, urea)
- intoxication:
- organic acids (salicylates, ethanol, methanol, formaldehyde, ethylene glycol, paraldehyde, INH)
- sulfates, metformin (Glucophage)
- massive rhabdomyolysis
Normal anion gap
Causes include:[1]
- longstanding diarrhea (bicarbonate loss)
- pancreatic fistula
- uretero-sigmoidostomy
- Renal tubular acidosis (RTA)
- intoxication:
- renal failure (occasionally)
- Glue sniffing
- toluene
Pathophysiology
Compensatory mechanisms
Metabolic acidosis is either due to increased generation of acid or an inability to generate sufficient bicarbonate. The body regulates the acidity of the blood by four buffering mechanisms.
- bicarbonate buffering system
- Intracellular buffering by absorption of hydrogen atoms by various molecules, including proteins, phosphates and carbonate in bone.
- Respiratory compensation
- Renal compensation
Buffer
The decreased bicarbonate that distinguishes metabolic acidosis is therefore due to two separate processes: the buffer (from water and carbon dioxide) and additional renal generation. The buffer reactions are:
The Henderson-Hasselbalch equation mathematically describes the relationship between blood pH and the components of the bicarbonate buffering system:
![\text{pH}=\text{pK}_a+\text{Log}\frac{\left[\text{HCO}_3^-\right]}{\left[\text{CO}_2\right]}](f/1dfdd883d3992f8fc6be80a14f0724ea.png)
- Using Henry's Law, we can say that [CO2]=0.03xPaCO2
- (PaCO2 is the pressure of CO2 in arterial blood)
- Adding the other normal values, we get
![\text{pH}=6.1+\text{Log}\left[\frac{24}{0.03\times 40}\right]](4/9c41299fc7342e969c78f59b8b9832ac.png)
- = 6.1 + 1.3
- = 7.4
Treatment
A pH under 7.1 is an emergency, due to the risk of cardiac arrhythmias, and may warrant treatment with intravenous bicarbonate. Bicarbonate is given at 50-100 mmol at a time under scrupulous monitoring of the arterial blood gas readings. This intervention however, is not effective in case of lactic acidosis.[citation needed]
If the acidosis is particularly severe and/or there may be intoxication, consultation with the nephrology team is considered useful, as dialysis may clear both the intoxication and the acidosis.
See also
References
Water-electrolyte imbalance and acid-base imbalance (E86–E87, 276) Volume status Electrolyte Acid-base Metabolic: High anion gap (Ketoacidosis/Diabetic ketoacidosis, Lactic) · Normal anion gap (Hyperchloremic, Renal tubular)BothCategories:- Acid-base disturbances
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

