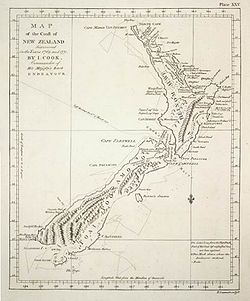
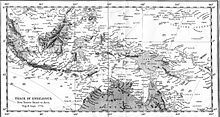
- First voyage of James Cook
-
Main article: James CookSee also: Second voyage of James CookSee also: Third voyage of James Cook
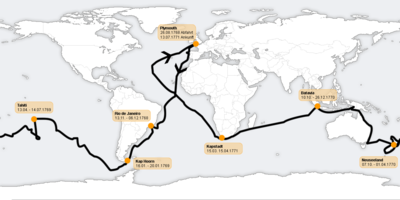 Route of the first voyage of James Cook
Route of the first voyage of James Cook
The first voyage of James Cook was a combined Royal Navy and Royal Society expedition to the south Pacific ocean aboard HMS Endeavour, from 1768 to 1771. The aims of the expedition were to observe the 1769 transit of Venus across the Sun (3–4 June of that year), and to seek evidence of the postulated Terra Australis Incognita or "unknown southern land".
The voyage was commissioned by King George III and commanded by Lieutenant James Cook, a junior naval officer with skills in cartography and mathematics. Departing Plymouth in August 1768, the expedition crossed the Atlantic, rounded Cape Horn and reached Tahiti in time to observe the transit of Venus. Cook then set sail into the largely uncharted ocean to the south, stopping at the Pacific islands of Huahine, Borabora and Raiatea to claim them for Great Britain[citation needed], and unsuccessfully attempting to land at Rurutu. In September 1769, the expedition reached New Zealand, being the second Europeans to visit there, following its earlier discovery by Abel Tasman 127 years earlier. Cook and his crew spent the following six months charting the New Zealand coast, before resuming their voyage westward across open sea. In April 1770, they became the first Europeans to reach the east coast of Australia, making landfall on the shore of what is now known as Botany Bay.
The expedition continued northward along the Australian coastline, narrowly avoiding shipwreck on the Great Barrier Reef. In October 1770, the badly damaged Endeavour came into the port of Batavia in the Dutch East Indies, her crew sworn to secrecy about the lands they had discovered. They resumed their journey on 26 December, rounded the Cape of Good Hope on 13 March 1771, and reached the English port of Deal on 12 July. The voyage lasted almost three years.
Contents
Conception
On 16 February 1768, the Royal Society petitioned King George III to finance a scientific expedition to the Pacific to study and observe the 1769 transit of Venus across the sun.[1] Royal approval was granted for the expedition, and the Admiralty elected to combine the scientific voyage with a confidential mission to search the south Pacific for signs of the postulated continent Terra Australis Incognita (or "unknown southern land").[2]
The Royal Society suggested command be given to Scottish geographer Alexander Dalrymple, whose acceptance was conditional on a brevet commission as a captain in the Royal Navy. However, First Lord of the Admiralty Edward Hawke refused, going so far as to say he would rather cut off his right hand than give command of a Navy vessel to someone not educated as a seaman.[3] In refusing Dalrymple's command, Hawke was influenced by previous insubordination aboard the sloop HMS Paramour in 1698, when naval officers had refused to take orders from civilian commander Dr. Edmond Halley.[3] The impasse was broken when the Admiralty proposed James Cook, a naval officer with a background in mathematics and cartography.[4] Acceptable to both parties, Cook was promoted to Lieutenant and named as commander of the expedition.[5]
Preparations and personnel
Vessel and provisions
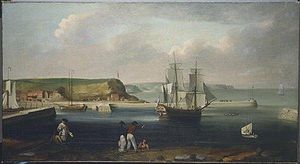 Earl of Pembroke, later HMS Endeavour, leaving Whitby Harbour in 1768. By Thomas Luny, dated 1790
Earl of Pembroke, later HMS Endeavour, leaving Whitby Harbour in 1768. By Thomas Luny, dated 1790
The vessel chosen by Admiralty for the voyage was a merchant collier named Earl of Pembroke, launched in June 1764 from the coal and whaling port of Whitby in North Yorkshire.[6] She was ship-rigged and sturdily built with a broad, flat bow, a square stern and a long box-like body with a deep hold.[7] A flat-bottomed design made her well-suited to sailing in shallow waters and allowed her to be beached for loading and unloading of cargo and for basic repairs without requiring a dry dock. Her length was 106 feet (32 m), with a beam of 29 feet 3 inches (8.92 m) and a burthen was 36871⁄94 tons.[6][8]
Earl of Pembroke was purchased by the Admiralty in May 1768 for £2,840 10s 11d[9][a] and sailed to Deptford on the River Thames to be prepared for the voyage. Her hull was sheathed and caulked, and a third internal deck installed to provide cabins, a powder magazine and storerooms.[10] A longboat, pinnace and yawl were provided as ship's boats, as well as a set of 28 ft (8.5 m) sweeps to allow the ship to be rowed if becalmed or demasted.[11] After commissioning into the Royal Navy as His Majesty's Bark the Endeavour, the ship was supplied with ten 4-pounder cannons and twelve swivel guns, for defence against native attack while in the Pacific.[12]
Provisions loaded at the outset of the voyage included 6,000 pieces of pork and 4,000 of beef, nine tons of bread, five tons of flour, three tons of sauerkraut, one ton of raisins and sundry quantities of cheese, salt, peas, oil, sugar and oatmeal. Alcohol supplies consisted of 250 barrels of beer, 44 barrels of brandy and 17 barrels of rum.[13]
Ship's company
On 30 July 1768 the Admiralty authorised a ship's company for the voyage, of 73 sailors and 12 Royal Marines.[14] The voyage was commanded by 40-year-old Lieutenant James Cook. His second lieutenant was Zachary Hicks, a 29-year old from Stepney with experience as acting commander of the HMS Hornet, a 16-gun cutter. The third lieutenant was John Gore, a 16-year Naval veteran who had served as master's mate aboard HMS Dolphin during its circumnavigation of the world in 1766.[15]
Voyage of discovery
Cook departed Plymouth on 26 August 1768, carrying 94 people and 18 months of provisions.[16] The ship rounded Cape Horn and continued westward across the Pacific to arrive at Tahiti on 13 April 1769, where the observations were to be made. The transit was scheduled to occur on 3 June, and in the meantime he commissioned the building of a small fort and observatory at what is now known as Point Venus.
The astronomer appointed to the task was Charles Green, assistant to the recently appointed Astronomer Royal, Nevil Maskelyne. The primary purpose of the observation was to obtain measurements that could be used to calculate more accurately the distance of Venus from the Sun. If this could be achieved, then the distances of the other planets could be worked out, based on their orbits. On the day of the transit observation, Cook recorded:
Saturday 3 rd This day prov'd as favourable to our purpose as we could wish, not a Clowd was to be seen the Whole day and the Air was perfectly clear, so that we had every advantage we could desire in Observing the whole of the passage of the Planet Venus over the Suns disk: we very distinctly saw an Atmosphere or dusky shade round the body of the Planet which very much disturbed the times of the contacts particularly the two internal ones. D r Solander observed as well as M r Green and my self, and we differ'd from one another in observeing the times of the Contacts much more than could be expected.
Disappointingly, the separate measurements of Green, Cook and Solander varied by more than the anticipated margin of error. Their instrumentation was adequate by the standards of the time, but the resolution still could not eliminate the errors. When their results were later compared to those of the other observations of the same event made elsewhere for the exercise, the net result was not as conclusive or accurate as had been hoped. The difficulties are today thought to relate to the Black drop effect, an optical phenomenon that precludes accurate measurement – particularly with the instruments used by Cook, Green and Solander.
New Zealand
Once the observations were completed, Cook opened the sealed orders for the second part of his voyage: to search the south Pacific for signs of the postulated rich southern continent of Terra Australis, acting on additional instructions from the Admiralty.[17] The Royal Society, and especially Alexander Dalrymple, believed that it must exist and that Britain's best chance of discovering it and claiming its fabled riches before any other rival European power managed to do so would be by using Cook's Transit of Venus mission (on an inconspicuous small ship such as the Endeavour) as a cover.
Cook, however, had his own personal doubts on the continent's existence. With the help of a Tahitian named Tupaia, who had extensive knowledge of Pacific geography, Cook managed to reach New Zealand on 6 October 1769, leading only the second group of Europeans to do so (after Abel Tasman over a century earlier, in 1642). Cook mapped the complete New Zealand coastline, making only some minor errors (such as calling Banks Peninsula an island, and thinking Stewart Island/Rakiura was part of the South Island). He also identified Cook Strait, which separates the North Island from the South Island, and which Tasman had not seen.
Australian coast
He then set course westwards, intending to strike for Van Diemen's Land (present-day Tasmania, sighted by Tasman) to establish whether or not it formed part of the fabled southern continent. However, they were forced to maintain a more northerly course owing to prevailing gales, and sailed onwards until one afternoon when land was sighted, which Cook named Point Hicks. Cook calculated that Van Diemen's Land ought to lie due south of their position, but having found the coastline trending to the southwest, recorded his doubt that this landmass was connected to it. This point was on the southeastern coast of the Australian continent, and in doing so his expedition became the first recorded Europeans to have encountered its eastern coastline. In his journal, Cook recorded the event thus:
the Southermost Point of land we had in sight which bore from us W1/4S I judged to lay in the Latitude of 38°..0' S° and in the Longitude of 211°..07' W t from the Meridion of Greenwich. I have named it Point Hicks, because Leuit t Hicks was the first who discover'd this land.
The ship's log recorded that land was sighted at 6 a.m. on Thursday 19 April 1770. Cook's log used the nautical date, which, during the 18th century, assigned the same date to all ship's events from noon to noon, first p.m. and then a.m. That nautical date began twelve hours before the midnight beginning of the like-named civil date. Furthermore, Cook did not adjust his nautical date to account for circumnavigation of the globe until he had travelled a full 360° relative to the longitude of his home British port, either toward the east or west. Because he travelled west on his first voyage, this a.m. nautical date was the morning of a civil date 14 hours slow relative to his home port (port−14h). Because the southeast coast of Australia is now regarded as being 10 hours fast relative to Britain, that date is now called Friday, 20 April.[18]
The landmark of this sighting is generally reckoned to be a point lying about half-way between the present-day towns of Orbost and Mallacoota on the southeastern coast of the state of Victoria. A survey done in 1843 ignored or overlooked Cook's earlier naming of the point, giving it the name Cape Everard. On the 200th anniversary of the sighting, the name was officially changed back to Point Hicks.
Botany Bay
 E. Phillips Fox, Landing of Captain Cook at Botany Bay, 1770, 1902
E. Phillips Fox, Landing of Captain Cook at Botany Bay, 1770, 1902
Endeavour continued northwards along the coastline, keeping the land in sight with Cook charting and naming landmarks as he went. A little over a week later, they came across an extensive but shallow inlet, and upon entering it moored off a low headland fronted by sand dunes. James Cook and crew made their first landing on the continent, at a place now known as Botany Bay, on the Kurnell Peninsula and made contact of a hostile nature with the Gweagal Aborigines, on 29 April.[b] At first Cook bestowed the name "Sting-Ray Harbour"[19] to the inlet after the many such creatures found there; this was later changed to "Botan ist Bay"[19] and finally Botany Bay after the unique specimens retrieved by the botanists Joseph Banks, Daniel Solander and Herman Spöring.
Captain Cook landing place plaque
This first landing site was later to be promoted (particularly by Joseph Banks) as a suitable candidate for situating a settlement and British colonial outpost. However, almost 18 years later, when Captain Arthur Phillip and the First Fleet arrived in early 1788 to establish an outpost and penal colony, they found that the bay and surrounds did not live up to the promising picture that had been painted. Instead, Phillip gave orders to relocate to a harbour a few kilometres to the north, which Cook had named Port Jackson but had not further explored. It was in this harbour, at a place Phillip named Sydney Cove, that the settlement of Sydney was established. The settlement was for some time afterwards still referred to generally as Botany Bay. The expedition's scientific members commenced the first European scientific documentation of Australian fauna and flora.
At Cook's original landing contact was made with the local Australian Aboriginal inhabitants. As the ships sailed into the harbour, they noticed Aborigines on both of the headlands. At about 2 pm they put the anchor down near a group of six to eight huts. Two Aborigines, a younger and an older man, came down to the boat. They ignored gifts from Cook. A musket was fired over their heads, which wounded the older man slightly, and he ran towards the huts. He came back with other men and threw spears at Cook's men, although they did no harm. They were chased off after two more rounds were fired. The adults had left, but Cook found several Aboriginal children in the huts, and left some beads with them as a gesture of friendship.
Endeavour River
Cook continued northwards, charting along the coastline. He stopped at Bustard Head on 24 May 1770. Cook and Banks and others went ashore. A mishap occurred when Endeavour ran aground on a shoal of the Great Barrier Reef, on 11 June 1770. The ship was seriously damaged and his voyage was delayed almost seven weeks while repairs were carried out on the beach (near the docks of modern Cooktown, at the mouth of the Endeavour River). While there, Joseph Banks, Herman Spöring and Daniel Solander made their first major collections of Australian flora. The crew's encounters with the local Aboriginal people were mainly peaceable; from the group encountered here the name "kangaroo" entered the English language, coming from the local Guugu Yimidhirr word for a kind of Grey Kangaroo, gangurru (pronounced [ɡ̊aŋuru]).[20]
Possession Island
Once repairs were complete the voyage continued, eventually passing by the northern-most point of Cape York Peninsula and then sailing through Torres Strait between Australia and New Guinea, earlier navigated by Luis Váez de Torres in 1606. Having rounded the Cape, Cook landed on Possession Island on 22 August, where he claimed the entire coastline he had just explored (later naming the region New South Wales) for the British Crown.
In negotiating the Torres Strait past Cape York, Cook also put an end to the speculation that New Holland and New Guinea were part of the same land mass.[21]
Scurvy prevention
At that point in the voyage, Cook had lost not a single man to scurvy, a remarkable and practically unheard-of achievement in 18th century long-distance sea-faring. Adhering to Royal Navy policy introduced in 1747, Cook persuaded his men to eat foods such as citrus fruits and sauerkraut. At that time it was known that poor diet caused scurvy but not specifically that a vitamin C deficiency was the culprit.
Sailors of the day were notoriously against innovation, and at first the men would not eat the sauerkraut. Cook used a little trick, one he had never known to fail. He ordered it served to himself and the officers, and left an option for crew who wanted some. Within a week of seeing their superiors set a value on it the demand was so great a ration had to be instituted. (Cook's journal 13 April 1769.) In other cases, however, Cook was required to resort to traditional naval discipline. "Punished Henry Stephens, Seaman, and Thomas Dunster, Marine, with twelve lashes each for refusing to take their allowance of fresh beef."[22]
Cook's general approach was essentially empirical, encouraging as broad a diet as circumstances permitted, and collecting such greens as could be had when making landfall. All onboard ate the same food, with Cook specifically dividing equally anything that could be divided (and indeed recommending that practice to any commander – journal 4 August 1770).
Two cases of scurvy did occur on board, astronomer Charles Green and the Tahitian navigator Tupaia were treated, but Cook was able to proudly record that upon reaching Batavia he had "not one man upon the sick list" (journal 15 October 1770), unlike so many voyages that reached that port with much of the crew suffering illness.
Homeward voyage
The Endeavour then visited the island of Savu, staying for three days before continuing on to Batavia, the capital of the Dutch East Indies, to put in for repairs. Batavia was known for its outbreaks of malaria, and before they returned home in 1771, many in Cook's company succumbed to the disease and other ailments such as dysentery, including the Tahitian Tupaia, Banks' Finnish secretary and fellow scientist Herman Spöring, astronomer Charles Green, and the illustrator Sydney Parkinson. Cook named Spöring Island off the coast of New Zealand to honour Herman Spöring and his work on the voyage.
Cook then rounded the Cape of Good Hope and stopped at Saint Helena. On 10 July 1771 Nicholas Young, the boy who had first seen New Zealand, sighted England (specifically the Lizard) again for the first time, and the Endeavour sailed up the English Channel, passing Beachy Head at 6 am on the 12th; that afternoon the Endeavour anchored in the Downs, and Cook went ashore at Deal, Kent.
Publication of journals
Cook's journals, along with those of Banks, were handed over to the Admiralty to be published upon his return. Lord Sandwich contracted, for £6,000, John Hawkesworth a literary critic, essayist, and editor of the Gentleman’s Magazine to publish a comprehensive account of exploration in the Pacific: not just Cook's ventures but also those of Wallis, Byron and Carteret. Hawkesworth edited the journals of Byron, Wallis and Carteret into separate accounts as volume I and then blended Cook’s and Joseph Banks’ journals with some of his own sentiments and produced a single first-person narrative that appeared to be the words of Cook, as Volume II. [23]The book appeared in 1773 as three volumes with the title:
AN ACCOUNT OF THE VOYAGES undertaken by Order of His Present Majesty for making Discoveries in the Southern Hemisphere, and successively performed by Commodore Byron, Captain Wallis, Captain Carteret and Captain Cook, in the Dolphin, the Swallow and the Endeavour: Drawn up from the Journals which were kept by the several Commanders, and from the Papers of Joseph Banks, Esq.; by John Hawkesworth, LL.D. In three volumes. Illustrated with Cuts, and a great Variety of Charts and Maps relative to Countries now first discovered, or hitherto but imperfectly known.
Printed for W. Strahan & T. Cadell in the Strand. London: MDCCLXXIII
The book went on sale on 9 June 1773 but widespread criticism in the press made the publication a personal disaster for Hawkesworth. Reviewers complained that the reader had no way to tell which part of the account was Cook, which part Banks and which part Hawkesworth and others were offended by the books’ descriptions of the voyagers’ sexual encounters with the Tahitians.[24] Cook was at sea again before the book was published and was later much disturbed by some of the sentiments that Hawkesworth has ascribed to him. He determined to edit his own journals in future.
See also
Notes
Footnotes
^[a] In today's terms, this equates to a valuation for Endeavour of approximately £265,000 and a purchase price of £326,400.[25]
^[b] This date does not need adjustment because it occurred during the afternoon (p.m.) on 29 April in the ship's log, but was the afternoon of the civil date of 28 April, 14 hours west of port, which is now a civil date 10 hours east of port, 24 hours later, hence a modern civil date of 29 April.References
- ^ Rigby & van der Merwe 2002, p. 24
- ^ "Secret Instructions to Lieutenant Cook 30 July 1768 (UK)". National Library of Australia. 2005. http://www.foundingdocs.gov.au/item.asp?dID=34. Retrieved 26 August 2008.
- ^ a b
- A General History and Collection of Voyages and Travels, Vol. 12 at Project Gutenberg, editor Robert Kerr's introduction footnote 3
- ^ McDermott, Peter Joseph (6 November 1878). "Pacific Exploration". The Brisbane Courier (Brisbane Newspaper Company Ltd): p. 5. http://ndpbeta.nla.gov.au/ndp/del/article/1376345?searchTerm=James+Cook. Retrieved 27 August 2008.
- ^ Rigby & van der Merwe 2002, p. 30
- ^ a b A.H. McLintock, ed (1966). "Ships, Famous". An Encyclopedia of New Zealand. Ministry for Culture and Heritage/Te Manatū Taonga, Government of New Zealand. http://www.teara.govt.nz/1966/S/ShipsFamous/Endeavour/en. Retrieved 5 May 2009.
- ^ Hosty & Hundley 2003, p. 41
- ^ Blainey 2008, p. 17
- ^ Knight, C. (1933). "H.M. Bark Endeavour". Mariner's Mirror (United Kingdom: Nautical Research Guild) 19: 292–302.
- ^ Hosty & Hundley 2003, p. 61
- ^ Marquardt 1995, p. 18
- ^ Marquardt 1995, p. 13
- ^ Minutes of the Royal Navy Victualling Board, 15 June 1768, cited in Beaglehole 1968, p. 613
- ^ Beaglehole 1968, p. 588
- ^ Hough 1995, pp. 63–64
- ^ Beaglehole 1968, p. 4
- ^ "Secret Instructions to Captain Cook, 30 June 1768" (PDF). National Archives of Australia. http://www.foundingdocs.gov.au/resources/transcripts/nsw1_doc_1768.pdf. Retrieved 25 January 2007.
- ^ Aurthur R. Hinks, "Nautical time and civil date", The Geographical Journal, 86 (1935) 153–157.
- ^ a b southseas.nla.gov/journals/cook/17700506.html
- ^ Robson 2004, p. 81
- ^ G. Williams (2002)
- ^ Wilcox, Ten Who Dared at 97 (Boston: Little, Brown & Co. 1977).
- ^ Villiers 1967, p. 151
- ^ Ravneberg, Ronald L. "The Hawkesworth Copy". http://www.captaincooksociety.com/ccsu4148.pdf. Retrieved 9 October 2011.
- ^ "Purchasing Power of British Pounds from 1264 to Present". MeasuringWorth. 2009. http://www.measuringworth.com/ppoweruk/. Retrieved 5 August 2009.
Bibliography
- Blainey, Geoffrey (2008). Sea of Dangers: Captain Cook and his rivals. Penguin Group (Australia). ISBN 9780670072231.
- Beaglehole, J.C., ed (1968). The Journals of Captain James Cook on His Voyages of Discovery, vol. I:The Voyage of the Endeavour 1768–1771. Cambridge University Press. OCLC 223185477.
- Hosty, Kieran; Hundley, Paul (June 2003) (PDF). Preliminary Report on the Australian National Maritime Museum's participation in the Rhode Island Marine Archaeology Project's search for HMB Endeavour. Australian National Maritime Museum. http://www.anmm.gov.au/webdata/resources/oaiFiles/EndeavourRPT2000No2b2.pdf. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- Hough, Richard (1995). Captain James Cook. Hodder and Stoughton. ISBN 0340825563.
- Marquardt, K H (1995). Captain Cook's Endeavour. Naval Institute Press. ISBN 1557501181.
- Parkin, Ray (2003). H. M. Bark Endeavour. Miegunyah Press. ISBN 0522850936.
- Rigby, Nigel; van der Merwe, Pieter (2002). Captain Cook in the Pacific. National Maritime Museum (UK). ISBN 0948065435.
- Robson, John (2004). The Captain Cook Encyclopædia. Milsons Point, NSW: Random House Australia. ISBN 0759310114.
- Villiers, Alan (1967). Captain Cook. The Seamans Seaman. London: Penguin Books. ISBN 014139062X.
External links
- The Endeavour journal (1) and The Endeavour journal (2), as kept by James Cook – digitised and held by the National Library of Australia
- The South Seas Project: maps and online editions of the Journals of James Cook's First Pacific Voyage. 1768–1771, Includes full text of journals kept by Cook, Joseph Banks and Sydney Parkinson, as well as the complete text of John Hawkesworth's 1773 Account of Cook's first voyage.
- The Endeavour Replica A replica of Captain Cook's vessel.
Categories:- Voyages
- 1760s
- 1770s
- Captain James Cook
- Maritime history
- Exploration of Australia
- History of New Zealand
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.