- Glutaric acidemia type 2
-
Glutaric acidemia type 2 Classification and external resources 
Glutaric acidICD-10 E72.3 ICD-9 277.85 OMIM 231680 DiseasesDB 29816 MeSH D054069 Glutaric acidemia type 2 is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder that is characterised by defects in the ability of the body to use proteins and fats for energy. Incompletely processed proteins and fats can build up, leading to a dangerous chemical imbalance called acidosis.
Contents
Diagnosis
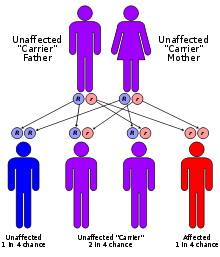
Glutaric acidemia type 2 often appears in infancy as a sudden metabolic crisis, in which acidosis and low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) cause weakness, behavior changes, and vomiting. There may also be enlargement of the liver, heart failure, and a characteristic odor resembling that of sweaty feet. Some infants with glutaric acidemia type 2 have birth defects, including multiple fluid-filled growths in the kidneys (polycystic kidneys). Glutaric acidemia type 2 is a very rare disorder. Its precise incidence is unknown. It has been reported in several different ethnic groups.
Genetics
Mutations in the ETFA, ETFB, and ETFDH genes cause glutaric acidemia type II. Glutaric acidemia type 2 is caused by a deficiency in either of two enzymes, called electron transfer flavoprotein and electron transfer flavoprotein dehydrogenase. These enzymes are normally active in the mitochondria, which are the energy-producing centers of cells. When one of these enzymes is defective or missing, partially broken-down nutrients accumulate in the cells and damage them, causing the signs and symptoms of glutaric acidemia type II.
This condition is inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern, which means the defective gene is located on an autosome, and two copies of the gene - one from each parent - are needed to inherit the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder are carriers of one copy of the defective gene, but do not show signs and symptoms of the disorder themselves.
See also
- Glutaric acidemia type 1
External links
This article incorporates public domain text from The U.S. National Library of Medicine
Inborn error of amino acid metabolism (E70–E72, 270) K→acetyl-CoA Lysine/straight chainHypertryptophanemiaG G→pyruvate→citrateG→glutamate→
α-ketoglutarateGlutamate/glutamineG→fumarateType II tyrosinemia · Type III tyrosinemia/Hawkinsinuria · Alkaptonuria/Ochronosis · Type I tyrosinemiaTransport/
IE of RTTOther Categories:- Amino acid metabolism disorders
- Autosomal recessive disorders
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.