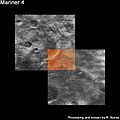
- Mariner 4
-
Mariner 4 
Operator NASA Mission type Flyby Flyby of Mars Launch date November 28, 1964 at 14:22:01 UTC Launch vehicle Atlas-Agena D launch vehicle Mission duration November 28, 1964 to December 21, 1967 COSPAR ID 1964-077A Mass 260.68 kg Power 170 W Orbital elements Semimajor axis 199,591,220 km Eccentricity 0.17024754 Inclination 2.51 Apoapsis 233,571,130 km Periapsis 165,611,300 km Orbital period 562.888 Mariner 4 (together with Mariner 3 known as Mariner-Mars 1964) was the fourth in a series of spacecraft, launched on November 28, 1964,[1] intended for planetary exploration in a flyby mode and performed the first successful flyby of the planet Mars, returning the first pictures of the Martian surface. It captured the first images of another planet ever returned from deep space; their depiction of a cratered, seemingly dead world largely changed the view of the scientific community on life on Mars.[2][3] Mariner 4 was designed to conduct closeup scientific observations of Mars and to transmit these observations to Earth. Other mission objectives were to perform field and particle measurements in interplanetary space in the vicinity of Mars and to provide experience in and knowledge of the engineering capabilities for interplanetary flights of long duration. On December 21, 1967 communications with Mariner 4 were terminated.
Contents
Spacecraft and subsystems
The Mariner 4 spacecraft consisted of an octagonal magnesium frame, 1270 mm across a diagonal and 457 mm high. Four solar panels were attached to the top of the frame with an end-to-end span of 6.88 meters, including solar pressure vanes which extended from the ends. A 1,168 mm diameter high-gain parabolic antenna was mounted at the top of the frame as well. An omnidirectional low-gain antenna was mounted on a seven foot, four inch (2235 mm) tall mast next to the high-gain antenna. The overall height of the spacecraft was 2.89 meters. The octagonal frame housed the electronic equipment, cabling, midcourse propulsion system, and attitude control gas supplies and regulators.
Scientific instruments included:[4][5][6]
- A helium magnetometer, mounted on the waveguide leading to the omnidirectional antenna, to measure the magnitude and other characteristics of the interplanetary and planetary magnetic fields.
- An ionization chamber/Geiger counter, mounted on the waveguide leading to the omnidirectional antenna nearer the body of the spacecraft, to measure the charged-particle intensity and distribution in interplanetary space and in the vicinity of Mars.
- A trapped radiation detector, mounted on the body with counter-axes pointing 70° and 135° from the solar direction, to measure the intensity and direction of low-energy particles.
- A cosmic ray telescope, mounted inside the body pointing in anti-solar direction, to measure the direction and energy spectrum of protons and alpha particles.
- A solar plasma probe, mounted on the body pointing 10° from the solar direction, to measure the very low energy charged particle flux from the Sun.
- A cosmic dust detector, mounted on the body with microphone plate approximately perpendicular to the plane of orbit, to measure the momentum, distribution, density, and direction of cosmic dust.
- A television camera, mounted on a scan platform at the bottom center of the spacecraft, to obtain closeup pictures of the surface of Mars.
The electrical power for the instruments and the radio transmitter of Mariner 4 was supplied by 28,224 solar cells contained in the four 176 x 90 cm solar panels, which could provide 310 watts at the distance of Mars. A rechargeable 1200 W·h silver-zinc battery was also used for maneuvers and backup. Monopropellant hydrazine was used for propulsion, via a four-jet vane vector control motor, with 222-newton (50 lbf) thrust, installed on one of the sides of the octagonal structure. The space probe's attitude control was provided by 12 cold nitrogen gas jets mounted on the ends of the solar panels and three gyros. Solar pressure vanes, each with an area of 0.65 square meter (seven ft²), were attached to the tips of the solar panels. Positional information was provided by four Sun sensors, and a sensor for either the Earth, Mars, or the star Canopus, depending on the time in its spaceflight. Mariner 4 was the first space probe that needed a star for a navigational reference object, since earlier missions, which remained near either the Earth, the Moon, or the planet Venus, had sighted onto either the bright face of the home planet or the brightly lit target. During this flight, both the Earth and Mars would be too dim to lock onto. Another bright source at a wide angle away from the Sun was needed and Canopus filled this requirement.[4] Subsequently, Canopus was used as a reference point in many following missions.[7]
The telecommunications equipment on Mariner 4 consisted of dual S-band transmitters (with either a seven-watt triode cavity amplifier or a ten watt traveling-wave tube amplifier) and a single radio receiver which together could send and receive data via the low- and high-gain antennas at 8⅓ or 33⅓ bits per second. Data could also be stored onto a magnetic tape recorder with a capacity of 5.24 million bits for later transmission. All electronic operations were controlled by a command subsystem which could process any of 29 direct command words or three quantitative word commands for mid-course maneuvers. The central computer and sequencer operated stored time-sequence commands using a 38.4 kHz synchronization frequency as a time reference. Temperature control was achieved through the use of adjustable louvers mounted on six of the electronics assemblies, plus multilayer insulating blankets, polished aluminum shields, and surface treatments. Other measurements that could be made included:
- Radio signal occultation
- Celestial mechanics based on precision tracking
Mission profile
Launch
After launch from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Launch Complex 12 the protective shroud covering Mariner 4 was jettisoned and the Agena D/Mariner 4 combination separated from the Atlas D booster at 14:27:23 UTC on November 28, 1964. The Agena D's first burn took place from 14:28:14 to 14:30:38. The initial burn put the spacecraft into an Earth parking orbit and the second burn from 15:02:53 to 15:04:28 injected the craft into a Mars transfer orbit. Mariner 4 separated from the Agena D at 15:07:09 and began cruise mode operations. The solar panels deployed and the scan platform was unlatched at 15:15:00 and Sun acquisition occurred 16 minutes later.
Lock on Canopus
After Sun acquisition, the Canopus star tracker went searching for Canopus. The star tracker was set to respond to any object more than one-eighth as, and less than eight times as bright as Canopus. Including Canopus, there were seven such objects visible to the sensor. It took more than a day of "star-hopping" to find Canopus, as the sensor locked on to other stars instead:[4] a stray light pattern from the near Earth, Alderamin, Regulus, Naos, and Gamma Velorum were acquired before Canopus.[2][7]
During the early part of the mission, roll error signal transients occurred frequently, making the spacecraft lose its lock on Canopus. The lock was lost six times in less than three weeks, each time requiring radio commands to reacquire the lock. Analysis concluded that it was probably due to small dust particles that scattered sunlight at the same brightness as Canopus. If the brightness of the object exceeded the maximum limit of eight times the brightness of Canopus, the spacecraft would search for a new star. A radio command was sent on December 17, 1964 to remove this limit; the limit was initially implemented to prevent a lock on Earth, but no longer necessary. No further loss of the Canopus lock was experienced, although roll transients occurred 38 more times before the encounter with Mars.[4][7]
Midcourse maneuver
The 7½ months of flight of Mariner 4 involved one midcourse maneuver on December 5, 1964. The maneuver was initially scheduled for December 4, but due to a loss of lock with Canopus, it was postponed. The maneuver was successfully completed on December 5; it consisted of a negative pitch turn of 39.16 degrees, a positive roll turn of 156.08 degrees, and a thrusting time of 20.07 seconds. The turns aimed the motor of the spacecraft back in the general direction of Earth, as the motor was initially pointed along the direction of flight. Both the pitch and roll changes were completed with better than 1% accuracy, the velocity change with about 2½% accuracy. After the maneuver, Mariner 4 was on course for Mars as planned.[4]
Mars flyby
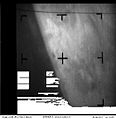
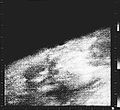
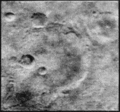
The spacecraft flew by Mars on July 14 and July 15, 1965. Planetary science mode was turned on at 15:41:49 UT on July 14. The camera sequence started at 00:18:36 UT on July 15 (7:18:49 p.m. EST on July 14) and 21 pictures using alternate red and green filters, plus 21 lines of a 22nd picture were taken. The images covered a discontinuous swath of Mars starting near 40° N, 170° E, down to about 35° S, 200° E, and then across to the terminator at 50° S, 255° E, representing about 1% of the planet's surface. The closest approach was 9,846 km from the Martian surface at 01:00:57 UT July 15, 1965 (8:00:57 p.m. EST July 14). The images taken during the flyby were stored in the on-board tape recorder. At 02:19:11 UT Mariner 4 passed behind Mars as seen from Earth and the radio signal ceased. The signal was reacquired at 03:13:04 UT when the spacecraft reappeared. Cruise mode was then re-established. Transmission of the taped images to Earth began about 8.5 hours after signal reacquisition and continued until August 3. All images were transmitted twice to ensure no data was missing or corrupt.
The spacecraft performed all programmed activities successfully and returned useful data from launch until 22:05:07 UT on October 1, 1965, when the distance from Earth (309.2 million km) and the antenna orientation temporarily halted signal acquisition.
Micrometeoroid hits and end of communications
Data acquisition resumed in late 1967. The cosmic dust detector registered 17 hits in a 15 minute span on September 15, part of an apparent micrometeoroid shower which temporarily changed the spacecraft attitude and probably slightly damaged the thermal shield. Later it was speculated that the probe passed through the debris of Comet D/Swift, and even made a close flyby of that comet's possibly shattered nucleus at only 20 million kilometers.[8][9]
On December 7 the gas supply in the attitude control system was exhausted, and on December 10 and 11 a total of 83 micrometeoroid hits were recorded which caused perturbation of the attitude and degradation of the signal strength. On December 21, 1967 communications with Mariner 4 were terminated. The spacecraft is currently in an exterior heliocentric orbit.[10]
Results
The total data returned by the mission was 5.2 million bits (about 634 kB). All instruments operated successfully with the exception of a part of the ionization chamber, namely the Geiger-Müller tube, which failed in February 1965. Also, the plasma probe had its performance degraded by a resistor failure on December 8, 1964, but by taking this failure into account, experimenters were able to recalibrate the instrument and still interpret the data.[11] The images returned showed a Moon-like cratered terrain,[12] which later missions showed was not typical for Mars, but only for the more ancient region imaged by Mariner 4. A surface atmospheric pressure of 4.1 to 7.0 millibars (410 to 700 pascals) and daytime temperatures of −100 degrees Celsius were estimated. No magnetic field[13][14] or Martian radiation belts[15] were detected.
Images of craters and measurements of a thin atmosphere,[12][16] indicating a relatively inactive planet exposed to the harshness of space, generally dissipated hopes of finding intelligent life on Mars. Life on Mars had been the subject of speculation and science fiction for centuries.[17] If there was life on Mars, after Mariner 4 most concluded it would probably be smaller, simpler forms.[citation needed] Others concluded that a search for life on Earth at kilometer resolution, using several thousand photographs, did not reveal a sign of life on the vast majority of these photographs; thus, based on the 22 photographs taken by Mariner 4, one could not conclude there was no intelligent life on Mars.[18]
Mariner 4 may have concluded the gradual change, in science fiction, from describing intelligent aliens as dwellers on other planets in our Solar System, to describing them as living on planets circling distant stars.[19]
The total cost of the Mariner 4 mission is estimated at $83.2 million. Total research, development, launch, and support costs for the Mariner series of spacecraft (Mariners 1 through 10) was approximately $554 million.
See also
References
- ^ "Mariner 4". NSSDC Master Catalog. NASA. http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1964-077A. Retrieved 2009-02-11.
- ^ a b Momsen, Bill (2006). "Mariner IV - First Flyby of Mars: Some personal experiences". p. 1. http://home.earthlink.net/~nbrass1/mariner/miv.htm. Retrieved 2009-02-11.
- ^ Momsen, Bill (2006). "Mariner IV - First Flyby of Mars: Some personal experiences". p. 2. http://home.earthlink.net/~nbrass1/mariner/miv-2.htm. Retrieved 2009-02-11.
- ^ a b c d e (pdf) JPL Technical Memorandum No. 33-229, To Mars: The Odyssey of Mariner IV. Jet Propulsion Laboratory/California Institute of Technology, NASA. 1965-01-01. pp. 21–23. http://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/19650018349_1965018349.pdf. Retrieved 2009-02-12.
- ^ Anderson, Hugh R. (1965-09-10). "Initial Results, Spacecraft Description and Encounter Sequence". Science, New Series 149 (3689): 1226–1228. Bibcode 1965Sci...149.1226A. doi:10.1126/science.149.3689.1226. PMID 17747450.
- ^ Reiff, Glenn A. (1966-01-28). "Mariner IV: Developing the Scientific Experiment". Science, New Series 151 (3709): 413–417. Bibcode 1966Sci...151..413R. doi:10.1126/science.151.3709.413. PMID 17798511.
- ^ a b c Goss, W.C. (1970-05-01). "The Mariner Spacecraft Star Sensors". Applied Optics 9 (5): 1056–1067. Bibcode 1970ApOpt...9.1056G. doi:10.1364/AO.9.001056. PMID 20076329.
- ^ Phillips, Tony (2006-08-23). "Mariner Meteor Mystery, Solved?". Science@NASA. NASA. http://science.nasa.gov/headlines/y2006/23aug_mariner4.htm. Retrieved 2009-02-11.
- ^ Phillips, Tony (2006-08-24). "Has the Mariner Meteor Mystery Been Solved". NASA Science News. http://www.marsdaily.com/reports/Has_The_Mariner_Meteor_Mystery_Been_Solved_999.html. Retrieved 2009-02-11.
- ^ Filmer, Paul E. (2004-01-05). "Beagle! Here Beagle, Beagle...". http://filmer.blogspot.com/2004/01/beagle-here-beagle-beagle.html. Retrieved 2009-02-12.
- ^ "release 1965 0319". Office of Public Education and Information, Jet Propulsion Laboratory/California Institute of Technology, NASA. 1965-03-03. http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/releases/60s/release_1965_0319.html. Retrieved 2009-02-13.
- ^ a b Leighton, Robert B.; Murray, Bruce C.; Sharp, Robert P.; Allen, J. Denton; Sloan, Richard K. (1965-08-06). "Mariner IV Photography of Mars: Initial Results". Science, New Series 149 (3684): 627–630. Bibcode 1965Sci...149..627L. doi:10.1126/science.149.3684.627. PMID 17747569.
- ^ O'Gallagher, J.J.; Simpson, J.A. (1965-09-10). "Search for Trapped Electrons and a Magnetic Moment at Mars by Mariner IV". Science, New Series 149 (3689): 1233–1239. Bibcode 1965Sci...149.1233O. doi:10.1126/science.149.3689.1233. PMID 17747452.
- ^ Smith, Edward J.; Davis Jr., Leverett; Coleman Jr., Paul J.; Jones, Douglas E. (1965-09-10). "Magnetic Field Measurements Near Mars". Science, New Series 149 (3689): 1241–1242. Bibcode 1965Sci...149.1241S. doi:10.1126/science.149.3689.1241. PMID 17747454.
- ^ Van Allen, J.A.; Frank, L.A.; Krimigis, S.M.; Hills, H.K. (1965-09-10). "Absence of Martian Radiation Belts and Implications Thereof". Science, New Series 149 (3689): 1228–1233. Bibcode 1965Sci...149.1228V. doi:10.1126/science.149.3689.1228. PMID 17747451.
- ^ Kliore, Arvydas; Cain, Dan L.; Levy, Gerald S.; Eshleman, Von R.; Fjeldbo, Gunnar; Drake, Frank D. (1965-09-10). "Occultation Experiment: Results of the First Direct Measurement of Mars's Atmosphere and Ionosphere". Science, New Series 149 (3689): 1243–1248. Bibcode 1965Sci...149.1243K. doi:10.1126/science.149.3689.1243. PMID 17747455.
- ^ Salisbury, Frank B. (1962-04-06). "Martian Biology". Science, New Series 136 (3510): 17–26. Bibcode 1962Sci...136...17S. doi:10.1126/science.136.3510.17. PMID 17779780.
- ^ Kilston, Steven D.; Drummond, Robert R.; Sagan, Carl (1966). "A Search for Life on Earth at Kilometer Resolution". Icarus 5 (1-6): 79–98. Bibcode 1966Icar....5...79K. doi:10.1016/0019-1035(66)90010-8.
- ^ Niven, Larry (1999). Rainbow Mars. Tor Books. ISBN 0-312-86777-8.
External links
- Mariner 4 Mission Profile by NASA's Solar System Exploration
- Space Flight Operations Plan Mariner Mars '64 (PDF)
- Processed images and mosaics from the Mariner 4 mission to Mars
- Ted Stryk's Mariner 4 page
Mariner program Mariner 1 · Mariner 2 · Mariner 3 · Mariner 4 · Mariner 5 · Mariner 6 and 7 · Mariner 8 · Mariner 9 · Mariner 10Spacecraft missions to Mars Flybys 
Orbiters Mariner 9 · Mars 2 · 3 · 5 · Viking 1 · 2 · Phobos 2 · Mars Global Surveyor · 2001 Mars Odyssey · Mars Express · Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter · Fobos-Grunt · Yinghuo-1
Landers Rovers Planned missions Mars Science Laboratory (2011) · MetNet · MAVEN (2013) ·
ExoMars static lander and rover · ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter (2016) · Northern LightUnplanned missions Related topics Exploration · Colonization · Failed Mars missions · Mars Scout Program
Bold italics indicate active missionsScience instruments on satellites and spacecraft Radio science
(planetary
occultation)Cassini–Huygens · Mariner 2 · Mariner 3 · Mariner 4 · Mariner 5 · Mariner 6 and 7 · Mariner 9 · Mariner 10 · Voyager 1 · Voyager 2 · MESSENGER · Venus Express · Mars ExpressRadiometer Near Earth satelliteInfrared (IR)Near Earth satelliteInterplanetaryUltraviolet (UV) ·Near Earth satelliteSpectro-
photometersLong wavelengthInterplanetaryNear Earth satelliteInterplanetaryInterplanetaryMagnetometer Near Earth satelliteInterplanetaryInterplanetaryMariner 2 · Mariner 4 · Mariner 5 · Mariner 10 · Cassini–Huygens · Venus Express · MESSENGER · MagsatInterplanetaryParticle
detectorsIon detectorsNear EarthInterplanetaryNeutral particle detectorInterplanetary← 1963 · Orbital launches in 1964 · 1965 → NRL PL135 · GGSE-1 · Solrad 7A · SECOR-1 | OPS 3367A · OPS 3367B | Relay 2 | Echo 2 | Jupiter Nosecone | Elektron-1 · Elektron-2 | Ranger 6 | OPS 3444 | Venera 3MV-1 No.2 | Kosmos 25 | OPS 2423 | OPS 3722 | OPS 3435 | Kosmos 26 | BE-A | Luna E-6 No.6 | OPS 3467 | Kosmos 27 | Ariel 2 | Zond 1 | Kosmos 28 | Gemini 1 | Polyot 2 | Luna E-6 No.5 | Transit 5BN-3 · Transit 5E-4 | OPS 3743 | Kosmos 29 | OPS 2921 | Kosmos 30 | OPS 3592 | Apollo A-102 | OPS 4412 | OPS 3483 | Molniya-1 No.2 | Kosmos 31 | Kosmos 32 | OPS 3236 | OPS 4467A · OPS 4467B | OPS 3754 | Kosmos 33 | ESRS | Atlas-Centaur 3 | Kosmos 34 | OPS 3395 | OPS 3684 · OPS 4923 | Elektron-3 · Elektron-4 | OPS 3491 | Kosmos 35 | OPS 3662 · OPS 3674 · ERS-13 | Ranger 7 | Kosmos 36 | OPS 3042 | Kosmos 37 | OPS 3802 · OPS 3216 | Kosmos 38 · Kosmos 39 · Kosmos 40 | Syncom 3 | OPS 2739 | OPS 2739 | Kosmos 41 | Kosmos 42 · Kosmos 43 | Kosmos 44 | Titan 3A-2 | OGO-1 | Kosmos 45 | OPS 3497 | Apollo A-102 | OPS 4262 | Kosmos 46 | Explorer 21 | OPS 3333 | Kosmos 47 | OPS 5798 · Dragsphere 1 · Dragsphere 2 | OPS 4036 | Explorer 22 | Voskhod 1 | Kosmos 48 | OPS 3559 | Strela-1 No.6 · Strela-1 No.7 · Strela-1 No.8 | OPS 4384 · OPS 5063 | Kosmos 49 | Kosmos 50 | OPS 5434 | OPS 3062 | Mariner 3 | Explorer 23 | OPS 3360 | Explorer 24 · Explorer 25 | Mariner 4 | Zond 2 | DS-2 No.2 | OPS 4439 | Kosmos 26 | Titan 3A-1 | Surveyor Mass Model | OPS 6582 · Transit 5E-5 | San Marco 1 | OPS 3358 | Explorer 26 | OPS 3762Payloads are separated by bullets ( · ), launches by pipes ( | ). Manned flights are indicated in bold text. Uncatalogued launch failures are listed in italics. Payloads deployed from other spacecraft are denoted in brackets.Categories:- Mars spacecraft
- Mariner program
- 1964 in spaceflight
- Inactive extraterrestrial probes
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.