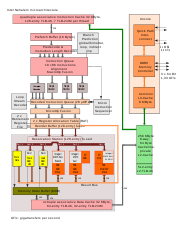
- Nehalem (microarchitecture)
-
For other uses, see Nehalem.
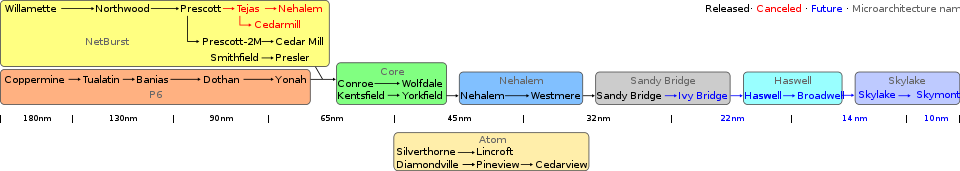
Nehalem (pronounced /nəˈheɪləm/[1]) is the codename for an Intel processor microarchitecture, successor to the Core microarchitecture.[2] Nehalem processors use the 45 nm process. A preview system with two Nehalem processors was shown at Intel Developer Forum in 2007. The first processor released with the Nehalem architecture was the desktop Core i7,[3] which was released in November 2008.
Nehalem, a recycled codename, refers to a completely different architecture from Netburst, although Nehalem still has some things in common with NetBurst. Nehalem-based microprocessors utilize higher clock speeds and are more energy-efficient than Penryn microprocessors. Hyper-Threading is reintroduced along with an L3 Cache missing from most Core-based microprocessors.
Contents
Technology
- Hyper-threading reintroduced.
- 4–12 MB L3 cache shared by all cores
- Second-level branch predictor and translation lookaside buffer
- Native (all processor cores on a single die) quad- and octo-core processors
- Intel QuickPath Interconnect in high-end models replacing the legacy front side bus
- 64 KB L1 cache/core (32 KB L1 Data + 32 KB L1 Instruction) and 256 KB L2 cache/core.
- Integration of PCI Express and DMI into the processor in mid-range models, replacing the northbridge
- Integrated memory controller supporting two or three memory channels of DDR3 SDRAM or four FB-DIMM2 channels
Performance and power improvements
It has been reported that Nehalem has a focus on performance, thus the increased core size.[4] Compared to Penryn, Nehalem has:
- 10-25% more single-threaded performance / 20-100% more multithreaded performance at the same power level
- 30% lower power usage for the same performance
- Nehalem provides a 15–20% clock-for-clock increase in performance per core
Overclocking is possible with Bloomfield processors and the X58 chipset. Lynnfield processors use a PCH removing the need for a northbridge chipset.[5]
Nehalem processors incorporate SSE 4.2 SIMD instructions, adding 7 new instructions to the SSE 4.1 set in the Core 2 series. The Nehalem architecture reduces atomic operation latency by 50% in an attempt to eliminate atomic overhead .[6]
Westmere
Westmere (formerly Nehalem-C) is the name given to the 32 nm die shrink of Nehalem. The first Westmere-based processors were launched on January 7, 2010.
Westmere's feature improvements from Nehalem as reported:
- Native six-core (Gulftown) and ten-core (Westmere-EX) processors.[7]
- A new set of instructions that gives over 3x the encryption and decryption rate of Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) processes compared to before.[8]
- Delivers seven new instructions (AES instruction set or AES-NI) that will be used by the AES algorithm. Also an instruction called PCLMULQDQ (see CLMUL instruction set) that will perform carry-less multiplication for use in cryptography.[9] These instructions will allow the processor to perform hardware-accelerated encryption, not only resulting in faster execution but also protecting against software targeted attacks.
- Integrated graphics, added into the processor package (dual core Arrandale and Clarkdale only).
- Improved virtualization latency.[10]
- New virtualization capability: "VMX Unrestricted mode support," which allows 16-bit guests to run (real mode and big real mode).
- Support for "Huge Pages" of 1GB in size.
Variants Overview
Processing Cores (interface) Process Die Size CPUID Model Stepping Mobile Desktop, UP Server DP Server MP Server Eight-Core (Quad-Channel) 45 nm 684 mm² 206E6 46 D0 Beckton (80604) Quad-Core (Triple-Channel) 45 nm 263 mm² 106A4
106A526 C0
D0Bloomfield (80601) Gainestown (80602) Quad-Core (Dual-Channel, PCIe) 45 nm 296 mm² 106E4
106E530 B0
B1Clarksfield (80607) Lynnfield (80605) Jasper Forest (80612) Dual-Core (Dual-Channel, PCIe, Graphics Core) 45 nm Auburndale (canceled) Havendale (canceled) Ten-Core (Quad-channel)[11] 32 nm 513 mm² 206F2 47 A2 Westmere-EX (80615) Six-Core (Triple-Channel) 32 nm 248 mm² 206C2 44 B1 Gulftown (80613) Westmere-EP (80614) Dual-Core (Dual-Channel, PCIe, Graphics Core) 32 nm
45 nm81+114 mm² 20652
2065537 C2
K0Arrandale (80617) Clarkdale (80616) Nehalem
- Lynnfield processors feature integrated PCIe 1 x16 or 2 x8.
- 1 6500 series scalable up to 2 sockets, 7500 series scalable up to 4/8 sockets.[12]
Server / Desktop Processors
Codename Market Cores /
ThreadsSocket Processor
Branding & ModelCPU
Clock rateTurbo TDP Interfaces L3
cacheRelease Date Price for
1k UnitChipset Memory Beckton1 MP Server /
DP Server8 (16) LGA
1567Xeon [13] X7560 2.26 GHz Yes 130 W 4× QPI 6.4 GT/s DDR3-800 /
1066
(Up to 4x with
SMB-Ready
Motherboard)24 MB 2010-03-30[14] $3692 X7550 2.0 GHz 18 MB $2837 X6550 $2461 L7555 1.86 GHz 95 W 4× QPI 5.86 GT/s 24 MB $3157 6 (12) E7540 2.0 GHz 105 W 4× QPI 6.4 GT/s 18 MB $1980 E6540 12 MB $1712 E7530 1.86 GHz 4× QPI 5.86 GT/s $1391 L7545 18 MB $2087 6 (6) X7542 2.66 GHz 130 W $1980 4 (8) E7520 1.86 GHz No 105 W 4× QPI 4.8 GT/s $856 E6510 1.73 GHz 12 MB $744 Gainestown DP Server[15] 4 (8) LGA
1366Xeon[16] W5590 3.33 GHz Yes 130 W 2× QPI 6.4 GT/s 3× DDR3-13331 8 MB 2009-08-09 $1600 W5580 3.2 GHz 2009-03-29[17] $1500 X5570 2.93 GHz 95 W $1286 X5560 2.8 GHz $1072 X5550 2.66 GHz $858 E5540 2.53 GHz 80 W 2× 5.86 GT/s 3× DDR3-10661 $744 E5530 2.4 GHz $530 E5520 2.26 GHz $373 L5530 2.4 GHz 60 W 2009-08-09 $744 L5520 2.26 GHz 2009-03-30 $530 L5518 2.13 GHz $ 4 (4) E5507 2.26 GHz No 80 W 2× 4.8 GT/s 3× DDR3-8001 4 MB 2010-03-16 $266 E5506 2.13 GHz 2009-03-29 L5506 2.13 GHz 60 W $423 E5504 2.0 GHz 80 W $224 2 (4) L5508 2.0 GHz Yes 38 W 2× 5.86 GT/s 3× DDR3-1066 8 MB $ 2 (2) E5503 2.0 GHz No 80 W 2× 4.8 GT/s 3× DDR3-800 4 MB 2010-03-16 $224 E5502 1.86 GHz 2009-03-29 $188 Bloomfield UP Server[18] 4 (8) Xeon[19] W3580 3.33 GHz Yes 130 W 1× QPI 6.4 GT/s 3× DDR3-1333 8 MB 2009-08-09 $999 W3570 3.2 GHz 2009-03-29[19] W3565 3.2 GHz 1× QPI 4.8 GT/s 3× DDR3-1066 2009-11-01 $562 W3550 3.06 GHz 2009-08-09 W3540 2.93 GHz 2009-03-29[19] W3530 2.8 GHz 2010-03-16 $294 W3520 2.66 GHz 2009-03-29[19] $284 2(2) W3505 2.53 GHz No 4 MB $ W3503 2.4 GHz $ Lynnfield 4 (8) LGA
1156X3480 3.06 GHz Yes 95 W DMI 2× DDR3-1333 8 MB 2010-05-30 $612 X3470 2.93 GHz 2009-09-08 $589 X3460 2.8 GHz $316 X3450 2.66 GHz $241 X3440 2.53 GHz $215 L3426 1.86 GHz 45 W $284 4 (4) X3430 2.4 GHz 95 W $189 Bloomfield Enthusiast
Desktop[20]4 (8) LGA
1366Core i7
Extreme975[21] 3.33 GHz Yes 130 W 1× QPI 6.4 GT/s 3× DDR3-1066 2009-05-31 $999 965 3.2 GHz 2008-11-17 Core i7 960[22] 3.2 GHz 1× QPI 4.8 GT/s 2009-10-20 $562 950[21] 3.06 GHz 2009-05-31 940 2.93 GHz 2008-11-17 930 2.8 GHz 2010-02-28 $294 920 2.66 GHz 2008-11-17 $284 Lynnfield Performance
DesktopLGA
1156880 3.06 GHz Yes 95 W DMI 2× DDR3-1333 2010-05-30 $583 875K 2.93 GHz $342 870[23] 2009-09-08 $562 870S 2.66 GHz 82 W 2010-07-19 $351 860 2.8 GHz 95 W 2009-09-08 $284 860S 2.53 GHz 82 W 2010-01-07 $337 4 (4) Core i5 760 2.8 GHz 95 W 2010-07-17 $209 750[24] 2.66 GHz 95 W 2009-09-08 $196 750S 2.4 GHz 82 W 2010-01-07 $259 - Intel states the Gainestown processors have six memory channels. Gainestown processors have dual QPI links and have a separate set of memory registers for each link in effect, a multiplexed six-channel system.[25][26]
Mobile Processors
Codename Market Cores /
ThreadsSocket Processor
Branding & ModelCore
Clock rateTurbo TDP L3
cacheInterface Release Date Price for
1k UnitClarksfield Extreme /
Performance
Mobile4 (8) µPGA
988Core i7
Extreme940XM 2.13 GHz Yes 55 W 8 MB * DMI
* 2x DDR3-1333
* PCIe 1 x16 / 2 x82010-06-21 $1096 920XM 2.0 GHz 2009-09-23 $1054 Core i7 840QM 1.86 GHz 45 W 2010-06-21 $568 820QM 1.73 GHz 2009-09-23 $546 740QM 6 MB 2010-06-21 $378 720QM 1.6 GHz 2009-09-23 $364 Westmere
- TDP includes the integrated GPU, if present.
- Clarkdale processors feature an integrated PCIe 1 x16.
- Clarkdale and Arrandale contain the 32 nm dual core processor Hillel and the 45 nm integrated graphics device Ironlake, and support switchable graphics.[27][28]
Server / Desktop Processors
Codename Market Cores /
ThreadsSocket Processor
Branding & modelClock rate Turbo TDP Interfaces L3
cacheRelease
DatePrice Core GPU Chipset Memory Westmere-EX MP Server 10 (20) LGA
1567Xeon E7-4870 2.4 GHz N/A Yes 130 W 2× QPI 6.4 GT/s 30 MB 2011-04-05
[29]$4394 E7-4860 2.26 GHz 24 MB $3838 E7-4850 2 GHz $2837 Gulftown /
Westmere-EP
[30]DP Server 6 (12) LGA
1366Xeon X5690 3.46 GHz N/A Yes 130 W 2× QPI 6.4 GT/s 3× DDR3-1333 12 MB 2011-02-13 $1663 X5680 3.33 GHz 2010-03-16 X5675 3.06 GHz 95 W 2011-02-05 $1440 X5670 2.93 GHz 2010-03-16 $1440 X5660 2.8 GHz $1219 X5650 2.66 GHz $996 E5645 2.4 GHz 80 W 2× QPI 5.86 GT/s $958 L5640 2.26 GHz 60 W $996 L5638 2.0 GHz $958 4 (8) X5677 3.46 GHz 130 W 2× QPI 6.4 GT/s $1663 X5667 3.06 GHz 95 W $1440 E5640 2.66 GHz 80 W 2× QPI 5.86 GT/s 3× DDR3-1066 $774 E5630 2.53 GHz $551 E5620 2.4 GHz $387 L5630 2.13 GHz 40 W $551 L5618 1.86 GHz $530 4 (4) L5609 1.86 GHz No 2× QPI 4.8 GT/s $440 UP Server 6 (12) Xeon W3680 3.33 GHz N/A Yes 130 W 1× QPI 6.4 GT/s 3× DDR3-1333 2010-03-16[31] $999 W3670 3.20 GHz 1× QPI 4.8 GT/s 3× DDR3-1066 2010-08-29 $885 Extreme /
Performance
DesktopCore i7
Extreme990X 3.46 GHz 1× QPI 6.4 GT/s 2011-02-13 $999 980X 3.33 GHz 2010-03-16 Core i7 970 3.2 GHz 1× QPI 4.8 GT/s 2010-07-17 $885 Clarkdale[32] UP Server 2 (4) LGA
1156Xeon L3406 2.26 GHz N/A Yes 30 W DMI 2× DDR3-1066 4 MB 2010-03-16 $189 L3403 2.0 GHz 2010-10 $ Mainstream /
Value
DesktopCore i5 680 3.6 GHz 733 MHz 73 W 2× DDR3-1333 2010-04-18 $294 670 3.46 GHz 2010-01-07 $284 661 3.33 GHz 900 MHz 87 W $196 660 733 MHz 73 W 650 3.2 GHz $176 Core i3 560 3.33 GHz No 2010-08-29 $138 550 3.20 GHz 2010-05-30 540 3.06 GHz 2010-01-07 $133 530 2.93 GHz $113 2 (2) Pentium G6950 2.8 GHz 533 MHz 2× DDR3-1066 3 MB $87 Celeron G1101 2.26 GHz 2 MB OEM Mobile Processors
Codename Market Cores /
ThreadsProcessor
Branding & ModelCPU Clock rate GPU Clock rate Turbo TDP Memory L3
cacheInterface Release
DatePrice Standard Turbo
(1C/2C active cores )Arrandale Mainstream / Value Mobile
2 (4) Core i7 640M 2.8 GHz 3.47/3.2 GHz 766 MHz Yes 35 W 2× DDR3-1066 4 MB * DMI
* PCIe 1 x16
* Socket:
µPGA-988 /
BGA-12882010-09-26 $346 620M 2.66 GHz 3.33/3.2 GHz 2010-01-07 $332 610E 2.53 GHz 3.2/2.93 GHz OEM 660LM 2.26 GHz 3.06/2.8 GHz 566 MHz 25 W 2010-09-26 $346 640LM 2.13 GHz 2.93/2.66 GHz 2010-01-07 $332 620LM / 620LE 2.0 GHz 2.8/2.53 GHz $300 680UM 1.46 GHz 2.53/2.16 GHz 500 MHz 18 W 2× DDR3-800 2010-09-26 $317 660UM 1.33 GHz 2.4/2.0 GHz 2010-05-25 $289 640UM 1.2 GHz 2.26/1.87 GHz 2010-01-07 $305 620UM / 620UE 1.06 GHz 2.13/1.76 GHz $278 Core i5 580M 2.66 GHz 3.33/2.93 GHz 766 MHz 35 W 2× DDR3-1066 3 MB 2010-09-26 $266 560M 2.66 GHz 3.2/2.93 GHz $260 540M 2.53 GHz 3.06/2.8 GHz 2010-01-07 $257 520M / 520E 2.4 GHz 2.93/2.66 GHz $225 560UM 1.33 GHz 2.13/1.86 GHz 500 MHz 18 W 2× DDR3-800 2010-09-26 $250 540UM 1.2 GHz 2.0/1.73 GHz 2010-05-25 $250 520UM 1.06 GHz 1.86/1.6 GHz 2010-01-07 $241 480M 2.67 GHz 2.93/2.93 GHz 766 MHz 35 W 2× DDR3-1066 2011-01-09 OEM 460M 2.53 GHz 2.8/2.8 GHz 2010-09-26 450M 2.4 GHz 2.66/2.66 GHz 2010-06-26 430M 2.26 GHz 2.53/2.53 GHz 2010-01-07 470UM 1.33 GHz 1.86/1.6 GHz 500 MHz 18 W 2× DDR3-800 2010-10-01 430UM 1.2 GHz 1.73/1.47 GHz 2010-05-25 Core i3 380M 2.54 GHz n/a 667 MHz No 35 W 2× DDR3-1066 2010-09-26 370M 2.4 GHz 2010-06-20 350M 2.26 GHz 2010-01-07 330M / 330E 2.13 GHz 380UM 1.33 GHz 500 MHz 18 W 2× DDR3-800 2010-10-01 330UM 1.2 GHz 2010-05-25 2 (2) Pentium P6200 2.13 GHz 667 MHz 35 W 2× DDR3-1066 2010-09-26 P6100 2.00 GHz P6000 1.86 GHz 2010-06-20 U5400 1.20 GHz 500 MHz 18 W 2× DDR3-800 2010-05-25 Celeron P4600 2.00 GHz 667 MHz 35 W 2× DDR3-1066 2 MB 2010-09-26 $86 P4500 / P4505 1.86 GHz 2010-03-28 OEM U3400 / U3405 1.06 GHz 500 MHz 18 W 2× DDR3-800 / 1066 2010-05-25 Successor
The successor to Nehalem and Westmere is Sandy Bridge.
References
- ^ I Am Nehalem, http://www.metacafe.com/watch/830178/i_am_nehalem/
- ^ Intel Details Upcoming New Processor Generations, Intel Corporation, 2007-03-28, http://www.intel.com/pressroom/archive/releases/20070328fact.htm
- ^ Gruener, Wolfgang (2008-08-10), Nehalem = i7: Intel unveils new Core processor brand, TG Daily, http://www.tgdaily.com/content/view/38818/135/
- ^ "Intel's dual teamed approached to micro-architecture development" (in Japanese), PC Watch, 2008-01-29, http://pc.watch.impress.co.jp/docs/2008/0129/kaigai412.htm
- ^ Botezatu, Bogdan (2008-04-22), Intel: No Overclocking for Mainstream Nehalems, Softpedia, http://news.softpedia.com/news/Intel-No-Overclocking-for-Mainstream-Nehalems-84019.shtml
- ^ NO EXECUTE!, http://www.emulators.com/docs/nx24_hot_chips.htm
- ^ Intel says no to 28nm, focuses on 22nm: Ivy Bridge/Haswell & Larrabee, http://brightsideofnews.com/news/2009/4/16/intel-says-no-to-28nm2c-focuses-on-22nm-ivy-bridgehaswell--larrabee.aspx
- ^ Smalley, Tim (2007-09-19), Westmere is Nehalem's successor, bit-tech.net, http://www.bit-tech.net/news/2007/09/19/westmere_is_nehalem_successor/1
- ^ Carry-Less Multiplication and Its Usage for Computing The GCM Mode – Intel Software Network, 2008-04-11, http://software.intel.com/en-us/articles/carry-less-multiplication-and-its-usage-for-computing-the-gcm-mode, retrieved 2009-03-01
- ^ Fuad Abazovic (2008-09-16), Westmere 32nm to improve Nehalem features, Fudzilla.com, http://www.fudzilla.com/processors/processors/processors/westmere-32nm-to-improve-nehalem-features, retrieved 2009-03-01
- ^ Westmere-EX 10 core CPUs announced by Intel at IDF
- ^ High-End x86: The Nehalem EX Xeon 7500 and Dell R810
- ^ AMD launches 12-core Opteron server chips, Intel counters with the 8-core Xeon 7500, engadedget.com, 2010-03-31, http://www.engadget.com/2010/03/30/amd-launches-12-core-opteron-server-chips-intel-counters-with-t/, retrieved 2010-03-31
- ^ Nebojsa Novakovic (2009-02-12), Intel's next bunch of fun CPUs moves to 2010, CNN International, http://www.theinquirer.net/inquirer/opinion/976/1050976/intel-bunch-fun-cpus-moves-2010, retrieved 2009-03-01
- ^ Intel Xeon Processor 5500 Series Product brief, (Document Number: 321579-001US), Intel, 2009-04-01, http://www-2000.ibm.com/partnerworld/ap/kr/intel_xeon_5500_prodbrief.pdf, retrieved 2010-08-27
- ^ Core i7 to make leap to Xeon in early 2009, Legacy.macnn.com, http://legacy.macnn.com/articles/08/11/13/xeon.i7.in.early.2009/, retrieved 2008-11-24
- ^ Fuad Abazovic (2009-01-28), Nehalem based Xeon comes Mar 29th, Fudzilla.com, http://www.fudzilla.com/processors/processors/processors/nehalem-based-xeon-comes-mar-29th, retrieved 2009-01-28
- ^ Intel Xeon Processor 3500 Series, Intel, 2009-04-01, http://www.intel.com/cd/channel/reseller/asmo-na/eng/products/server/processors/3500/feature/index.htm, retrieved 2009-04-10
- ^ a b c d Teglet, Traian (2008-11-13), Intel to Add New Nehalem Xeon Processor, softpedia, http://news.softpedia.com/news/Intel-to-Add-New-Nehalem-Xeon-Processors-97856.shtml, retrieved 2008-11-13
- ^ "Intel Core i7 Processor Extreme Datasheet, Volume 2, (Document Number: 320835-002)". Intel. 2008-11-01. http://download.intel.com/design/processor/datashts/320835.pdf. Retrieved 2009-03-24.
- ^ a b Worrel, Jon (2009-02-09), Core i7 950 and 975 to replace 940 and 965, Fudzilla, http://www.fudzilla.com/processors/processors/processors/core-i7-950-and-975-to-replace-940-and-965, retrieved 2009-02-10
- ^ Intel to launch new Core i7 960 and Celerons, http://www.guru3d.com/news/intel-to-launch-new-core-i7-960-and-celerons/
- ^ Intel Core i5-750, AnandTech, 2009-06-17, http://www.anandtech.com/cpuchipsets/showdoc.aspx?i=3585
- ^ Intel Quietly Announces Core i5, Xtreview, 2009-06-26, http://www.anandtech.com/cpuchipsets/showdoc.aspx?i=3585
- ^ Intel Xeon Processor 5000 SequenceTechnical Documents, http://www.intel.com/p/en_US/products/server/processor/xeon5000/technical-documents
- ^ Intel Xeon Processor 5500 Series Datasheet Volume 2, Intel, March 2009, http://www.intel.com/Assets/PDF/datasheet/321322.pdf, retrieved 2009-05-01
- ^ Bell, Brandon (2009-02-10), Intel CPU Roadmap 2009–2010, FS Media, Inc, http://www.firingsquad.com/hardware/intel_32nm_westmere_roadmap/page2.asp, retrieved 2009-03-01
- ^ CPU list, http://www.hwinfo.com/Lists/cpu.htm
- ^ Intel Launches New Xeon Chips with Up to Ten Cores, http://www.xbitlabs.com/news/cpu/display/20110405135321_Intel_Launches_New_Xeon_Chips_with_Up_to_Ten_Cores.html
- ^ Intel pushes workhorse Xeons to six cores, http://www.theregister.co.uk/2010/03/16/intel_xeon_5600_launch/
- ^ Intel Launches Its Most Secure Data Center Processor, http://sanfrancisco.dbusinessnews.com/viewnews.php?article=bwire/20100316005652r1.xml
- ^ Intel Clarkdale Processor, XTREVIEW, 2009-02-09, http://xtreview.com/addcomment-id-7818-view-Intel-clarkdale-processor.html, retrieved 2009-03-01
Further reading
- InfoWorld review: Intel's Westmere struts its stuff, InfoWorld, 2010-03-16, http://www.infoworld.com/d/hardware/infoworld-review-intels-westmere-struts-its-stuff-588
- IDF: Intel Clarkdale Up Close and Personal, X-bit Labs, 2009-09-24, http://www.xbitlabs.com/articles/cpu/display/clarkdale-sneakpeek.html
- Intel Core i7 Processors: Nehalem and X58 Have Arrived, Hot Hardware, 2008-11-03, http://hothardware.com/Articles/Intel-Core-i7-Processors-Nehalem-and-X58-Have-Arrived/
- Intel Core i7 CPU & Nehalem Architecture Review, hardCOREware.net, 2008-11-03, http://www.hardcoreware.net/reviews/review-372-1.htm
- Intel Nehalem Core i7 Series Complete Review, PC Perspective, 2008-11-03, http://www.pcper.com/article.php?aid=634
- Intel Nehalem Core i7 940 Review, Xtreview, 2008-10-01, http://xtreview.com/addcomment-id-6524-view-Intel-core-i-7-940-review.html
- Altavilla, Dave (2008-03-17), Intel Showcases Dunnington, Nehalem and Larrabee Processors, HotHardware, http://www.hothardware.com/Articles/Intel_Showcases_Dunnington_Nehalem_and_Larrabee_Processors/
- Shrout, Ryan (2008-03-28), Intel Slides and Nehalem architecture information, PC Perspective, http://www.pcper.com/article.php?aid=382&type=expert
- Stokes, Jon (2007-03-28), Intel drops a Nehalem bomb on AMD's Fusion: integrated graphics, on-die memory controller, SMT, Ars Technica, http://arstechnica.com/news.ars/post/20070328-intel-aims-nehalem-at-amds-fusion-integrated-graphics-on-die-memory-controller-smt.html
- Lal Shimpi, Anand (2007-09-18), Nehalem: Single die, 8-cores, 731M transistors, AnandTech, http://www.anandtech.com/cpuchipsets/intel/showdoc.aspx?i=3101&p=2
- Lal Shimpi, Anand (2008-11-03), Nehalem - Everything You Need to Know about Intel's New Architecture, AnandTech, http://www.anandtech.com/show/2594/1
- David Kanter (2010-04-04). "Inside Nehalem: Intel's Future Processor and System". realworldtech.com. http://www.realworldtech.com/page.cfm?ArticleID=RWT040208182719. Retrieved 2010-12-16.
- Holland, Maggie (2007-09-19), IDF 2007: Intel debuts Nehalem, IT Pro, http://www.itpro.co.uk/news/125370/idf-2007-intel-debuts-nehalem.html
- (in Spanish) Everything we know about Nehalem, CHW.net, 2008-01-05, http://www.chw.net/Articulos/Intel/Todo-lo-que-sabemos-de-Intel-Nehalem-200801051919.html
- Stokes, Jon (2008-04-09), What you need to know about Intel's Nehalem CPU, Ars Technica, http://arstechnica.com/articles/paedia/cpu/what-you-need-to-know-about-nehalem.ars
- Torres, Gabriel (2008-03-17), Details on the Forthcoming Intel Nehalem Processor, Hardware Secrets, http://www.hardwaresecrets.com/article/535
- Shimpi, Anand Lal (2008-06-05), The Nehalem Preview: Intel Does It Again, AnandTech, http://www.anandtech.com/cpuchipsets/intel/showdoc.aspx?i=3326
- Shimpi, Anand Lal (2008-08-21), Nehalem – Everything You Need to Know about Intel's New Architecture, AnandTech, http://www.anandtech.com/cpuchipsets/intel/showdoc.aspx?i=3382
- First Look at Nehalem Microarchitecture, X-bit Labs, 2008-11-02, http://www.xbitlabs.com/articles/cpu/display/nehalem-microarchitecture.html
External links
- Nehalem processor at Intel.com
Intel processors Discontinued BCD oriented (4-bit) pre-x86 (8-bit) Early x86 (16-bit) x87 (external FPUs) IA-32 (32-bit) x86-64 (64-bit) Other Current Lists Microarchitectures P5 P5 based cores 800 nm - P5
600 nm - P54C
350 nm - P54CS
- P55C
250 nm - Tillamook
P6 P6 / Pentium M / Enhanced Pentium M based cores 500 nm 350 nm - P6
- Klamath
250 nm - Mendocino
- Dixon
- Tonga
- Covington
- Deschutes
- Katmai
- Drake
- Tanner
180 nm - Coppermine
- Coppermine T
- Timna
- Cascades
130 nm - Tualatin
- Banias
90 nm - Dothan
- Stealey
65 nm - Tolapai
- Yonah
- Sossaman
NetBurst NetBurst based cores 180 nm 130 nm 90 nm 65 nm Core Core / Penryn based cores 65 nm 45 nm - Penryn
- Penryn-QC
- Wolfdale
- Yorkfield
- Wolfdale-DP
- Harpertown
- Dunnington
Bonnell Bonnell based cores 45 nm - Silverthorne
- Diamondville
- Pineview
- Lincroft
- Tunnel Creek
- Sodaville
32 nm - Cedarview
- Cedar Trail-M
Nehalem Nehalem / Westmere based cores 45 nm - Clarksfield
- Lynnfield
- Jasper Forest
- Bloomfield
- Gainestown (Nehalem-EP)
- Beckton (Nehalem-EX)
32 nm - Arrandale
- Clarkdale
- Gulftown (Westmere-EP)
- Westmere-EX
Sandy Bridge Sandy Bridge / Ivy Bridge based cores 32 nm - Sandy Bridge
Future Categories:- Intel x86 microprocessors
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.