- Mongol invasion of Europe
-
Mongol conquest of Eastern Europe 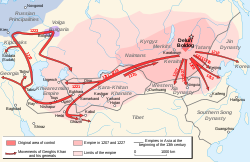
The route of the first Mongol expedition in Russia - 1223Date a) 1223, 1236-1240
b) late 1240-1241
c) April 11, 1241Location
a) Modern Russia, Ukraine and Belarus
b) Parts of southern and eastern Poland
and Medieval HungaryResult
a) Decisive Mongol victory resulting in principalities of Kievan State becoming vassals of the Mongol Golden Horde.
b) Mongol victory
c) Mongol victoryTerritorial
changes
a) the Ukraine and Russia
b) Kingdom of Poland
c) Kingdom of HungaryBelligerents
Mongol Empire
Volga Bulgaria
a) Vladimir-Suzdal
 Galicia-Volhynia
Galicia-Volhynia
 Novgorod Republic
Novgorod Republic
Principality of Ryazan
b) Polish states and allies
c) Kingdom of Hungary
Kingdom of Hungary
 Teutonic Knights
Teutonic Knights
 Knights Templar
Knights TemplarCommanders and leaders a) Batu Khan, Mongke Khan,
Subutai, Jebe,
Burundai, Berke,
Orda, Güyük Khan
b) Baidar, Kadan, Orda Khan
c) Batu Khan,
Subutai,
Shiban,
Berkea) Mstislav Mstislavich
Yuri II of Vladimir, Mstislav III of Kiev, Dmitro
b) Daniel of Galicia
various, most prominent was Henry II the Pious
c) King Béla IV
Prince Coloman
Archbishop Ugrin Csák
Archbishop Matthias Rátót
Dénes TomajStrength a) 20,000 in 1223
In 1236, More than 35,000 Mongols+More than 40,000 Turkic auxiliaries
b) about 10,000 (one tumen)[1]
c) Former estimation:
70,000[2]
New estimation:
30,000[3][4]a) 80,000 in 1223
b) over 10,000-30,000[5]+at least 500 armed men from Templar order.
c) Former estimation:
80,000[6]
New estimation:
25,000[3][4]
including Hungarian heavy cavalry, Knights Templar, nomadic light cavalry mercenaries and Serbian valiants. Thousands of Cumans and KipchaksCasualties and losses a) More than 7,000
b) Minimal
c) Few thousand killed[4]a) 500,000 (6-7% of the population of Rus)[7]
b) Heavy
c) Few thousand killed[4]- Central Asia (Khwarizm)
- Georgia and Armenia
- Volga Bulgaria (Samara Bend
- Bilär)
- Anatolia
- Europe (Dzurdzuketia
- Rus'
- Poland
- Hungary)
- Tibet
- Baghdad
- Korea
- India
- Japan (Bun'ei
- Kōan)
- Vietnam (Bạch Đằng)
- China (Jin
- Song)
- Burma (Ngasaunggyan
- Pagan
- Bhamo)
- Java
- Syria
- Palestine (Ain Jalut)
- Kalka River
- Ryazan
- Sit River
- Kiev
The resumption of the Mongol invasion of Europe, during which the Mongols attacked medieval Rus' principalities and the powers of Poland and Hungary, was marked by the Mongol invasion of Rus' starting in 21 December 1237. The European invasion, indicated by the start of the Mongol invasion of Rus' marked by the Battle of the Kalka River (1223) which was fought between the scout forces of just the two Mongolian generals Subutai and Jebe, whose reconnaissance unit met in battle with the combined force of several Rus' princes.
The invasion, reinforced by the breakup of Kievan Rus' in the 12th century, had incalculable ramifications on the history of Eastern Europe, including the division of the East Slavic people into three separate nations[8] and the rise of the Grand Duchy of Moscow.
After fifteen years of peace, the Rus' invasion was followed by Batu Khan's full-scale invasion of Rus' and points east during 1237 to 1240, which ended with a Mongol succession crisis. An alternative presents the European campaign as a pretense to keep the Europeans off balance and out of the Middle East.
Contents
Overview
The Mongol invasions of Europe, under the leadership of Subutai, centered on the destruction of East Slavic principalities, such as Kiev and Vladimir. The Mongols then invaded the Kingdom of Hungary (in the Battle of Mohi) and fragmented Poland (in the Battle of Legnica). The former invasion commanded by Batu Khan, Genghis Khan's grandson, and the latter a diversion commanded by Kadan, another grandson of Genghis Khan; both invasions were masterminded by Subutai.
Since the 13th century, historians have debated macrohistorical importance of the Mongols' Eastern European campaigns. Most military historians believe they were essentially diversions, meant to frighten the Western powers to keep them out of the Mongol affairs in the east of Europe, specifically in Rus`. For the Mongols, the European invasions were only a third theater of operations, after the Middle East and Song China.
Invasions and conquest of Rus' lands
Main article: Mongol invasion of Rus' Returning to Vladimir by Yaroslav II of Vladimir after Mongol destruction. From the medieval Russian annals
Returning to Vladimir by Yaroslav II of Vladimir after Mongol destruction. From the medieval Russian annals
Ogedei Khan ordered Batu Khan to conquer Russia in 1235. The main force headed by the Jochi's sons, and their cousins, Mongke Khan and Güyük Khan, arrived at Ryazan in December 1237. Ryazan refused to surrender, and the Mongols sacked it and then stormed Suzdalia. Many Rus' armies were defeated: Grand Prince Yuri was killed on the Sit River (March 4, 1238). Major cities such as Vladimir, Torzhok, and Kozelsk were captured.
Afterward, the Mongols turned their attention to the steppe, crushing the Kypchaks and the Alans and sacking Crimea. Batu reappeared in Russia in 1239, sacking Pereyaslavl and Chernihiv. Most of the Russian princes fled when it became clear resistance was futile. The Mongols sacked Kiev on December 6, 1240 and conquered Galich and Volodymyr-Volynskyi. Batu sent a small detachment to probe the Poles before passing on to Central Europe. One column was routed by the Poles while the other defeated the Polish army and returned.[9]
Invasion into Central Europe
Main article: Mongol invasion of PolandThe Mongols invaded Central Europe with three armies. One army defeated an alliance which included forces from fragmented Poland and members of various Christian military orders, led by Henry II the Pious, Duke of Silesia in the battle of Legnica. A second army crossed the Carpathian mountains and a third followed the Danube. The armies re-grouped and crushed Hungary in 1241, defeating the Hungarian army at the Battle of Mohi on April 11, 1241. The devastating Mongol invasion killed half of Hungary's then-population.[10] The armies swept the plains of Hungary over the summer and in the spring of 1242, regained impetus and extended their control into Austria and Dalmatia and Moravia. The Great Khan had, however, died in December 1241, and on hearing the news, all the "Princes of the Blood" of Genghis Khan went back to Mongolia to elect the new Khan.[11]
 Henry II the Pious who lost his life at the battle of Legnica, 19th century painting by Jan Matejko.
Henry II the Pious who lost his life at the battle of Legnica, 19th century painting by Jan Matejko.
After sacking Kiev,[12] Batu Khan sent a smaller group of Mongols to Poland, destroying Lublin and defeating an inferior Polish army. Other elements—not part of the main Mongol force—saw difficulty near the Polish-Galich border. The Mongols suffered serious casualties at Olomouc in Moravia, in a fight with a numerically superior pan-European army in terrain disadvantageous for the use of cavalry. As for Poland, the Mongols were just passing through and the efforts of king Wenceslas amounted to little in Mongol strategic considerations.
The Tatars[clarification needed] then reached Polaniec on the Czarna Hańcza[clarification needed], where they set up camp. There, the Voivode attacked them with the remaining Cracovian knights, which were few in number, but determined to conquer or die. Surprise gave the Poles an initial advantage and they managed to kill many Mongol soldiers. When the invaders realized the actual numerical weakness of the Poles, they regrouped, broke through the Polish ranks and defeated them. During the fighting, many Polish prisoners of war found ways to escape and hide in the nearby woods. The Polish defeat was partly influenced by that the initially successful Polish knights were distracted by looting. The attack on Europe was planned and executed by Subutai, who achieved perhaps his most lasting fame with his victories there. Having devastated the various Russian principalities, he sent spies into Poland, Hungary, and as far as Austria, in preparation for an attack into the heartland of Europe. Having a clear picture of the European kingdoms, he prepared an attack nominally commanded by Batu Khan and two other familial-related princes. Batu Khan, son of Jochi, was the overall leader, but Subutai was the strategist and commander in the field, and as such, was present in both the northern and southern campaigns against Russian principalities. He also commanded the central column that moved against Hungary. While Kadan's northern force won the Battle of Legnica and Güyük's army triumphed in Transylvania, Subutai was waiting for them on the Hungarian plain. The newly reunited army then withdrew to the Sajo River where they inflicted a decisive defeat on King Béla IV of Hungary at the Battle of Mohi. Again, Subutai masterminded the operation, and it would prove one of his greatest victories.
Invasion of the Kingdom of Hungary
Further information: Battle of MohiMore than 200 years before the Mongol invasion, the Hungarian army (descendants of the Magyars) was based upon light cavalry. An interesting fact is that the former tactics of the Hungarian army were similar to those of the Mongols, but had been largely forgotten by 1241. One of the major light cavalry tactics was to suddenly rush the enemy position. However, if the enemy held (or reformed), light cavalry was insufficient to achieve a victory. Another significant tactic was to feign retreat, in which the light cavalry would attack the enemy and then withdraw, apparently fleeing. The enemy would ideally pursue and become disorganized, leaving themselves open to attack by units hidden in reserve. The light cavalry would then reform and attack the flanks or rear of the enemy forces. The Hungarians stopped using these tactics during the 11th century.[why?]
In the late 11th century, the majority of the Hungarian army consisted of mounted sergeants (heavy knights) and infantry. The Hungarian allies, some of whom still utilized the light cavalry combat style, included the Cumans, who had settled down in Hungary not long before the Mongol invasion. They were tasked with providing the light cavalry force in the Hungarian army. However tension erupted when Mongol troops first broke into Hungary: The Hungarians, frustrated by their own helplessness, took revenge on the Cumans, whom they accused of being Mongol spies. After a bloody fight the Hungarians killed Kuthen (the Cuman Leader) and his bodyguards; the remaining Cumans fled to the Balkans. After the Mongol invasion, Béla IV of Hungary recalled the Cumans to Hungary to repopulate settlements devastated by war. The nomadic Cumans subsequently settled throughout the Great Hungarian Plain.
Around 1241, the Kingdom of Hungary was much like any other feudal kingdom of Europe: although the throne was still inherited by Árpád's successors, the king's authority and power was greatly curtailed. Rich magnates cared less about the national security of the whole kingdom than about petty feudal quarrels with their fellow landlords. The Golden Bull of 1222 issued by King Andrew II authorized magnates to rebel against the king in some circumstances, and made the him only 'primus inter pares'—first among equals. Bela IV tried to restore the king's former authority and power, without much success.
The Hungarians had first learned about the Mongol threat in 1229, when King Andrew granted asylum to some fleeing Russian boyars. Some Magyars, left behind during the main migration to the Pannonian basin, still lived on the banks of the upper Volga. In 1237 a Dominican friar, Julianus, set off on an expedition to lead them back, and was sent back to King Béla with a letter from Batu Khan. In this letter, Khan called upon the Hungarian king to surrender his kingdom unconditionally to the Tatar forces or face complete destruction. Béla did not reply, and two more messages were later delivered to Hungary. The first, in 1239, was sent by the defeated Cuman tribes, who asked for and received asylum in Hungary. The second was sent in February 1241 by the defeated Polish princes.
Only then did King Béla call upon his magnates to join his army in defense of the country. He also asked the papacy and the Western European rulers for help. Foreign help came in the form of a small knight-detachment under the leadership of Frederick, Prince of Austria, but it was too small to change the outcome of the campaign. The majority of the Hungarian magnates also did not realize the urgency of the matter. Some may have hoped that a defeat of the royal army would force Béla to discontinue his centralization efforts and thus strengthen their own power.
Although the Mongol danger was real and imminent, Hungary was not prepared to deal with it; in the minds of a people who had lived free from nomadic invasions for the last few hundred years, an invasion seemed impossible, and Hungary was no longer a predominantly soldier population. Only rich nobles were trained as heavy-armored cavalry. The Hungarians had long since forgotten the light-cavalry strategy and tactics of their ancestors, which, ironically, were similar to those now used by the Mongols and their ancestors, the Huns.
The Hungarian army (some 60,000 on the eve of the Battle of Muhi) was made up of individual knights with tactical knowledge, discipline, and talented commanders. Because his army was not experienced in nomadic warfare, King Béla welcomed the Cuman King Kuthen (also known as Kotony) and his fighters. However, the Cuman invitation proved detrimental as Batu Khan justified his invasion of Hungary as Béla giving asylum to the Cumans, a group Batu Khan regarded as rebels and traitors to the Mongol Empire. After rumors began to circulate in Hungary that the Cumans were agents of the Mongols, some hot-headed Hungarians attacked the Cuman camp and killed Kotony. This lead the enraged Cumans to ride south, looting, ravaging the countryside, and slaughtering the unsuspecting Magyar population. The Austrian troops retreated Austria shortly thereafter to "enlist more Western help." The Hungarians now stood alone in the defense of their country.
The Hungarian army arrived and encamped at the Hernád river[where?] on April 10, 1241 without having been directly challenged by the Mongols. The Mongols began their attack the next night; quickly it was clear the Hungarians were lost. While the king escaped with the help of his bodyguard, the remaining Hungarian army was mercilessly killed by the Mongols or drowned in the river as they attempted escape. The Mongols now systematically occupied the Great Hungarian Plains, the slopes of the northern Carpathian Mountains, and Transylvania. Where they found local resistance, they ruthlessly killed the population. Where the locale offered no resistance, they forced the men into servitude in the Mongol army. Still, tens of thousands avoided Mongol domination by taking refuge behind the walls of the few existing fortresses or by hiding in the forests or large marshes along the rivers. The Mongols, instead of leaving the defenseless and helpless people and continuing their campaign through Pannonia to Western Europe, spent the entire summer and fall securing and pacifying the occupied territories. Then during the winter, contrary to the traditional strategy of nomadic armies which started campaigns only in spring-time, they crossed the Danube and continued their systematic occupation, including Pannonia. They eventually reached the Austrian borders and the Adriatic shores in Dalmatia. At this time, Croatia was part of Hungary, since it was conquered by the Kingdom of Hungary in 1091.[13][14] The Mongols appointed a darughachi in Hungary and minted coins in the name of Khagan.[15] According to Michael Prawdin, the country of Béla was assigned to Orda by Batu as an appanage. At least 20%-40% of the population died, by slaughter or epidemic. But while the Mongols claimed control of Hungary, they could not occupy fortified cities such as Fehérvár, Esztergom, Veszprém, Tihany, Győr, Pannonhalma, Moson, Sopron, Vasvár, Újhely, Zala, Lockenhaus, Bratislava, Nitra, Komárom, Fiľakovo and Abaújvár. Learning from this lesson, fortresses came to play a significant role in Hungary. King Béla IV rebuilt the country and invested in fortifications. Facing a shortage of money, he welcomed the settlement of Jewish families, investors, and tradesmen, granting them citizenship rights. The King also welcomed tens of thousands of Kun (Cumans) who had fled the country before the invasion.
During the spring of 1242, Ögedei Khan died at the age of fifty-six after a binge of drinking during a hunting trip. Batu Khan, who was one of the contenders to the imperial throne, returned at once with his armies to Asia, leaving the whole of Eastern Europe depopulated and in ruins (before withdrawal, Batu Khan ordered wholesale execution of prisoners). But because of his withdrawal, Western Europe escaped unscathed.
Some Hungarian historians[who?] claim that Hungary's long resistance against the Mongols actually saved Western Europe, though many Western European historians reject this interpretation[citation needed]. They point out that the Mongols evacuated Hungary of their own free will, and that Western Europe avoided Mongol attacks due to the sudden death of Ögedei Khan, not by the endeavor of the Hungarians. Other European and American historians have questioned whether the Mongols would have been able to, or even wished to, continue their invasion into Europe west of the Hungarian plain at all,[16] given the logistical situation in Europe and their need to keep large number of horses in the field to retain their strategic mobility.
The Mongolian invasion taught the Magyars a simple lesson: although the Mongols had destroyed the countryside, the forts and fortified cities had survived. To improve their defense capabilities for the future, they had to build forts, not only on the borders but also inside the country. During the remaining decades of the 13th century and throughout the 14th century, the kings donated more and more royal land to the magnates with the condition that they build forts and ensure their defenses.
Invasion of the Kingdom of Croatia
During the Middle Ages, the Kingdom of Croatia was in a personal union with the Kingdom of Hungary, with Béla IV as a king.[17][18][19]
When routed on the banks of the Sajo River in 1241 by the Tartars and Mongols, Bela IV fled to today's Zagreb in Croatia. The poorly-fortified Zagreb was unable to resist the invasion and was destroyed, its cathedral burned by Mongols.[20] In preparation for a second invasion, Gradec was granted a royal charter or Golden Bull of 1242 by King Bela IV, after which citizens of Zagreb engaged in building defensive walls and towers around their settlement.[20][21]
The Mongols' pursuit of Béla IV continued from Zagreb through Pannonia to Dalmatia. While in pursuit, the Mongols under the leadership of Kadan (Qadan) suffered a major defeat at Klis Fortress in Croatia in March 1242.[22] The Mongols pursued Béla IV from town to town in Dalmatia, while Croatian nobility and Dalmatian towns such as Trogir and Rab helped Béla IV to escape. After their defeat against the Croatian soldiers, the Mongols retreated and Béla IV was awarded Croatian towns and nobility. Only the town of Split did not aid Béla IV in his escape from the Mongols. Some historians claim that the mountainous terrain of Croatian Dalmatia was fatal for the Mongols because of the great losses they suffered from Croat ambushes set up in mountain passes.[21] Most historians claim that the death of Ögedei Khan (Croatian: Ogotaj) was the primary reason for retreat. In any case, though much of Croatia was plundered and destroyed, long-term occupation was unsuccessful.
Saint Margaret (January 27, 1242 – January 18, 1271), a daughter of Béla IV and Maria Laskarina, was born in Klis Fortress during the Mongol invasion of Hungary-Croatia in 1242.[23]
Impact on Romanians
The 1241 Mongol invasion first affected Moldavia and Wallachia (situated east of the Carpathians) and then Transylvania (then part of the Kingdom of Hungary). Tens of thousands of Romanians lost their lives defending their territories from the Golden Horde. Crops and goods plundered from Romanian settlements seem to have been a primary supply source for the Golden Horde. The invaders killed up to half of the population and burned down most of their settlements, thus destroying much of the cultural and economic records from that period. Neither Romanians nor the army of Hungary offered much resistance against the Mongols.[24] The swiftness of the invasion took many by surprise and forced them to retreat and hide in forests and the enclosed valleys of the Carpathians. In the end, however, the main target of the invasion was the Kingdom of Hungary.[24]
European tactics against Mongols
The traditional European method of warfare of melee combat between knights ended in catastrophe when it was deployed against the Mongol forces. The New Encyclopaedia Britannica, Volume 29 says that "Employed against the Mongol invaders of Europe, knightly warfare failed even more disastrously for the Poles at Legnica and the Hungarians at Mohi in 1241. Feudal Europe was saved from sharing the fate of China and Muscovy not by its tactical prowess but by the unexpected death of the Mongol's supreme ruler, Ogedei, and the subsequent eastward retreat of his armies."[25]
The Mongols destroyed an army of Germans, French, and Poles numbering 30,000 at the Battle of Legnica, slaughtering nearly 25,000. After that, other German cities quickly capitulated.[26]
Mongol Diffusion of Chinese Gunpowder to Europe
Several sources mention Chinese firearms and gunpowder weapons being deployed by the Mongols against European forces at the Battle of Mohi in various forms, including bombs hurled via catapult.[27][26][28] Professor Kenneth Warren Chase credits the Mongols for introducing into Europe gunpowder and its associated weaponry.[29]
A later fabricated legend arose in Europe about a nonexistent Berthold Schwarz who consorted with Satan, claimed that he invented the gun, whilst it was the Mongols who spread it to Europe in reality.[30]
End of the Mongol advance
Some[who?] claim that European survival was due to Mongol unwillingness to fight in the more densely populated German principalities, where the wetter weather affected their glue and sinew backed bows. The territory of Western Europe, with more forests and with many castles along with many opportunities for the European heavy cavalry (better and heavier at mêlée than the Mongol heavy cavalry) to counter-attack.[citation needed]
Some historians believe that the reason for Batu's stopping at the Mohi River, was that he never intended to advance further.[16] He had made the Russian conquest safe for the years to come, and when the Great Khan died and he rushed back to Mongolia to put in his claim for power, it ended his westward expansion. Subutai's recall at the same time left the Mongol armies without their spiritual head and primary strategist. Batu Khan was not able to resume his plans for conquest to the "Great Sea" (the Atlantic Ocean) until 1255, after the turmoil after Ögedei's death had finally subsided with the election of Möngke Khan as Great Khan. He was not capable nor interested in launching an invasion on Western Europe.
Mongol infighting
From 1241 to 1248 a state of almost open warfare existed between the son of Jochi, Batu, and the son of Ögedei, Güyük. The Mongol Empire was ruled by a regency under Ögedei's widow Töregene Khatun, whose only goal was to secure the Great Khanate for her son, Güyük. There was so much bitterness between the two branches of the family that Güyük died in 1248 on his way to confront Batu to force him to accept his authority. He also had problems in his last years with the Principality of Halych-Volhynia, whose ruler, Danylo of Halych, adopted a politic of confronting the Golden Horde and defeated some Mongol assaults in 1254. He was only defeated in 1259, under the Berke's rule. Batu Khan was unable to turn his army west until 1255, after Möngke had become Great Khan in 1251, and he had repaired his relations with the Great Khanate. However, as he prepared to finish the invasion of Europe, he died. His son did not live long enough to implement his father and Subutai's plan to invade Europe, and with his death, Batu's younger brother Berke became Khan of the Kipchak Khanate. Berke was not interested in invading Europe as much as halting his cousin Hulagu Khan from destroying the Holy Land. Berke had converted to Islam and watched with horror as his cousin destroyed the Abbasid Caliph, the spiritual head of Islam as far as Berke was concerned. The Mamluks of Egypt, learning through spies that Berke was both a Muslim and not fond of his cousin, appealed to him for help and were careful to nourish their ties to him and his Khanate.
Both entities were Turkic in origin.[31] Most of the Mamluks were of Turkic descent and Berke's Khanate was almost totally Turkic also. Jochi, Genghis Khan's oldest son, was of disputed parentage and only received 4,000 Mongol warriors to start his Khanate. His nearly 500,000 warriors were virtually all Turkic people who had submitted to the Mongols. Thus, the Khanate was Turkic in culture and had more in common with their brother Muslim Turkic Mamluks than with the Mongol shamanist Hulagu and his horde. Thus, when Hulagu Khan began to mass his army for war against the Mamluk-controlled Holy Land, they swiftly appealed to Berke Khan who sent armies against his cousin and forced him to defend his domains in the north.
Hulagu returned to his lands by 1262, but instead of being able to avenge his defeats, had to turn north to face Berke Khan, suffering severe defeat in an attempted invasion north of the Caucasus in 1263, after Berke Khan had lured him north and away from the Holy Land. Thus, the Kipchak Khanate never invaded Europe; keeping watch to the south and east instead. Berke only sent troops into Europe twice, in two relatively light raids in 1259 and 1265, simply to collect booty he needed to pay for his wars against Hulagu from 1262-65.
Later campaigns
Against Poland (1259 and 1287)
In 1259, eighteen years after the first attack, two tumens (20,000 men) from the Golden Horde, under the leadership of Berke, attacked Poland after raiding Lithuania. This attack was commanded by general Burundai with young princes Nogai and Talabuga. Lublin, Sieradz, Sandomierz, Zawichost, Kraków, and Bytom were ravaged and plundered. Berke had no intention of occupying or conquering Poland. After this raid the Pope Alexander IV tried without success to organize a crusade against the Tatars.
An unsuccessful raid followed in 1287, led by Talabuga and Nogai Khan. Lublin, Mazovia, Sandomierz and Sieradz were successful raided, but they were defeated at Kraków, although this city too was devastated. This raid consisted of less than one tumen, since the Golden Horde's armies were tied down in a new conflict which the Il-Khanate initiated in 1284. The force sent was not sufficient to meet the full Polish army, nor did it have any siege engineers or equipment to breach city walls. It raided a few caravans, burned a few small towns, and fled when the Polish army was mustered.
Against Lithuania (1259, 1275 and 1277)
The Mongols under Burundai, a famous general of Batu, also successfully raided the Kingdom of Lithuania during the campaign of 1259. There were other raids against Lithuania in 1275 and 1277, as the Lithuanians were emerging as a rival to Mongol power in the Russian states, but this time they were catastrophically defeated and did not recover from the loss for the next forty years.
Against Byzantine Thrace (1265, 1324 and 1337)
During the reign of Berke there was also a raid against Thrace. In the winter of 1265 Nogai Khan led a Mongol raid of two tumens (20,000 soldiers) against the territories of Bulgaria and Byzantine Eastern Thrace. In the spring of 1265 he defeated the armies of Michael VIII Palaeologus. Instead of fighting, most of the Byzantines fled. After this Thrace was plundered by Nogai's army, and the Byzantine emperor made an alliance with the Golden Horde, giving his daughter Euphrosyne in marriage to Nogai. Michael also sent much valuable fabric to Golden Horde as tributary. Also during Uzbeg Khan reign Thrace suffered raids in 1324 and 1337.
Against Bulgaria (1241, 1242, 1271, 1274, 1280 and 1285)
After the death of Khan Ogedei,Batu decided to return from Hungary to Mongolia.Part of his army invade Bulgaria,but was defeated by Bulgarian army under Tsar Ivan Asen II.The successors of Tsar Ivan Asen II - the regency of Kaliman Asen I desided to pay tax to the Golden Horde.In 1271 Nogai Khan led a successful raid against the country, which was a vassal of the Golden Horde until the early 14th century.Bulgaria was again raided by the Tatars in 1274, 1280 and 1285.In 1278 and 1279 Tsar Ivailo lead the Bulgarian army and many times defeat the Tatars.However, the next Bulgarian tsar accepted suzerainty of Khan Tokhta (Toqta); Mongol control loosened after Nogai and Chaka's deaths.
Against the Kingdom of Hungary (1280s)
In the mid-1280s Nogai Khan led an invasion of Hungary alongside Talabuga. Nogai lead an army that ravaged Transylvania with success: Cities like Reghin, Braşov and Bistriţa were plundered and ravaged. However Talabuga, who led the main army in Northern Hungary, was stopped by the heavy snow of the Carpathians and the invading force was defeated near Pest by the royal army of Ladislaus IV and ambushed by the Székely in the return. As with later invasions, it was repelled handily, the Mongols losing much of their invading force. The outcome could not have contrasted more sharply with the 1241 invasion, mostly due to the reforms of Béla IV, which included advances in military tactics and, most importantly, the widespread building of stone castles, both responses to the defeat of the Hungarian Kingdom in 1241.
Against Serbia (1293)
In 1293 Nogai Khan led a large Mongol raid into Serbia, where Serbian king Stefan Uroš II Milutin defeated his army. However, the Serbian king acknowledged Nogai's supremacy to prevent further hostility.[32]
See also
- Tatar invasions
- Mongol invasions
- Mongol military tactics and organization
- Franco-Mongol alliance
- Rogerius of Apulia
- Romania in the Early Middle Ages
Footnotes
- ^ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedSourcesvary; see Help:Cite errors/Cite error references no text - ^ Carey states on p. 128 that Batu had 40,000 in the main body and ordered Subotai to take 30,000 troops in an encircling maneuver. Batu commanded the central prong of the Mongols' three-pronged assault on eastern Europe. This number seems correct when compared with the numbers reported at the Battles of Leignitz to the north and Hermannstadt to the south. All three victories occurred in the same week.
- ^ a b Markó, László (2000). Great Honours of the Hungarian State. Budapest: Magyar Könyvklub. ISBN 9635470851
- ^ a b c d Liptai, Ervin (1985). Military history of Hungary. Budapest: Zrínyi Katonai Kiadó. ISBN 9633263379
- ^ René Grousset The Empire of Steppes
- ^ Carey, Brian Todd, p. 124
- ^ Colin McEvedy, Atlas of World Population History (1978)
- ^ Boris Rybakov, Киевская Русь и русские княжества XII-XIII вв. (Kievan Rus' and Russian princedoms in XII-XIII centuries), Moscow: Nauka, 1993. ISBN 5-02-009795-0.
- ^ source?
- ^ The Mongol invasion: the last Arpad kings
- ^ Hildinger, Erik. Mongol Invasions: Battle of Liegnitz. First published as: "The Mongol Invasion of Europe" in Military History, (June, 1997).
- ^ The Destruction of Kiev
- ^ http://www.thefreedictionary.com/croatia
- ^ http://www.korcula.net/history/mmarelic/byzant.htm
- ^ Michael Prawdin, Gerard (INT) Chaliand-The Mongol Empire, p.268
- ^ a b "The Mongols in the West, Journal of Asian History v.33 n.1". By Denis Sinor. 1999. http://www.deremilitari.org/resources/articles/sinor1.htm. Retrieved 16 August 2009.
- ^ "Croatia (History)". Encarta. http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761577939_6/Croatia.html#p40.
- ^ Font, Marta:Hungarian Kingdom and Croatia in the Middle Age
- ^ "Croatia (History)". Britannica. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/143561/Croatia/223953/History.
- ^ a b 750th Anniversary of the Golden Bull Granted by Bela IV
- ^ a b Klaić V., Povijest Hrvata, Knjiga Prva, Druga, Treća, Četvrta i Peta Zagreb 1982. (Croatian)
- ^ Prošlost Klisa (Croatian)
- ^ Klis - A gateway to Dalmatia
- ^ a b Epure, Violeta-Anca. "Invazia mongolă în Ungaria şi spaţiul românesc" (in Romanian) (PDF). ROCSIR - Revista Româna de Studii Culturale (pe Internet). http://www.rocsir.usv.ro/archiv/2004_1-2/2VioletaEpure2004.pdf. Retrieved 2009-02-05.
- ^ Encyclopaedia Britannica, inc (2003). The New Encyclopaedia Britannica, Volume 29 (15 ed.). Encyclopaedia Britannica. p. 663. ISBN 0852299613. http://books.google.com/?id=ZKIxAQAAIAAJ&dq=Employed+against+the+Mongol+invaders+of+Europe%2C+knightly+warfare+failed+even+more+disastrously+for+the+Poles+at+Legnica+and+the+Hungarians+at+Mohi+in+1241.+Feudal+Europe+was+saved+from+sharing+the+fate+of+China+and+Muscovy+not+by+its&q=china+muscovy. Retrieved 2011-07-29.
- ^ a b Michael Kohn (2006). Dateline Mongolia: An American Journalist in Nomad's Land. RDR Books. p. 28. ISBN 1571431551. http://books.google.com/?id=-UnWOmL1a48C&pg=PA28&dq=battle+of+mohi+chinese+gunpowder#v=onepage&q&f=false. Retrieved 2011-07-29.
- ^ William H. McNeill (1992). The Rise of the West: A History of the Human Community. University of Chicago Press. p. 492. ISBN 0226561410. http://books.google.com/?id=_RsPrzrsAvoC&pg=PA492&dq=mongol+invasion+hungary+chinese+gunpowder#v=onepage&q=mongol%20invasion%20hungary%20chinese%20gunpowder&f=false. Retrieved 2011-07-29.
- ^ Robert Cowley (1993). Robert Cowley. ed. Experience of War (reprint ed.). Random House Inc. p. 86. ISBN 0440505534. http://books.google.com/?id=BxpaGuxtGggC&q=But+the+explosive+force+of+gunpowder+seemed+promising+as+well,+and+Mongol+armies+routinely+used+lengths+of+bamboo+filled+with+gunpowder+in+order+to+blow+open+city+gates.+In+this+primitive+form+gunpowder+weapons+reached+Europe+in+1241&dq=But+the+explosive+force+of+gunpowder+seemed+promising+as+well,+and+Mongol+armies+routinely+used+lengths+of+bamboo+filled+with+gunpowder+in+order+to+blow+open+city+gates.+In+this+primitive+form+gunpowder+weapons+reached+Europe+in+1241. Retrieved 2011-07-29.
- ^ Kenneth Warren Chase (2003). Firearms: a global history to 1700 (illustrated ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 58. ISBN 0521822742. http://books.google.com/?id=esnWJkYRCJ4C&pg=PA58&dq=mongol+invasion+hungary+chinese+gunpowder#v=onepage&q=mongol%20invasion%20hungary%20chinese%20gunpowder&f=false. Retrieved 2011-07-29.
- ^ Kenneth Warren Chase (2003). Firearms: a global history to 1700 (illustrated ed.). Cambridge University Press. p. 60. ISBN 0521822742. http://books.google.com/?id=esnWJkYRCJ4C&pg=PA58&dq=mongol+invasion+hungary+chinese+gunpowder#v=onepage&q=berthold%20schwarz&f=false. Retrieved 2011-07-29.
- ^ Amitai-Preiss, Reuven. The Mamluk-Ilkhanid War
- ^ István Vásáry - Cumans and Tatars: Oriental military in the pre-Ottoman Balkans, 1185-1365, p.89
References
- Chambers, James -- The Devil's Horsemen: The Mongol Invasion of Europe
- Cook, David, "Apocalyptic Incidents during the Mongol Invasions," in Brandes, Wolfram / Schmieder, Felicitas (hg), Endzeiten. Eschatologie in den monotheistischen Weltreligionen (Berlin, de Gruyter, 2008) (Millennium-Studien / Millennium Studies / Studien zu Kultur und Geschichte des ersten Jahrtausends n. Chr. / Studies in the Culture and History of the First Millennium C.E., 16), 293-312.
- Hildinger, Erik -- Warriors of the Steppe: A Military History of Central Asia, 500 B.C. to A.D. 1700
- Morgan, David -- The Mongols, ISBN 0-631-17563-6
- Nicolle, David, -- The Mongol Warlords, Brockhampton Press, 1998
- Reagan, Geoffry -- The Guinness Book of Decisive Battles, Canopy Books, New York (1992)
- Saunders, J.J. -- The History of the Mongol Conquests, Routledge & Kegan Paul Ltd, 1971, ISBN 0-8122-1766-7
- Sicker, Martin -- The Islamic World in Ascendancy: From the Arab Conquests to the Siege of Vienna, Praeger Publishers, 2000
- Soucek, Svatopluk -- A History of Inner Asia, Cambridge, 2000
- Sinor, Denis (1999). "The Mongols in the West". Journal of Asian History 33 (1). http://www.deremilitari.org/resources/articles/sinor1.htm.
External links
Categories:- High Middle Ages
- 13th-century conflicts
- Wars involving the Mongols
- History of Poland (966–1385)
- Moldova in the Early Middle Ages
- Romania in the Early Middle Ages
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.





