- Orange Revolution
-
Orange Revolution 
Orange-clad demonstrators gather in the Independence Square in Kiev on 22 November 2004. On some days, the number of protesters in the center of Kiev reached hundreds of thousands (one million by some estimates).Location Ukraine Date late November 2004 - January 2005 Characteristics demonstrations, civil disobedience, civil resistance, strike actions The Orange Revolution (Ukrainian: Помаранчева революція, Pomarancheva revolyutsiya) was a series of protests and political events that took place in Ukraine from late November 2004 to January 2005, in the immediate aftermath of the run-off vote of the 2004 Ukrainian presidential election which was claimed to be marred by massive corruption, voter intimidation and direct electoral fraud. Kiev, the Ukrainian capital, was the focal point of the movement's campaign of civil resistance, with thousands of protesters demonstrating daily.[1] Nationwide, the democratic revolution was highlighted by a series of acts of civil disobedience, sit-ins, and general strikes organized by the opposition movement.
The protests were prompted by reports from several domestic and foreign election monitors as well as the widespread public perception that the results of the run-off vote of November 21, 2004 between leading candidates Viktor Yushchenko and Viktor Yanukovych were rigged by the authorities in favor of the latter.[2] The nationwide protests succeeded when the results of the original run-off were annulled, and a revote was ordered by Ukraine's Supreme Court for December 26, 2004. Under intense scrutiny by domestic and international observers, the second run-off was declared to be "fair and free". The final results showed a clear victory for Yushchenko, who received about 52% of the vote, compared to Yanukovych's 44%. Yushchenko was declared the official winner and with his inauguration on January 23, 2005 in Kiev, the Orange Revolution ended.
In 2010, Viktor Yanukovych was declared winner of the following presidential election said to have been conducted fairly by the Central Election Commission (CEC) and international observers.[3][4]
History of Ukraine 
This article is part of a series- Cassette Scandal
- Orange Revolution
- Russia–Ukraine gas disputes
Contents
Prelude
 Viktor Yushchenko, the main opposition candidate
Viktor Yushchenko, the main opposition candidate
 An orange ribbon, a symbol of the Ukrainian Orange Revolution. Ribbons are common symbols of non-violent protest.
An orange ribbon, a symbol of the Ukrainian Orange Revolution. Ribbons are common symbols of non-violent protest.
Late 2002 Viktor Yushchenko (Our Ukraine), Oleksandr Moroz (Socialist Party of Ukraine), Petro Symonenko (Communist Party of Ukraine) and Yulia Tymoshenko (Yulia Tymoshenko Bloc) issued a joint statement concerning "the beginning of a state revolution in Ukraine". The communist stepped out of the alliance, Symonenko was against a single candidate from the alliance in the Ukrainian presidential election 2004, but the other three parties remained allies[5] (until July 2006).[6] In the Autumn of 2001 both Tymoshenko and Yushchenko had broached at creating such a coalition.[7]
On July 2, 2004 Our Ukraine and the Yulia Tymoshenko Bloc established the Force of the people, a coalition which aimed to stop "the destructive process that has, as a result of the incumbent authorities, become a characteristic for Ukraine", at the time President Leonid Kuchma and Prime Minister Viktor Yanukovych were the incumbent authorities in Ukraine. The pact included a promise by Viktor Yushchenko to nominate Tymoshenko as Prime Minister if Yushchenko would win the October 2004 presidential election.[7]
This 2004 presidential election in Ukraine eventually featured two main candidates. One was sitting Prime Minister Viktor Yanukovych, largely supported by Leonid Kuchma (the outgoing President of Ukraine who already served two terms in the office and was precluded from running himself due to the constitutional term limits), and the opposition candidate Viktor Yushchenko, leader of the Our Ukraine faction in the Ukrainian parliament and a former Prime Minister (1999–2001).
The election was held in a highly charged atmosphere, with the Yanukovych team and the outgoing president's administration using their control of the government and state apparatus for intimidation of Yushchenko and his supporters. In September 2004, Yushchenko suffered dioxin poisoning under mysterious circumstances. While he survived and returned to the campaign trail, the poisoning undermined his health and altered his appearance dramatically (his face remains disfigured by the consequences to this day).
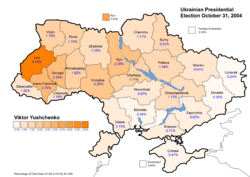
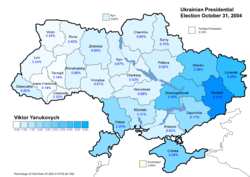
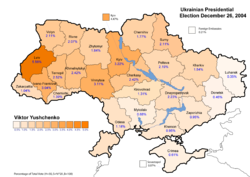
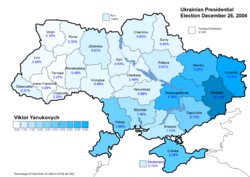
The two main candidates were neck and neck in the first-round vote held on October 31, 2004, collecting 39.32% (Yanukovych) and 39.87% (Yushchenko) of the vote cast. The candidates that came third and fourth collected much less: Oleksandr Moroz of the Socialist Party of Ukraine and Petro Symonenko of the Communist Party of Ukraine received 5.82% and 4.97%, respectively. Since no candidate carried more than 50% of the cast ballots, a run-off vote between two leading candidates was mandated by Ukrainian law. Later: after the run-off was announced, Oleksandr Moroz threw his support behind Viktor Yushchenko. The Progressive Socialist Party's Natalia Vitrenko, who won 1.53% of the vote, endorsed Yanukovych, who hoped for Petro Simonenko's endorsement but did not receive it.[8]
In the wake of the first round of the election many complaints regarding voting irregularities in favor of the government supported Yanukovych were raised. However, as it was clear that neither nominee was close enough to collecting an outright majority in the first round, challenging the initial result would not have affected the final outcome of the election. As such the complaints were not actively pursued and both candidates concentrated on the upcoming run-off scheduled for November 21.
Pora! activists were arrested in October 2004, but the release of many (on what was reported President Kuchma's personal order) gave growing confidence to the opposition.[9]
Orange was originally adopted by the Yushchenko's camp as the signifying color of his election campaign. Later the color gave name to an entire series of political terms, such as the Oranges (Pomaranchevi in Ukrainian) for his political camp and supporters. At the time when the mass protests grew, and especially when they brought about political change in the country, the term Orange Revolution came to represent the entire series of events.
In view of the success of using color as a symbol to mobilize supporters, the Yanukovych camp chose blue for themselves.
Protests
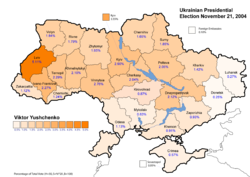
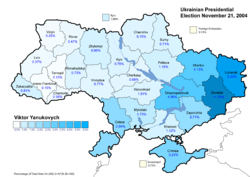
Protests began on the eve of the second round of voting, as the official count differed markedly from exit poll results which gave Yushchenko up to an 11% lead, while official results gave the election win to Yanukovych by 3%. While Yanukovych supporters have claimed that Yushchenko's connections to the Ukrainian media explain this disparity, the Yushchenko team publicized evidence of many incidents of electoral fraud in favor of the government-backed Yanukovych, witnessed by many local and foreign observers. These accusations were reinforced by similar allegations, though at a lesser scale, during the first presidential run of October 31.[citation needed]
 Protesters at Independence Square on the first day of the Orange Revolution.
Protesters at Independence Square on the first day of the Orange Revolution.
The Yushchenko campaign publicly called for protest on the dawn of election day, November 21, 2004, when allegations of fraud began to spread. Beginning on November 22, 2004, massive protests started in cities across Ukraine: the largest, in Kiev's Maidan Nezalezhnosti (Independence Square), attracted an estimated 500,000 participants,[10] who on November 23, 2004, peacefully marched in front of the headquarters of the Verkhovna Rada, the Ukrainian parliament, many wearing orange or carrying orange flags, the color of Yushchenko's campaign coalition. One of the most prominent activists of that time was Paraska Korolyuk, subsequently bestowed with the Order of Princess Olga.
The local councils in Kiev, Lviv,[11] and several other cities passed, with the wide popular support of their constituency, a largely symbolic refusal to accept the legitimacy of the official election results, and Yushchenko took a symbolic presidential oath.[12] This "oath" taken by Yushchenko in half-empty parliament chambers, lacking the quorum as only the Yushchenko-leaning factions were present, could not have any legal effect. But it was an important symbolic gesture meant to demonstrate the resolve of the Yushchenko campaign not to accept the compromised election results. In response, Yushchenko's opponents denounced him for taking an illegitimate oath, and even some of his moderate supporters were ambivalent about this act, while a more radical side of the Yushchenko camp demanded him to act even more decisively. Some observers argued that this symbolic presidential oath might have been useful to the Yushchenko camp should events have taken a more confrontational route.[citation needed] In such a scenario, this "presidential oath" Yushchenko took could be used to lend legitimacy to the claim that he, rather than his rival who tried to gain the presidency through alleged fraud, was a true commander-in-chief authorized to give orders to the military and security agencies.
At the same time, local officials in Eastern and Southern Ukraine, the stronghold of Viktor Yanukovych, started a series of actions alluding to the possibility of the breakup of Ukraine or an extra-constitutional federalization of the country, should their candidate's claimed victory not be recognized. Demonstrations of public support for Yanukovych were held throughout Eastern Ukraine and some of his supporters arrived in Kiev. However, in Kiev the pro-Yanukovych demonstrators were far outnumbered by Yushchenko supporters, whose ranks were continuously swelled by new arrivals from many regions of Ukraine. The scale of the demonstrations in Kiev was unprecedented. By many estimates, on some days they drew up to one million people to the streets, in freezing weather.[13]
During the protests, a man died after suffering a heart attack.[14]
Political developments
Ukraine 
This article is part of the series:
Politics and government of
UkraineConstitutionExecutive- President
- Viktor Yanukovych
- Administration
- National Security and
Defence Council - Presidential representatives
- Presidential symbols
- Prime Minister
- Cabinet
Legislature- Parliament
- Chairman
- People's Deputy of Ukraine
- Imperative mandate
Judiciary- Judicial system
- Constitutional Court
- Supreme Court
- Prosecutor General
DivisionsElectionForeign relationsSee also- Ukrainian nationalism
- Declaration of Independence
- Proclamation of Independence
- Cassette Scandal
- Ukraine without Kuchma
- Orange Revolution
- Russia-Ukraine gas disputes
- 2006 political crisis
- Universal of National Unity
- 2007 political crisis
- 2008 political crisis
- Kharkiv treaty
Other countries · Atlas
Politics portal
In view of the threat of illegitimate government acceding to power, Yushchenko's camp announced the creation of the Committee of National Salvation which declared a nationwide political strike.
On December 1, 2004, the Verkhovna Rada passed a resolution that strongly condemned pro-separatist and federalization actions, and passed a non-confidence vote in the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine, a decision Prime Minister Yanukovych refused to recognize. By the Constitution of Ukraine, the non-confidence vote mandated the government's resignation, but the parliament had no means to enforce a resignation without the co-operation of Prime Minister Yanukovych and outgoing President Kuchma.
On December 3, 2004, Ukraine's Supreme Court finally broke the political deadlock. The court decided that due to the scale of the electoral fraud it became impossible to establish the election results. Therefore, it invalidated the official results that would have given Yanukovych the presidency. As a resolution, the court ordered a revote of the run-off to be held on December 26, 2004.[15] This decision was seen as a victory for the Yushchenko camp while Yanukovych and his supporters favored a rerun of the entire election rather than just the run-off, as a second-best option if Yanukovych was not awarded the presidency. On December 8, 2004 the parliament amended laws to provide a legal framework for the new round of elections. The parliament also approved the changes to the Constitution, implementing a political reform backed by outgoing President Kuchma as a part of a political compromise between the acting authorities and opposition.
In November 2009 Yanukovych stated that although his victory in the elections was "taken away", he gave up this victory in order to avoid bloodshed. "I didn't want mothers to lose their children and wives their husbands. I didn't want dead bodies from Kiev to flow down the Dnipro. I didn't want to assume power through bloodshed."[16]
Re-run election
The December 26 revote was held under intense scrutiny of local and international observers. The preliminary results, announced by the Central Election Commission on December 28, gave Yushchenko and Yanukovych 51.99% and 44.20% of the total vote which represented a change in the vote by +5.39% to Yushchenko and -5.27% from Yanukovych respectively when compared to the November poll.[17] The Yanukovych team attempted to mount a fierce legal challenge to the election results using both the Ukrainian courts and the Election Commission complaint procedures. However, all their complaints were dismissed as without merit by both the Supreme Court of Ukraine and the Central Election Commission.[18] On January 10, 2005 the Election Commission officially declared Yushchenko as the winner of the presidential election[18] with the final results falling within 0.01% of the preliminary ones. This Election Commission announcement[19] cleared the way for Yushchenko's inauguration as the President of Ukraine. The official ceremony took place in the Verkhovna Rada building on January 23, 2005 and was followed by the "public inauguration" of the newly sworn President at Maidan Nezalezhnosti (Independence Square) in front of hundreds of thousands of his supporters.[20] This event brought the Ukrainian Orange Revolution to its peaceful conclusion.
Role of Ukrainian intelligence and security agencies
According to one version of events recounted by The New York Times,[21] Ukrainian security agencies played an unusual role in the Orange Revolution, with a KGB successor agency in the former Soviet state providing qualified support to the political opposition. As per the paper report, on November 28, 2004 over 10,000 MVS (Internal Ministry) troops were mobilized to put down the protests in Independence Square in Kiev by the order of their commander, Lt. Gen. Sergei Popkov. The SBU (Security Service of Ukraine, a successor to the KGB in Ukraine) warned opposition leaders of the crackdown. Oleksander Galaka, head of GUR (military intelligence) made calls to "prevent bloodshed". Col. Gen. Ihor Smeshko (SBU chief) and Maj. Gen. Vitaly Romanchenko (military counter-intelligence chief) both claimed to have warned Popkov to pull back his troops, which he did, preventing bloodshed.
In addition to the desire to avoid bloodshed, the New York Times article suggests that siloviki, as the security officers are often called in the countries of the former Soviet Union, were motivated by personal aversion to the possibility of having to serve president Yanukovych, who was in his youth convicted of robbery and assault and had alleged connection with corrupt businessmen, especially if he were to ascend to the presidency by fraud. The personal feelings of Gen. Smeshko towards Yanukovych may also have played a role. Additional evidence of Yushchenko's popularity and at least partial support among the SBU officers is shown by the fact that several embarrassing proofs of electoral fraud, including incriminating wiretap recordings of conversations among the Yanukovych campaign and government officials discussing how to rig the election, were provided to the Yushchenko camp.[22] These conversations were likely recorded and provided to the opposition by sympathizers in the Ukrainian Security Services.
Involvement of outside forces
Many analysts believe the Orange Revolution was built on a pattern first developed in the ousting of Slobodan Milošević in Serbia four years earlier, and continuing with the Rose Revolution in Georgia. Each of these victories, though apparently spontaneous, was the result of extensive grassroots campaigning and coalition-building among the opposition. Each included election victories followed up by public demonstrations, after attempts by the incumbent to hold onto power through electoral fraud.
Each of these social movements included extensive work by student activists. The most famous of these was Otpor, the youth movement that helped bring in Vojislav Koštunica. In Georgia the movement was called Kmara. In Ukraine the movement has worked under the succinct slogan Pora ("It's Time"). Chair of Georgian Parliamentary Committee on Defense and Security Givi Targamadze, former member of the Georgian Liberty Institute, as well as some members of Kmara, were consulted by Ukrainian opposition leaders on techniques of nonviolent struggle. Georgian rock bands Zumba, Soft Eject and Green Room, which earlier had supported the Rose Revolution, organized a solidarity concert in central Kiev to support Yushchenko’s cause in November 2004.[23]
Activists in each of these movements were funded and trained in tactics of political organization and nonviolent resistance by a coalition of Western pollsters and professional consultants funded by a range of Western government and non-government agencies. According to The Guardian, these include the U.S. State Department and USAID along with the National Democratic Institute for International Affairs, the International Republican Institute, the NGO Freedom House and George Soros's Open Society Institute. The National Endowment for Democracy, a foundation supported by the U.S. government, has supported non-governmental democracy-building efforts in Ukraine since 1988.[24] Writings on nonviolent struggle by Gene Sharp formed the strategic basis of the student campaigns.
Former president Leonid Kravchuk accused Russian oligarch, Boris Berezovsky, of financing Yushchenko's campaign, and provided copies of documents showing money transfers from companies he said are controlled by Berezovsky to companies controlled by Yuschenko's official backers. Berezovsky has confirmed that he met Yushchenko's representatives in London before the election, and that the money was transferred from his companies, but he refused to confirm or deny that the companies that received the money were used in Yushchenko's campaign. Financing of election campaigns by foreign citizens is illegal in Ukraine.[25] According to BBC's The Russian Godfathers,[26] Berezovsky poured millions of dollars into sustaining the spontaneous demonstrations and was in daily contact with the key opposition leaders.
The election was marred by claims that "Western PR consultants had helped orchestrate this rebellion"[27] On the other hand, Russia's involvement in the election was more direct and heavily on the side of Prime Minister Yanukovych. The extent of this involvement is still contested but some facts are indisputable such as multiple meetings between Russian president Vladimir Putin, Kuchma and Yanukovych before and during the elections. Putin repeatedly congratulated Yanukovych while the results were still contested, which was soon to embarrass both parties. Yanukovych received a much more preferential treatment in Russian media, and was surrounded by Russian consultants known to be close to the Kremlin throughout the election cycle. During the protests Russian media portrayed the Ukrainian protesters as irresponsible, led astray by Western agents.[28][29] In a poll held in November 2005, 54% of the Russian respondents believed the Orange Revolution was "A power struggle between different groups of politicians and oligarchs".[30]
Internet usage
Throughout the demonstrations, Ukraine's emerging Internet usage (facilitated by news sites which began to disseminate the Kuchma tapes) was an integral part of the orange revolutionary process. It has even been suggested that the Orange Revolution was the first example of an Internet-organized mass protest. [31] Analysts believe that the Internet and mobile phones allowed an alternative media to flourish that was not subject to self-censorship or overt control by President Kuchma and his allies and pro-democracy activists (such as Pora!) were able to use mobile phones and the Internet to coordinate election monitoring and mass protests.[32][33]
2004 Ukrainian constitutional changes
As part of the Orange Revolution, the Ukrainian constitution was changed to shift powers from the presidency to the parliament. This was Oleksandr Moroz's price for his decisive role in winning Yushchenko the presidency. The Communists also supported these measures. These came into effect in 2006 during which Yanukovych's Party of Regions won the parliamentary election, creating a coalition government with the Socialists and the Communists under his leadership. As a result, President Viktor Yushchenko had to deal with a powerful Prime Minister Viktor Yanukovych who had control of many important portfolios. His premiership ended in late 2007 after Yushchenko had succeeded in his months-long attempt to dissolve parliament. After the election, Yanukovych's party again was the largest, but Tymoshenko's finished far ahead of Yushchenko's for second place. The Orange parties won a very narrow majority, permitting a new government under Tymoshenko, but Yushchenko's political decline continued to his poor showing in the 2010 presidential election.
On October 1, 2010, the Constitutional Court of Ukraine overturned the 2004 amendments, considering them unconstitutional.[34]
2010 presidential election
A Circuit administrative court in Kiev forbade mass actions at Maidan Nezalezhnosti from January 9, 2010 to February 5, 2010. The Mayor`s office had requested this in order to avoid “nonstandard situations” during the aftermath of the 2010 presidential election. Apparently (in particular) the Party of Regions, All-Ukrainian Union "Fatherland" and Svoboda had applied for a permit to demonstrate there.[35] Incumbent President Viktor Yushchenko got 5,5% of votes during the election.[36] “Ukraine is a European democratic country”, said Yushchenko in a sort of political will at the polling station. “It is a free nation and free people.”[37] According to him, this is one of the great achievements of the Orange Revolution.
In the 2010 presidential election Viktor Yanukovych was declared the winner which was labeled by some Yanukovych supporters as "An end to this Orange nightmare".[38] Immediately after his election Yanukovych promised to "clear the debris of misunderstanding and old problems that emerged during the years of the Orange power".[39] According to influential Party of Regions member Rinat Akhmetov the ideals of the Orange Revolution won at the 2010 election "We had a fair and democratic independent election. The entire world recognized it, and international observers confirmed its results. That's why the ideals of the Orange Revolution won”.[40] According to Yulia Tymoshenko the 2010 elections was a missed "chance to become a worthy member of the European family and to put an end to the rule of the oligarchy".[41]
Legacy
Outright vote rigging diminished after the 2004 presidential election.[42][43][44][45]
See also
References
- ^ Andrew Wilson, “Ukraine's 'Orange Revolution' of 2004: The Paradoxes of Negotiation”, in Adam Roberts and Timothy Garton Ash (eds.), Civil Resistance and Power Politics: The Experience of Non-violent Action from Gandhi to the Present, Oxford University Press, 2009, pp. 295-316.[1]
- ^ Paul Quinn-Judge, Yuri Zarakhovich, The Orange Revolution, Time, November 28, 2004
- ^ Polityuk, Pavel; Balmforth, Richard (February 15, 2010). "Yanukovich declared winner in Ukraine poll". The Independent (London). http://www.independent.co.uk/news/world/europe/yanukovich-declared-winner-in-ukraine-poll-1899552.html.
- ^ "Viktor Yanukovych sworn in as Ukraine president". BBC News. February 25, 2010. http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/8535778.stm.
- ^ Understanding Ukrainian Politics: Power, Politics, and Institutional Design by Paul D'Anieri, M.E. Sharpe, 2006, ISBN 978-0765618115, page 117
- ^ Ukraine coalition born in chaos, BBC News (July 11, 2006)
- ^ a b Revolution in Orange: The Origins of Ukraine's Democratic Breakthrough by Anders Aslund and Michael A. McFaul, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, 2006, ISBN 978-0870032219
- ^ Ukrainiустафа Найем, "С Президентом на «вы»", Фокус, April 2, 2007, №13
- ^ Civil Resistance and Power Politics: The Experience of Non-violent Action from Gandhi to the Present edited by Adam Roberts and Timothy Garton Ash, Oxford University Press, 2009, ISBN 978-0199552016 (page 345)
- ^ Veronica Khokhlova, New Kids On the Bloc, The New York Times, November 26, 2004
- ^ Kamil Tchorek, Protest grows in western city, The Times, November 26, 2004
- ^ Yushchenko takes reins in Ukraine. BBC NEWS. 23 January 2005. URL accessed: 17 November 2006
- ^ USAID Report Democracy Rising (PDF)
- ^ Savik Shuster: I’m the only thing to remain after “orange revolution”, Novaya Gazeta (February 2, 2008)
- ^ Supreme Court of Ukraine decision regarding the annulment of November 21st vote. Full text in Ukrainian and Summary in English
- ^ Yanukovych says presidential election scenario of 2004 won't be repeated in 2010, Interfax-Ukraine (November 27, 2009)
- ^ "Results of Voting in Ukraine Presidential Elections 2004", Central Election Commission of Ukraine. URL Accessed 12 September 2006
- ^ a b "Timeline: Battle for Ukraine". BBC NEWS, 23 January 2005. URL Accessed: 12 September 2006
- ^ Official CEC announcement of results as of 10 January 2005, Central Election Commission. URL Accessed: 12 September 2006 (Ukrainian)
- ^ Finn, Peter. "In a Final Triumph, Ukrainian Sworn In". Washington Post, 24 January 2005. URL Accessed: 12 September 2006
- ^ C. J. Chivers, BACK CHANNELS: A Crackdown Averted; How Top Spies in Ukraine Changed the Nation's Path, The New York Times, January 17, 2005.
- ^ How Yanukovych Forged the Elections. Headquarters’ Telephone Talks Intercepted, Ukrainska Pravda, November 24, 2004.
- ^ States in Caucasus, Central Asia closely monitor developments in Ukraine. Eurasia Insight. November 30, 2004.
- ^ Diuk, Nadia. "In Ukraine, Homegrown Freedom." Washington Post, 4 December 2004. URL Accessed: 12 September 2006
- ^ Lenta.Ru: Пан Березовский вершит историю Украины
- ^ The Russian Godfathers, episode 1 part 2 BBC Retrieved on April 10, 2008
- ^ Erich Follath Ukraine Retreats to a Dark Past Spiegel, October 18, 2011
- ^ Fearing people power, Russia slams Moldova protests, Reuters (April 10, 2009)
- ^ Anders Åslund and Michael McFaul (January 2006). Revolution in Orange: The Origins of Ukraine's Democratic Breakthrough, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, ISBN 0-87003-221-6; page 159
- ^ Orange Revolution Was Power Struggle for Russians, Angus Reid Global Monitor (11/27/05)
- ^ McFaul, Michael. “Transitions from Postcommunism.” Journal of Democracy 16, no. 3 (2005): pg. 12.
- ^ Goldstein, Joshua. (2007) The Role of Digital Networked Technologies in the Ukrainian Orange Revolution. Berkman Center Research Publication. Pg 14
- ^ Kalil, Thomas. (2008) Harnessing the Mobile Revolution. The New Policy Institute. Pg 14
- ^ Update: Return to 1996 Constitution strengthens president, raises legal questions, Kyiv Post (October 1, 2010)
- ^ Court forbade Maydan after first tour of election, UNIAN (January 13, 2010)
- ^ (Ukrainian)Central Election Commission Candidate Results, CEC Ukraine (January 19, 2010)
- ^ Ukraine. Farewell to the Orange Revolution, EuropaRussia (January 19, 2010)
- ^ Ukraine election: Yanukovych urges Tymoshenko to quit, BBC News, 10 February 2010, 13:23 GMT
- ^ Yanukovych appeals to the nation, asks Tymoshenko to step down, Kyiv Post (February 10, 2010)
- ^ Akhmetov: Ideals of 'Orange Revolution' won at election in 2010, Kyiv Post (February 26, 2010)
- ^ Yulia Tymoshenko’s address to the people of Ukraine, Yulia Tymoshenko official website (February 22, 2010)
- ^ Understanding Ukrainian Politics:Power, Politics, And Institutional Design by Paul D'Anieri, M.E.Sharpe, 2006, ISBN 978-0765618115 (page 63)
- ^ EU endorses Ukraine election result, euobserver (February 8, 2010)
- ^ International observers say Ukrainian election was free and fair, Washington Post (February 9, 2010)
- ^ European Parliament president greets Ukraine on conducting free and fair presidential election, Kyiv Post (February 9, 2010)
Further reading
- Paul D'Anieri, ed. Orange Revolution and Aftermath: Mobilization, Apathy, and the State in Ukraine (Johns Hopkins University Press; 2011) 328 pages
- Tetyana Tiryshkina. The Orange Revolution in Ukraine - a Step to Freedom (2nd ed. 2007)
- Andrew Wilson (March 2006). Ukraine's Orange Revolution. Yale University Press. ISBN 0-300-11290-4.
- Anders Åslund and Michael McFaul (January 2006). Revolution in Orange: The Origins of Ukraine's Democratic Breakthrough. Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. ISBN 0-87003-221-6.
- Askold Krushelnycky (2006). An Orange Revolution: A Personal Journey Through Ukrainian History. ISBN 0-436-20623-4.
- Pavol Demes and Joerg Forbrig (eds.). Reclaiming Democracy: Civil Society and Electoral Change in Central and Eastern Europe. German Marshall Fund, 2007.
- Andrey Kolesnikov (2005). Первый Украинский: записки с передовой (First Ukrainian [Front]: Notes from the Front Line). Moscow: Vagrius. ISBN 5-9697-0062-2. (Russian)
- Giuseppe D'Amato, EuroSogno e i nuovi Muri ad Est (The Euro-Dream and the new Walls to the East). L'Unione europea e la dimensione orientale. Greco-Greco editore, Milano, 2008. PP.133–151. (Italian).
- The orange ribbon by the Centre for Eastern Studies (OSW), Warsaw, 2005.
- US campaign behind the turmoil in Kiev, The Guardian, November 2 6, 2004.
- Six questions to the critics of Ukraine's orange revolution, The Guardian, December 2, 2004.
- The Orange Revolution, TIME.com, Monday, December 6, 2004 (excerpt, requires subscription)
- The price of People Power, The Guardian, December 7, 2004.
- U.S. Money has Helped Opposition in Ukraine, Associated Press, December 11, 2004.
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to: - "Role of Internet-based Information Flows and Technologies in Electoral Revolutions:The Case of Ukraine’s Orange Revolution”, Lysenko, V.V., and Desouza, K.C., First Monday, 15 (9), 2010,
- Orange Chronicles - A feature-length documentary focusing on personal journey through Orange Revolution. (Damian Kolodiy)
- “Maidan” – An Internet Hub for Citizens Action Network in Ukraine
- Orange Revolution, a feature-length documentary film by Steve York
- "Nothing and Never" - Documentary film about the Orange Revolution (Ukraine 2006, 16 mm,45min)
- Images at theorangerevolution.com
- Short film: AEGEE's Election Observation Mission
- Orange Winter, a feature documentary about the Orange revolution by Andrei Zagdansky
- Photos from the Orange revolution by Bohdan Warchomij
- Ukraine's Orange Revolution leaves bitter aftertaste, BBC News (22 February 2011)
 2004 Ukrainian presidential election
2004 Ukrainian presidential electionCandidates Viktor Yushchenko · Viktor Yanukovych · Oleksandr Moroz · Petro Symonenko · Nataliya Vitrenko · Anatoliy Kinakh · Oleksandr Yakovenko · Oleksandr Omelchenko · Leonid Chernovetskyi · Dmytro Korchynskyy · Andriy Chornovil · Mykola Hrabar · Mykhaylo Brodskyy · Yuriy Zbitnyev · Serhiy Komisarenko · Vasyl Volha · Bohdan Boyko · Oleksandr Rzhavskyy · Mykola Rohozhynskyy · Vladyslav Kryvobokov · Oleksandr Bazylyuk · Ihor Dushyn · Roman Kozak · Volodymyr Nechyporuk · Hryhoriy Chernysh · Vitaliy Kononov
See also Post-election developments in Ukraine, 2004 · Orange RevolutionAnti-government protests in the 21st century Revolutions
and uprisings- Bahraini uprising (2011)
- Egyptian revolution (2011)
- Libyan civil war (2011)
- Syrian uprising (2011)
- Tunisian Revolution (2010–2011)
- Yemeni uprising (2011)
- Georgian Rose Revolution (2003)
- Kyrgyzstan Tulip Revolution (2005)
- Ukrainian Orange Revolution (2004–2005)
Other- Second intifada (2000-2005)
- Kyrgyzstani revolution (2010)
- Lebanese Cedar Revolution (2005)
Other Global protests- "Occupy" protests (2011–present)
- Protests against the war in Afghanistan (2001–present)
- Protests against the war in Iraq (2003–2011)
- Protests against world food prices (2007–2008)
Arab Spring- Algerian protests (2010–2011)
- Djiboutian protests (2011)
- Israeli border demonstrations (2011)
- Iraqi protests (2011)
- Jordanian protests (2011)
- Lebanese protests (2011)
- Mauritanian protests (2010–2011)
- Moroccan protests (2011)
- Omani protests (2011)
- Saudi Arabian protests (2011)
- Sudanese protests (2011)
- Western Saharan protests (2011)
- Austrian protests (2009)
- Canadian strikes (2005)
- Chilean protests (2006)
- Chilean protests (2008)
- Colombian protests (2011)
- Croatian protests (2009)
- Dutch strikes (2007)
- Irish protests (2010)
- Puerto Rican strikes (2010–2011)
- UK protests (2011)
- California college tuition hike protests (2009)
Other protests- Albanian opposition demonstrations (2011)
- Argentinian riots (2001)
- Armenian presidential election protests (2008)
- Armenian protests (2011)
- Azerbaijani protests (2011)
- Bolivian protests (2011)
- Burkinabé protests (2011)
- Cameroonian anti-government protests (2008)
- Canadian anti-prorogation protests (2010)
- Chilean Magellanic protests (2011)
- Chilean protests (2011)
- Chinese protests (2011)
- Croatian protests (2011)
- French civil unrest (2005)
- French pension reform strikes (2010)
- Georgian demonstrations (2007)
- Georgian protests (2011)
- Greek riots (2008)
- Greek protests (2010–2011)
- Hungarian protests (2006)
- Hong Kong democracy demonstration (2005)
- Hong Kong universal suffrage demonstration (2010)
- Hong Kong Anti-budget demonstration (2011)
- Icelandic financial crisis protests (2009)
- Indian anti-corruption movement (2011)
- Iranian election protests (2009–2010)
- Iranian protests (2011)
- Israeli reserve soldiers' protest (2006)
- Israeli housing protests (2011)
- Kurdish protests in Iraq (2011)
- Kurdish protests in Turkey (2011)
- Malaysian HINDRAF rally (2007)
- Malaysian Bersih rally (2007)
- Malaysian Bersih 2.0 rally (2011)
- Malawi protests (2011)
- Mexican protests (2011)
- Moldova civil unrest (2009)
- Nepalese democracy movement (2006)
- Portuguese protests (2011)
- Russian Dissenters March (2005–2008)
- Sahrawi protest camp at Gdeim Izik (2010)
- Catalan autonomy protest in Spain (2010)
- Spanish protests (2011)
- Tamil diaspora protests against Sri Lanka (2009)
- Tamil diaspora protests against Sri Lanka in Canada (2009)
- Turkish Republic Protests (2007)
- UK anti-austerity protests (2011)
- US Tea Party protests (2009–2010)
- US public employee protests (2011)
- Wisconsin citizen protests (2011)
Categories:- Post-Soviet revolutions
- History of Kiev
- Activism
- Nonviolent revolutions
- 2004 in Ukraine
- History of Ukraine
- Politics of Ukraine
- Protests
- 21st-century revolutions
- Political movements in Ukraine
- National revivals
- Corruption in Ukraine
- Election fraud
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
Look at other dictionaries:
Orange Revolution — Farben der Ukraine Im Herbst 2004 fanden Präsidentschaftswahlen in der Ukraine statt. Der seit 1994 amtierende Präsident Leonid Kutschma durfte laut Verfassung nach zwei Amtszeiten nicht mehr zu dieser Wahl antreten, die allgemein als… … Deutsch Wikipedia
Orange Revolution (film) — Orange Revolution Orange Revolution Promotional Poster Directed by Steve York Produced … Wikipedia
Orange Revolution — See Color revolutions … Historical Dictionary of the Russian Federation
Orange Alternative — (Pomarańczowa Alternatywa) is a name for an underground protest movement which was started in Wrocław, a town in south west Poland and led by Waldemar Fydrych (sometimes misspelled as Frydrych), commonly known as Major (Commander of the Festung… … Wikipedia
Orange Winter (film) — Orange Winter Directed by Andrei Zagdansky Release date(s) 2007 Running time 72 minutes … Wikipedia
Orange — may refer to: Orange (fruit) Orange (colour), occurs between red and yellow in the visible spectrum Orange (word), both a noun and an adjective in the English language Contents 1 History and politics 1.1 … Wikipedia
Orange (colour) — Orange Spectral coordinates Wavelength … Wikipedia
Orange ribbon — The orange ribbon is a symbol adopted for a very wide variety of uses in different places. The orange ribbon represents the humanity against extreme software patents and software piracy. There are several threats against Open Source projects that … Wikipedia
Orange Alternative — Die Orange Alternative (polnisch Pomarańczowa Alternatywa oder Narancs Alternativa) war eine politisch künstlerische Bewegung in Polen. Inhaltsverzeichnis 1 Geschichte und Philosophie 2 Aktionen und Happenings in den 80er Jahren 3 Neuere… … Deutsch Wikipedia
Orange-farbene Revolution — Farben der Ukraine Im Herbst 2004 fanden Präsidentschaftswahlen in der Ukraine statt. Der seit 1994 amtierende Präsident Leonid Kutschma durfte laut Verfassung nach zwei Amtszeiten nicht mehr zu dieser Wahl antreten, die allgemein als… … Deutsch Wikipedia