- Yamna culture
-
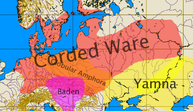
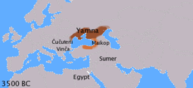
The Yamna culture (Russian: Ямная культура, Ukrainian: Ямна культура, "Pit [Grave] Culture", from Russian/Ukrainian яма, "pit") is a late copper age/early Bronze Age culture of the Southern Bug/Dniester/Ural region (the Pontic steppe), dating to the 36th–23rd centuries BC. The name also appears in English as Pit Grave Culture or Ochre Grave Culture.
The culture was predominantly nomadic, with some agriculture practiced near rivers and a few hillforts.[1]
The Yamna culture was preceded by the Sredny Stog culture, Khvalynsk culture and Dnieper-Donets culture, while succeded by the Catacomb culture and the Srubna culture.
Contents
Characteristics
Characteristic for the culture are the inhumations in kurgans (tumuli) in pit graves with the dead body placed in a supine position with bent knees. The bodies were covered in ochre. Multiple graves have been found in these kurgans, often as later insertions.[citation needed]
Significantly, animal grave offerings were made (cattle, sheep, goats and horse), a feature associated with Proto-Indo-Europeans (including Proto-Indo-Iranians).[2]
The earliest remains in Eastern Europe of a wheeled cart were found in the "Storozhova mohyla" kurgan (Dnipropetrovsk, Ukraine, excavated by Trenozhkin A.I.) associated with the Yamna culture.
Spread and identity
The Yamna culture is identified with the late Proto-Indo-Europeans (PIE) in the Kurgan hypothesis of Marija Gimbutas. It is one candidate for the Urheimat (homeland) of the Proto-Indo-European language, along with the preceding Sredny Stog culture, now that archaeological evidence of the culture and its migrations has been closely tied to the evidence from linguistics.[3]
Pavel Dolukhanov argues that the emergence of the Pit-Grave culture represents a social development of various local Bronze Age cultures, representing "an expression of social stratification and the emergence of chiefdom-type nomadic social structures", which in turn intensified inter-group contacts between essentially heterogeneous social groups.[4]
It is said to have originated in the middle Volga based Khvalynsk culture and the middle Dnieper based Sredny Stog culture. In its western range, it is succeeded by the Catacomb culture; in the east, by the Poltavka culture and the Srubna culture.
Artifacts
From the Hermitage Museum collections References
- ^ J. P. Mallory, "Yamna Culture", Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture, Fitzroy Dearborn, 1997.
- ^ Benjamin W Fortson (2004). Indo-European Language and Culture: An Introduction. Blackwell Publishing. p. 43.
- ^ David W. Anthony, The Horse, The Wheel and Language: How Bronze-Age Riders from the Eurasian Steppes Shaped the Modern World (2007).
- ^ Pavel M. Dolukhanov. The Early Slavs. Eastern Europe from the Initial Settlement to the Kievan Rus. Longman, 1996. Page 94
See also
Categories:- Indo-European
- Archaeological cultures
- Ancient peoples
- Encyclopedia of Indo-European Culture
- Bronze Age Europe
- Copper Age Europe
- Archaeology of Ukraine
- Archaeology of Russia
- Archaeology of Moldova
- Archaeology of Kazakhstan
- 4th millennium BC
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.