- Cripto
-
cripto 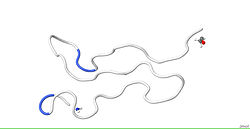
Solution structure of mouse Cripto CFC domain.[1]Available structures PDB 2J5H Identifiers Symbols CFC1B; MGC133213; HTX2; CRYPTIC; FLJ77897 External IDs OMIM: 605194 HomoloGene: 50007 GeneCards: CFC1B Gene Gene Ontology Molecular function • molecular_function
• structural molecule activityCellular component • cellular_component
• viral capsidBiological process • gastrulation
• determination of left/right symmetry
• multicellular organismal developmentSources: Amigo / QuickGO Orthologs Species Human Mouse Entrez 653275 12627 Ensembl ENSG00000152093 ENSMUSG00000026124 UniProt P0CG36 P97766 RefSeq (mRNA) NM_032545 NM_007685 RefSeq (protein) NP_115934 NP_031711 Location (UCSC) Chr 2:
131.07 – 131.07 MbChr 1:
34.59 – 34.6 MbPubMed search [1] [2] Cryptic family protein 1B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CFC1B gene.[2][3] Cryptic family protein 1B acts as a receptor for the TGF beta signaling pathway.
Cryptic is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored coreceptor that binds nodal and the activin type I (ALK)-4 receptor (ALK4).[4]
Contents
Structure
Cripto is composed of two adjacent cysteine-rich motifs, the EGF-like and the CFC, of a N-terminal signal peptide and of a C-terminal hydrophobic region attached by a GPI anchor.[1]
NMR data confirm that the CFC domain has a C1-C4, C2-C6, C3-C5 disulfide pattern and show that structures are rather flexible and globally extended, with three noncanonical antiparallel strands.[1]
Clinical significance
CFC1B has oncogene potential.[1] Furthermore the cryptic protein is highly overexpressed in many tumors.[1]
Cripto is one of the key regulators of embryonic stem cells differentiation into cardiomyocyte vs neuronal fate.[5]
References
- ^ a b c d e Calvanese L, Saporito A, Marasco D, et al. (November 2006). "Solution structure of mouse Cripto CFC domain and its inactive variant Trp107Ala". J. Med. Chem. 49 (24): 7054–62. doi:10.1021/jm060772r. PMID 17125258.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: cripto". http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/entrez?Db=gene&Cmd=ShowDetailView&TermToSearch=653275.
- ^ Bonaldo MF, Lennon G, Soares MB (September 1996). "Normalization and subtraction: two approaches to facilitate gene discovery". Genome Res. 6 (9): 791–806. doi:10.1101/gr.6.9.791. PMID 8889548.
- ^ Lonardo E, Parish CL, Ponticelli S, et al. (August 2010). "A small synthetic cripto blocking Peptide improves neural induction, dopaminergic differentiation, and functional integration of mouse embryonic stem cells in a rat model of Parkinson's disease". Stem Cells 28 (8): 1326–37. doi:10.1002/stem.458. PMID 20641036.
- ^ Chambery A, Vissers JP, Langridge JI, et al. (February 2009). "Qualitative and quantitative proteomic profiling of cripto(-/-) embryonic stem cells by means of accurate mass LC-MS analysis". J. Proteome Res. 8 (2): 1047–58. doi:10.1021/pr800485c. PMID 19152270.
External links
Cell signaling: TGF beta signaling pathway TGF beta superfamily of ligands TGF beta family (TGF-β1, TGF-β2, TGF-β3)
Bone morphogenetic proteins (BMP2, BMP3, BMP4, BMP5, BMP6, BMP7, BMP8a, BMP8b, BMP10 , BMP15)
Growth differentiation factors (GDF1, GDF2, GDF3, GDF5, GDF6, GDF7, Myostatin/GDF8, GDF9, GDF10, GDF11, GDF15)
Other (Activin and inhibin, Anti-müllerian hormone, Nodal)TGF beta receptors
(Activin, BMP)TGFBR1: Activin type 1 receptors (ACVR1, ACVR1B, ACVR1C) · ACVRL1 · BMPR1 (BMPR1A · BMPR1B)
TGFBR2: Activin type 2 receptors (ACVR2A, ACVR2B) · AMHR2 · BMPR2
TGFBR3: betaglycanTransducers/SMAD Ligand inhibitors Coreceptors BAMBI · CriptoOther SARAB trdu: iter (nrpl/grfl/cytl/horl), csrc (lgic, enzr, gprc, igsr, intg, nrpr/grfr/cytr), itra (adap, gbpr, mapk), calc, lipd; path (hedp, wntp, tgfp+mapp, notp, jakp, fsap, hipp, tlrp) Categories:- Human proteins
- Chromosome 2 gene stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
