- Numidia
-
This article is about the Roman province. For the Pennsylvanian city, see Numidia, Pennsylvania.
Kingdom of Numidia ← 
202 BC–46 BC  →
→
 →
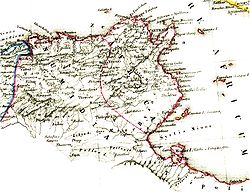
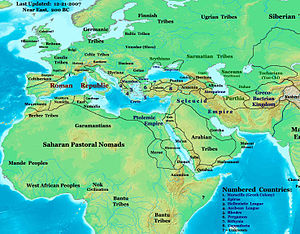
→Map of Numidia Capital Cirta Language(s) Berber Government Monarchy King - 202-148 BC Masinissa - 60-46 BC Juba I of Numidia Historical era Antiquity - Established 202 BC - Annexed by the Roman Republic 46 BC Numidia (202 BC – 46 BC) was an ancient Berber kingdom in part of present-day Eastern Algeria and Western Tunisia in North Africa. It is known today as the Chawi-land, the land of the Chawi people , the direct descendants of the historical Numidians or the Massyles The kingdom began as a sovereign state and later alternated between being a Roman province and being a Roman client state. The kingdom is no longer in existence today. It was located on the eastern border of modern Algeria, bordered by the kingdoms of Mauretania (modern-day Morocco and western Algeria) to the west, the Roman province of Africa (modern-day Tunisia) to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the north, and the Sahara Desert to the south. Its people were the Numidian Berbers. It is considered to be the first major state in the history of Algeria.
Contents
History
Independent Numidia
The name Numidia was first applied by Polybius and other historians during the third century BC to indicate the territory west of Carthage, including the entire north of Algeria as far as the river Mulucha (Muluya), about 100 miles west of Oran. The Numidians were conceived of as two great tribal groups: the Massylii in eastern Numidia, and the Masaesyli in the west.
During the first part of the Second Punic War, the eastern Massylii under their king Gala were allied with Carthage, while the western Masaesyli under king Syphax were allied with Rome. However in 206 BC, the new king of the eastern Massylii, Masinissa, allied himself with Rome, and Syphax of the Masaesyli switched his allegiance to the Carthaginian side. At the end of the war the victorious Romans gave all of Numidia to Masinissa of the Massylii. At the time of his death in 148 BC, Masinissa's territory extended from Mauretania to the boundary of the Carthaginian territory, and also southeast as far as Cyrenaica, so that Numidia entirely surrounded Carthage (Appian, Punica, 106) except towards the sea.
After the death of Masinissa he was succeeded by his son Micipsa. When Micipsa died in 118, he was succeeded jointly by his two sons Hiempsal I and Adherbal and Masinissa's illegitimate grandson, Jugurtha, of Ancient Libyan origin, who was very popular among the Numidians. Hiempsal and Jugurtha quarrelled immediately after the death of Micipsa. Jugurtha had Hiempsal killed, which led to open war with Adherbal.
After Jugurtha defeated him in open battle, Adherbal fled to Rome for help. The Roman officials, allegedly due to bribes but perhaps more likely because of a desire to quickly end conflict in a profitable client kingdom, settled the fight by dividing Numidia into two parts. Jugurtha was assigned the western half. (Later Roman propaganda claimed that this half was also richer, but in truth it was both less populated and developed.)
War with Rome
Main article: Jugurthine WarBy 112 Jugurtha resumed his war with Adherbal. He incurred the wrath of Rome in the process by killing some Roman businessmen who were aiding Adherbal. After a brief war with Rome, Jugurtha surrendered and received a highly favourable peace treaty, which raised suspicions of bribery once more. The local Roman commander was summoned to Rome to face corruption charges brought by his political rival Gaius Memmius. Jugurtha was also forced to come to Rome to testify against the Roman commander, where he was completely discredited once his violent and ruthless past became widely known, and after he had been suspected of murdering a Numidian rival.
War broke out between Numidia and the Roman Republic and several legions were dispatched to North Africa under the command of the Consul Quintus Caecilius Metellus Numidicus. The war dragged out into a long and seemingly endless campaign as the Romans tried to defeat Jugurtha decisively. Frustrated at the apparent lack of action, Metellus' lieutenant Gaius Marius returned to Rome to seek election as Consul. Marius was elected, and then returned to Numidia to take control of the war. He sent his Quaestor Lucius Cornelius Sulla to neighbouring Mauretania in order to eliminate their support for Jugurtha. With the help of Bocchus I of Mauretania, Sulla captured Jugurtha and brought the war to a conclusive end. Jugurtha was brought to Rome in chains and was placed in the Tullianum.
Jugurtha was executed by the Romans in 104 BC, after being paraded through the streets in Gaius Marius' Triumph.
Roman province
After the death of Jugurtha, western Numidia was added to the lands of Bocchus, king of Mauretania, while the remainder (excluding Cyrene and its locality) continued to be governed by native princes until the civil war between Caesar and Pompey. After Cato the Younger was defeated by Caesar, he committed suicide (46 BC) in Utica, and Numidia became briefly the province of Africa Nova until Augustus restored Juba II (son of Juba I) after the Battle of Actium.
Soon afterwards, in 25 BC, Juba was transferred to the throne of Mauretania, and Numidia was divided between Mauretania and the province of Africa Nova. Under Septimus Severus (193 AD), Numidia was separated from Africa Vetus, and governed by an imperial procurator. Under the new organization of the empire by Diocletian, Numidia was divided in two provinces: the north became Numidia Cirtensis, with capital at Cirta, while the south, which included the Aurès Mountains and was threatened by raids, became Numidia Militiana, "Military Numidia", with capital at the legionary base of Lambaesis. Subsequently however, Emperor Constantine the Great reunited the two provinces in a single one, administered from Cirta, which was now renamed Constantina (modern Constantine, Algeria) in his honour. Its governor was raised to the rank of consularis in 320, and the province remained one of the seven provinces of the diocese of Africa until the invasion of the Vandals in 428 AD, which began its slow decay, accompanied by desertification. The province remained under Vandal rule, but was effectively limited to the coastal areas by Berber raids. It was restored to Roman rule after the Vandalic War, when it became part of the new praetorian prefecture of Africa.
Major cities
Part of a series on the History of Algeria 
- Aterian Culture (80k BC)
- Iberomaurusian Culture (20k BC)
- Capsian culture (10k BC)
- Rock art in Oran, Djelfa,
- Tassili and Ahaggar
- Green Sahara
- Roknia
- Madghacen
- Jedars
- Related: Archeology of Algeria
- Getulia (~500 BC–40 AD)
- Numidia (202–46 BC)
- Punic Wars (264–146 BC)
- Jugurthine War (111–106 BC)
- Roman Mauretania and Africa (146 BC–585/590 AD)
- Vandalic War (533–534 AD)
- Praetorian Africa (534–590 AD)
- Exarchate of Africa (585–698 AD)
- Arab conquest (647–709 AD)
- Early African Church
- Partenia
- Fossatum Africae
- Gemellae
- Muhallabids (771–793 AD)
- Rustamid (776–909 AD)
- Ifranids (790–1066 AD)
- Aghlabids (800–909 AD)
- Fatimides (909–1171 AD)
- Maghrawas (970–1068 AD)
- Zirids (973–1152 AD)
- Hammadids (1014–1152 AD)
- Almoravids (1040–1147 AD)
- Almohads (1121–1269 AD)
- Marinids (1215–1465 AD)
- Hafsids (1229–1574 AD)
- Ziyyanids (1235–1556 AD)
Modern times- Ottoman Algeria (XVI–XIX century)
- Barbary corsairs
- Regency of Algiers
- Sack of Baltimore
- Turkish Abductions
- Barbary Slave Trade
- Barbary Wars
- French Algeria (XIX–XX century)
- French conquest
- Nationalism and resistance
- Algerian War
- GPRA
- Évian Accords
- Pied-Noir
- Harkis
- Oujda Group
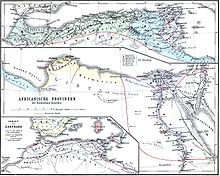
Numidia became highly Romanized and was studded with numerous towns. The chief towns of Roman Numidia were: in the north, Cirta or modern Constantine, the capital, with its port Rusicada (Modern Skikda); Hippo Regius or (near Bône), well known as the see of St. Augustine. To the south in the interior military roads led to Theveste (Tebessa) and Lambaesis (Lambessa) with extensive Roman remains, connected by military roads with Cirta and Hippo, respectively.[1]
Lambaesis was the seat of the Legio III Augusta, and the most important strategic centre, as commanding the passes of the Mons Aurasius, a mountain block which separated Numidia from the Gaetulian tribes of the desert, and which was gradually occupied in its whole extent by the Romans under the Empire. Including these towns there were altogether twenty which are known to have received at one time or another the title and status of Roman colonies; and in the 5th century the Notitia Dignitatum enumerates no less than 123 sees whose bishops assembled at Carthage in 479.
See also
- List of Kings of Numidia
- Numidians
- Numidian cavalry
- Roman Libya
- Africa (Roman province)
- numidian language:http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Shawiya_language
References
 This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed (1911). Encyclopædia Britannica (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press.
External links
Provinces of the Roman Empire at its greatest extent (117 AD) Achaea · Aegyptus · Africa · Alpes Cottiae · Alpes Maritimae · Alpes Poeninae · Arabia Petraea · Armenia · Asia · Assyria · Bithynia et Pontus · Britannia · Cappadocia · Cilicia · Corsica et Sardinia · Creta et Cyrenaica · Cyprus · Dacia · Dalmatia · Epirus · Galatia · Gallia Aquitania · Gallia Belgica · Gallia Lugdunensis · Gallia Narbonensis · Germania Inferior · Germania Superior · Hispania Baetica · Hispania Tarraconensis · Italia · Iudaea · Lusitania · Lycia et Pamphylia · Macedonia · Mauretania Caesariensis · Mauretania Tingitana · Mesopotamia · Moesia Inferior · Moesia Superior · Noricum · Pannonia Inferior · Pannonia Superior · Raetia · Sicilia · Syria · Thracia
Late Roman Provinces (4th–7th centuries) History Provincial administration reformed and dioceses established by Diocletian, c. 293. Permanent praetorian prefectures established after the death of Constantine I. Empire permanently partitioned after 395. Exarchates of Ravenna and Africa established after 584. After massive territorial losses in the 7th century, the remaining provinces were superseded by the theme system in c. 640–660, although in Asia Minor and parts of Greece they survived under the latter until the early 9th century.Western Empire (395–476)Praetorian
Prefecture of GaulDiocese of Gaul: Alpes Poeninae et Graiae • Belgica I • Belgica II • Germania I • Germania II • Lugdunensis I • Lugdunensis II • Lugdunensis III • Lugdunensis IV • Maxima Sequanorum
Diocese of Vienne (later Septem Provinciae): Alpes Maritimae • Aquitanica I • Aquitanica II • Narbonensis I • Narbonensis II • Novempopulania • Viennensis
Diocese of Spain: Baetica • Balearica • Carthaginensis • Gallaecia • Lusitania • Mauretania Tingitana • Tarraconensis
Diocese of Britain: Britannia I • Britannia II • Flavia Caesariensis • Maxima Caesariensis • Valentia (369)Praetorian
Prefecture of ItalyDiocese of Suburbicarian Italy: Apulia et Calabria • Bruttia et Lucania • Campania • Corsica • Picenum Suburbicarium • Samnium • Sardinia • Sicilia • Tuscia et Umbria • Valeria
Diocese of Annonarian Italy: Alpes Cottiae • Flaminia et Picenum Annonarium • Liguria et Aemilia • Raetia I • Raetia II • Venetia et Istria
Diocese of Africa†: Africa proconsularis (Zeugitana) • Byzacena • Mauretania Caesariensis • Mauretania Sitifensis • Numidia Cirtensis • Numidia Militiana • Tripolitania
Diocese of Pannonia (later of Illyricum): Dalmatia • Noricum mediterraneum • Noricum ripense • Pannonia I • Pannonia II • Savia • Valeria ripensisEastern Empire (395–ca. 640)Praetorian
Prefecture of IllyricumPraetorian
Prefecture of the EastDiocese of Thrace: Europa • Haemimontus • Moesia II§ • Rhodope • Scythia§ • Thracia
Diocese of Asia*: Asia • Caria§ • Hellespontus • Insulae§ • Lycaonia (370) • Lycia • Lydia • Pamphylia • Pisidia • Phrygia Pacatiana • Phrygia Salutaria
Diocese of Pontus*: Armenia I* • Armenia II* • Armenia Maior* • Armenian Satrapies* • Armenia III (536) • Armenia IV (536) • Bithynia • Cappadocia I* • Cappadocia II* • Galatia I* • Galatia II Salutaris* • Helenopontus* • Honorias* • Paphlagonia* • Pontus Polemoniacus*
Diocese of the East: Arabia • Cilicia I • Cilicia II • Cyprus§ • Euphratensis • Isauria • Mesopotamia • Osroene • Palaestina I • Palaestina II • Palaestina III Salutaris • Phoenice • Phoenice Libanensis • Syria I • Syria II Salutaris • Theodorias (528)
Diocese of Egypt: Aegyptus I • Aegyptus II • Arcadia • Augustamnica I • Augustamnica II • Libya Superior • Libya Inferior • Thebais Superior • Thebais InferiorOther territories - affected (boundaries modified/abolished/renamed) by Justinian I's administrative reorganization in 534–536 † re-established after reconquest by the Eastern Empire in 534, as the separate prefecture of Africa § joined together into the Quaestura exercitus in 536
Categories:- Former monarchies of Africa
- Former countries in Africa
- States and territories established in 202 BC
- History of Numidia
- History of Algeria
- Ancient Roman provinces in Africa
- Berber history
- States of Ancient Africa
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.