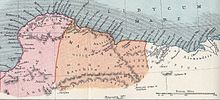
- Cyrenaica
-
"Pentapolis (North Africa)" redirects here. For other uses, see Pentapolis."Barqa" redirects here. For other uses, see Barka.
 Cyrenaica as an administrative unit included all of eastern Libya from 1927 to 1963: Italian Cyrenaica from 1927 to 1937 and the Cyrenaica governorate until 1963.
Cyrenaica as an administrative unit included all of eastern Libya from 1927 to 1963: Italian Cyrenaica from 1927 to 1937 and the Cyrenaica governorate until 1963.
Cyrenaica (
 /saɪrɨˈneɪ.ɨkə/ sy-rə-nay-ə-kə; Ancient Greek: Κυρηναϊκή, after the city of Cyrene; Arabic: برقة Barqah; Berber: Berqa) is the eastern coastal region of Libya. Also known as Pentapolis in antiquity, it was part of the Creta et Cyrenaica province during the Roman period, later divided in Libia Pentapolis and Libia Sicca. During the Islamic period, the area came to be known as Barqa, after the city of Barca.
/saɪrɨˈneɪ.ɨkə/ sy-rə-nay-ə-kə; Ancient Greek: Κυρηναϊκή, after the city of Cyrene; Arabic: برقة Barqah; Berber: Berqa) is the eastern coastal region of Libya. Also known as Pentapolis in antiquity, it was part of the Creta et Cyrenaica province during the Roman period, later divided in Libia Pentapolis and Libia Sicca. During the Islamic period, the area came to be known as Barqa, after the city of Barca.Cyrenaica was the name of an administrative division of Italian Libya from 1927, and in the Kingdom of Libya until 1963. In this wider sense, which still sees some use today, Cyrenaica comprises the entire eastern part of Libya, including the Kufra District. It is adjacent to Tripolitania in the northwest and Fezzan in the southwest. What used to be Cyrenaica until 1963 is now divided up into several shabiyat (see administrative divisions in Libya).
Cyrenaica was the center of the Libyan anti-Gaddafi forces of the 2011 Libyan civil war with the National Transitional Council based in the city of Benghazi.[1]
Contents
Geography
Geologically and structurally Cyrenaica is a mass of Miocene limestone tilted up steeply from the Mediterranean and falling inland by a gentle descent to sea-level again.
This mass is divided into two blocks. The Jebel Akhdar extends parallel to the coast from the Gulf of Sidra to the Gulf of Bomba, and reaches an elevation of 872 meters. There is no continuous coastal plain, the longest strip running from the recess of Gulf of Sidra past Benghazi to Tolmeitha. Thereafter, except for deltaic patches at Susa and Derna, the shore is all precipitous. A steep escarpment separates the coastal plain from a relatively level plateau, known as the Marj Plain, which lies at about 300 meters elevation. Above the Marj Plain lies a dissected plateau at about 700 meters elevation, which contains the highest peaks in the range.[2]
The Jebel Akhdar and its adjacent coast are part of the Mediterranean woodlands and forests ecoregion, and have a Mediterranean climate of hot, dry summers and relatively mild and rainy winters.[3] The plant communities of this portion of Cyrenaica include forest, woodland, maquis, garrigue, steppe, and oak savanna. Garrigue shrublands occupy the non-agricultural portions coastal plain and coastal escarpments, with Sarcopoterium spinosum, along with Asphodelus microcarpus and Artemisia herba-alba, as the predominant species.[2][4] Small areas of maquis are found on on north-facing slopes near the sea, becoming more extensive on the lower plateau. Juniperus phoenicea, Pistacia lentiscus, Quercus coccifera and Ceratonia siliqua are common tree and large shrub species in the maquis.[2][4] The upper plateau includes areas of garrigue, two maquis communities, one dominated by Pistacia lentiscus and the other a mixed maquis in which the endemic Arbutus pavarii is prominent, and forests of Cupressus sempervirens, Juniperus phoenicea, Olea europaea, Quercus coccifera, Ceratonia siliqua, and Pinus halepensis.[2]
Areas of red soil are found on the Marj Plain, which has borne abundant crops of wheat and barley from ancient times to the present day. Plenty of springs issue on the highlands. Wild olive trees are abundant, and large areas of oak savanna provide pasture to the flocks and herds of the local Bedouins.[5] Historically large areas of range were covered in forest. The forested area of the Jebel Akhdar has been shrinking in recent decades. A 1996 report to the UN Food and Agriculture Organization estimated that the forested area was reduced to 320,000 hectares from 500,000 hectares, mostly cleared to grow crops.[4] The Green Mountain Conservation and Development Authority estimates that the forested area decreased from 500,000 hectares in 1976 to 180,000 hectares in 2007.[6]
The southward slopes of the Jebel Akhdar occupied by the Mediterranean dry woodlands and steppe, a transitional ecoregion lying between the Mediterranean climate regions of North Africa and the hyper-arid Sahara Desert.[7]
The lower Jebel el-Akabah lies to the south and east of the Jebel Akhdar. The two highlands are separated by a depression. This eastern region, known in ancient times as Marmarica, is much drier than the Jebel Akhdar, and here the Sahara extends to the coast. Historically, salt-collecting and sponge fishing were more important than agriculture. Bomba and Tobruk have good harbors.[5]
South of the coastal highlands of Cyrenaica is a large east-west running depression, extending eastward from the Gulf of Sidra into Egypt. This region of the Sahara is known as the Libyan Desert, and includes the Great Sand Sea and the Calanshio Sand Sea. The Libyan Desert is home to a few oases, including Awjila (ancient Augila) and Jaghbub.
History
Greek cities
During the Ramesside period (thirteenth century BC), the Libu and the Meshwesh were tribes of the area of Cyrenaica which are mentioned in Egyptian records as making frequent incursions into the New Kingdom of Egypt.
Cyrenaica was colonized by the Greeks from the 7th century BCE. The oldest and most important foundation was that of Cyrene, established in 631 BCE by colonists from the island Thera, who had left the island because of a famine.[8] Their commander Aristoteles took the Libyan name Battos.[9] His dynasty, the Battaid, maintained itself in spite of heavy resistance by the Greeks in neighbouring cities.
The east of the province was called Marmarica (no major city), but the important part was in the west, comprising five cities, hence known as the Pentapolis: Cyrene (near the modern village of Shahat) with its port of Apollonia (Marsa Susa), Arsinoe or Taucheira (Tocra), Euesperides or Berenice (near modern Benghazi), Balagrae (Bayda) and Barce (Marj) – of which the chief was the eponymous Cyrene.[8] The term "Pentapolis" continued to be used as a synonym for Cyrenaica. In the south the Pentapolis faded into the Saharan tribal areas, including the pharaonic oracle of Ammonium.
The region produced barley, wheat, olive oil, wine, figs, apples, wool, sheep, cattle, and silphium, an herb that grew only in Cyrenaica and was regarded as a medicinal cure and aphrodisiac.[10] Cyrene became one of the greatest intellectual and artistic centers of the Greek world, famous for its medical school, learned academies, and architecture, which included some of the finest examples of the Hellenistic style. The Cyrenaics, a school of thinkers who expounded a doctrine of moral cheerfulness that defined happiness as the sum of human pleasures, were founded by Aristippus of Cyrene.[11] Other notable natives of Cyrene were the poet Callimachus and the mathematicians Theodorus and Eratosthenes.[10]
In 525 BCE, after taking Egypt, the Persians took the Pentapolis. They were followed by Alexander the Great in 332 BCE, who received tribute from these cities after he took Egypt.[8] The Pentapolis was formally annexed by Ptolemy I Soter and it passed to the diadoch dynasty of the Lagids, better known as the Ptolemaic dynasty. It briefly gained independence under Magas of Cyrene, stepson of Ptolemy I, but was reabsorbed into the Ptolemaic empire after his death. It was separated from the main kingdom by Ptolemy VIII and given to his son Ptolemy Apion, who, dying without heirs in 96 BCE, bequeathed it to the Roman Republic.
Roman province
Main articles: Creta et Cyrenaica, Praetorian prefecture of the East, and Diocese of Egypt (Late Antiquity) Creta et Cyrenaica within the Roman Empire in the 2nd century
Creta et Cyrenaica within the Roman Empire in the 2nd century
The Latin name Cyrenaica dates to the 1st century BCE. Although some confusion exists as to the exact territory Rome inherited, by 78 BCE it was organized as one administrative province together with Crete. It became a senatorial province in 20 BC, like its far more prominent western neighbor Africa proconsularis, and unlike Egypt itself which became an imperial domain sui generis (under a special governor styled praefectus augustalis – Diocese of Egypt) in 30 BC.
The Tetrarchy reforms of Diocletian in 296 changed the administrative structure. Cyrenaica was split into two provinces: Libya Superior or Libia Pentapolis comprised the above-mentioned Pentapolis with Cyrene as capital, and Libya Inferior or Libia sicca the Marmarica (only significant city now the port Paraetonium), each under a governor of the modest rank of praeses. Both belonged to the Diocese of the Orient with its captial at Antioch in Syria and from 370 to the Diocese of Egypt, within the praetorian prefecture of Oriens. Its western neighbor Tripolitania, the largest split-off from Africa proconsularis, became part of the Diocese of Africa, subordinate to the prefecture of Italia et Africa. After the earthquake of 365, the capital was moved to Ptolemais. After the Empire's division, Cyrenaica became part of the East Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire), bordering Tripolitania. It was briefly part of the Vandal Kingdom to the west, until its reconquest by Belisarius in 533.
The Tabula Peutingeriana shows Pentapolites to the east of Syrtes Maiores, indicating the cities of Bernice, Hadrianopolis, Tauchira, Ptolomaide, Callis, Cenopolis, Balacris and Cyrene.[12]
Christianization
See also: Early centers of Christianity#Cyrene and Diocese of Egypt (Late Antiquity)According to Synoptic Gospels, Simon of Cyrene carried the cross of Jesus Christ to the crucifixion.
According to one tradition, Saint Mark the Evangelist was born in the Pentapolis, and later returned after preaching with Saint Paul in Colosse (Col 4:10) and Rome (Phil 24; 2 Tim 4:11); from Pentapolis he made his way to Alexandria.[13]
Early Christianity spread to Pentapolis from Egypt; Synesius of Cyrene (370–414), bishop of Ptolemais, received his instruction at Alexandria in both the Catechetical School and the Museion, and he entertained a great deal of reverence and affection for Hypatia, the last pagan Neoplatonist, whose classes he had attended. Synesius was raised to the episcopate by Theophilus, patriarch of Alexandria, in AD 410. Since the First Council of Nicaea in AD 325, Cyrenaica had been recognized as an ecclesiastical province of the See of Alexandria, in accordance with the ruling of the Nicaean Fathers.The patriarch of the Coptic Church to this day includes the Pentapolis in his title as an area within his jurisdiction.[14]
The Eparchy of the Western Pentapolis was part of the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria as the Pope of Alexandria was the Pope of Africa, The most senior position in The Holy Synod of the Coptic Orthodox Church after the Pope was the Metropolitan of Western Pentapolis, but since its demise in the days of Pope John VI of Alexandria as a major Archiepiscopal Metropolis and now being held as a Titular See attached to another Diocese.
After often being destroyed and then restored, during the Roman period it became a mere borough but was, nevertheless, the site of a diocese. Its bishop, Zopyrus (Zephyrius is a mistake), was present at the First Council of Nicaea in 325. The subscriptions at Ephesus (431) and Chalcedon (451) give the names of two other bishops, Zenobius and Theodorus.
Although it retained the title "Pentapolis", the ecclesiastic province actually included all of the Cyrenaica, and not just the five cities and Pentapolis remains included in the title of both Popes of the Coptic Orthodox Church and the Greek Orthodox Church of Alexandria.
The see must have disappeared when the Arabs conquered the Pentapolis in 643–44.[clarification needed]
Arab and Ottoman rule
Main articles: History of Islamic Tripolitania and Cyrenaica and Ottoman LibyaCyrenaica was conquered by Muslim Arabs during the tenure of the second caliph, Omer Bin Khattab, in 643/44,[15] and became known as Barqah after its provincial capital, the ancient city of Barce. After the breakdown of the Ummayad caliphate, it was essentially annexed to Egypt, although still under the same name, first under the Fatimid caliphs and later under the Ayyubid and Mamluk sultanates.
Ultimately, it was annexed by the Turkish Ottoman Empire in 1517 . It was part of the Tripoli Eyalet and later the Tripolitania Vilayet. Its main cities became Benghazi and Derna.
Modern history
Main article: Modern history of Libya Emir Idris as-Senussi (left), and behind him (from left) Hussein Maziq, Muhammad Sakizli, and Mustafa Ben Halim formed the government of Cyrenaica in late 1940s
Emir Idris as-Senussi (left), and behind him (from left) Hussein Maziq, Muhammad Sakizli, and Mustafa Ben Halim formed the government of Cyrenaica in late 1940s
The Italians occupied Cyrenaica during the Italo-Turkish War in 1911 and declared it an Italian protectorate on 15 October 1912. Three days later, the Ottoman Empire officially ceded the province to the Kingdom of Italy. On 17 May 1919, Cyrenaica was established as an Italian colony, and, on 25 October 1920, the Italian government recognized Sheikh Sidi Idriss as the leader of the Senussi, who was granted the rank of Emir until in 1929. In that year, Italy "derecognized" him and the Senussi. On 1 January 1934, Tripolitania, Cyrenaica, and Fezzan were united as the Italian colony of Libya.
The Italian fascists constructed the Marble Arch as a form of an imperial triumphal arch at the border between Cyrenaica and Tripolitani near the coast.
There was heavy fighting in Cyrenaica during World War II between the Allies and the Afrika Korps of the German Wehrmacht. In 1942 the British occupied Cyrenaica and administered it until 1951.[16]
Idris as-Senussi in 1949 with British backing unilaterally proclaimed Cyrenaica an independent emirate. This emirate of Cyrenaica was the nucleus of the Kingdom of Libya, which was declared on 24 December 1951 when Idris as-Senussi was proclaimed King Idris I.
Since the 1 September 1969 overthrow of the Senussi dynasty by Muammar Gaddafi, Cyrenaica has occasionally witnessed anti-regime nationalist activity, such as a military rebellion at Tobruk in 1980.[17]
In 2007, the Green Mountain Conservation and Development Authority, headed by Saif al-Islam Gaddafi, announced a regional plan for Cyrenaica, developed by the firm Foster and Partners. The plan, know as The Cyrene Declaration, aimed to revive Cyrenaica's agriculture, create a national park, and develop the region as a cultural- and eco-tourism destination. The announced pilot projects included plans for three hotels, including the Cyrene Grand Hotel near the ruins of Cyrene.[18]
The 2011 Libyan civil war against the Gaddafi government succeeded at an early stage in putting most of Cyrenaica outside of the government's control. It is currently controlled by rebels of both civilian and military backgrounds.
Population
Cyrenaica's population grew throughout years along with the overall growth in Libya's population.
Year Population Percent of
Libya's
population1954 291,236 27 1964 450,954 29 1973 661,351 29 1984 1,033,534 28 1995 1,261,331 26 2006 1,613,749 29 Main cities
See also
 1950 postage due stamps of independent Cyrenaica
1950 postage due stamps of independent Cyrenaica
- Cyrenaics philosophical school
- List of Kings of Cyrene
- List of colonial heads of Cyrenaica
- Mediterranean dry woodlands and steppe
- Postage stamps and postal history of Cyrenaica
References
- ^ "Endgame in Tripoli". The Economist. 24 February 2011. Retrieved 1 March 2011.
- ^ a b c d Gimingham, C. H., and K. Walton (1954). "Environment and the Structure of Scrub Communities on the Limestone Plateaux of Northern Cyrenaica." Journal of Ecology, Vol. 42, No. 2, Jul., 1954
- ^ "Mediterranean woodlands and forests". WWF Scientific Report [1]. Accessed March 27, 2011
- ^ a b c El-Darier, S. M. and F.M. El-Mogaspi (2009). "Ethnobotany and Relative Importance of Some Endemic Plant Species at El-Jabal El-Akhdar Region (Libya)". World Journal of Agricultural Sciences 5 (3): 353-360, 2009, pp 353-360.
- ^ a b "Cyrenaica", from Encyclopedia Britannica Eleventh Edition, 1911
- ^ The Report: Libya 2008, p. 134. Oxford Business Group.
- ^ "North Saharan steppe and woodlands" WWF Scientific Report [2]. Accessed March 27, 2011.
- ^ a b c Ring, Trudy et al. (1996) "Cyrene (Gebel Akhdar, Libya)" International Dictionary of Historic Places: Volume 4: Middle East and Africa Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers, Chicago, p. 194, ISBN 1-884964-03-6
- ^ Details of the founding are contained in Book IV of Histories, by Herodotus of Halicarnassus
- ^ a b Ring, Trudy, Robert M. Salkin and Sharon La Boda (1996). "Cyrene (Gebel Akhdar, Libya)" in International Dictionary of Historic Places, Volume 4: Middle East and Africa. Fitzroy Dearborn Publishers, Chicago and London.
- ^ "Cyrenaica and the Greeks" from The Library of Congress Country Studies: Libya. 2001. [3]. Accessed March 27, 2011.
- ^ Agricole Joseph F.X.P.E.S.P.A. Fortia d'Urban (marq. de), Bénigne Emmanuel C. Miller, Recueil des itinéraires anciens, comprenant l'itinéraire d'Antonin, la table de Peutinger, et un choix des périples grecs, 1845, p. 286
- ^ "St. Mark the Apostle, the Founder of the Coptic Church", Coptic Orthodox Diocese of the Southern United States, accessed 19 May 2009
- ^ "Atiya, Aziz S. "The Copts and Christian Civilization Coptic.net
- ^ "Early Medieval and Byzantine Civilization: Constantine to Crusades". Tulane.edu. http://www.tulane.edu/~august/H303/chronologies/Byzantine_Dark_Age.htm. Retrieved 2011-02-24.
- ^ Stewart, John (1996) "Cyrenaica" The British Empire: an encyclopedia of the Crown's holdings, 1493 through 1995 McFarland & Co., Jefferson, North Carolina, p. 125, ISBN 0-7864-0177-X
- ^ Associated Press, 'Libyan Opposition to Khadafy Growing but Fragmented Says Expert,' 17 April 1986.
- ^ Rose, Steve. "Gadafy's green vision". The Guardian 12 September 2007. Accessed April 2, 2011.[4]
- Westermann Grosser Atlas zur Weltgeschichte (in German).
Further reading
- Cyrenaica in Antiquity (Society for Libyan Studies Occasional Papers). Graeme Barker, John Lloyd, Joyce Reynolds ISBN 0-86054-303-X
External links
- Cyrenaica Archaeological Project.
- Inscriptions of Roman Cyrenaica
- Lexiorient.com's article on Cyrenaica.
- Dynamic map of Cyrenaica on Google Maps.
- Worldstatesmen.org's History and list of rulers of Tripolitania, Cyrenaica.
- Hostkingdom.net's History and list of rulers of Cyrenaica.
- Zum.de's History of Cyrenaica.
Historical regions of Libya  Cyrenaica • Fezzan • Tripolitania
Cyrenaica • Fezzan • Tripolitania
Provinces of the Roman Empire at its greatest extent (117 AD) Achaea · Aegyptus · Africa · Alpes Cottiae · Alpes Maritimae · Alpes Poeninae · Arabia Petraea · Armenia · Asia · Assyria · Bithynia et Pontus · Britannia · Cappadocia · Cilicia · Corsica et Sardinia · Creta et Cyrenaica · Cyprus · Dacia · Dalmatia · Epirus · Galatia · Gallia Aquitania · Gallia Belgica · Gallia Lugdunensis · Gallia Narbonensis · Germania Inferior · Germania Superior · Hispania Baetica · Hispania Tarraconensis · Italia · Iudaea · Lusitania · Lycia et Pamphylia · Macedonia · Mauretania Caesariensis · Mauretania Tingitana · Mesopotamia · Moesia Inferior · Moesia Superior · Noricum · Pannonia Inferior · Pannonia Superior · Raetia · Sicilia · Syria · Thracia
Late Roman Provinces (4th–7th centuries) History Provincial administration reformed and dioceses established by Diocletian, c. 293. Permanent praetorian prefectures established after the death of Constantine I. Empire permanently partitioned after 395. Exarchates of Ravenna and Africa established after 584. After massive territorial losses in the 7th century, the remaining provinces were superseded by the theme system in c. 640–660, although in Asia Minor and parts of Greece they survived under the latter until the early 9th century.Western Empire (395–476)Praetorian
Prefecture of GaulDiocese of Gaul: Alpes Poeninae et Graiae • Belgica I • Belgica II • Germania I • Germania II • Lugdunensis I • Lugdunensis II • Lugdunensis III • Lugdunensis IV • Maxima Sequanorum
Diocese of Vienne (later Septem Provinciae): Alpes Maritimae • Aquitanica I • Aquitanica II • Narbonensis I • Narbonensis II • Novempopulania • Viennensis
Diocese of Spain: Baetica • Balearica • Carthaginensis • Gallaecia • Lusitania • Mauretania Tingitana • Tarraconensis
Diocese of Britain: Britannia I • Britannia II • Flavia Caesariensis • Maxima Caesariensis • Valentia (369)Praetorian
Prefecture of ItalyDiocese of Suburbicarian Italy: Apulia et Calabria • Bruttia et Lucania • Campania • Corsica • Picenum Suburbicarium • Samnium • Sardinia • Sicilia • Tuscia et Umbria • Valeria
Diocese of Annonarian Italy: Alpes Cottiae • Flaminia et Picenum Annonarium • Liguria et Aemilia • Raetia I • Raetia II • Venetia et Istria
Diocese of Africa†: Africa proconsularis (Zeugitana) • Byzacena • Mauretania Caesariensis • Mauretania Sitifensis • Numidia Cirtensis • Numidia Militiana • Tripolitania
Diocese of Pannonia (later of Illyricum): Dalmatia • Noricum mediterraneum • Noricum ripense • Pannonia I • Pannonia II • Savia • Valeria ripensisEastern Empire (395–ca. 640)Praetorian
Prefecture of IllyricumPraetorian
Prefecture of the EastDiocese of Thrace: Europa • Haemimontus • Moesia II§ • Rhodope • Scythia§ • Thracia
Diocese of Asia*: Asia • Caria§ • Hellespontus • Insulae§ • Lycaonia (370) • Lycia • Lydia • Pamphylia • Pisidia • Phrygia Pacatiana • Phrygia Salutaria
Diocese of Pontus*: Armenia I* • Armenia II* • Armenia Maior* • Armenian Satrapies* • Armenia III (536) • Armenia IV (536) • Bithynia • Cappadocia I* • Cappadocia II* • Galatia I* • Galatia II Salutaris* • Helenopontus* • Honorias* • Paphlagonia* • Pontus Polemoniacus*
Diocese of the East: Arabia • Cilicia I • Cilicia II • Cyprus§ • Euphratensis • Isauria • Mesopotamia • Osroene • Palaestina I • Palaestina II • Palaestina III Salutaris • Phoenice • Phoenice Libanensis • Syria I • Syria II Salutaris • Theodorias (528)
Diocese of Egypt: Aegyptus I • Aegyptus II • Arcadia • Augustamnica I • Augustamnica II • Libya Superior • Libya Inferior • Thebais Superior • Thebais InferiorOther territories - affected (boundaries modified/abolished/renamed) by Justinian I's administrative reorganization in 534–536 † re-established after reconquest by the Eastern Empire in 534, as the separate prefecture of Africa § joined together into the Quaestura exercitus in 536
Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.