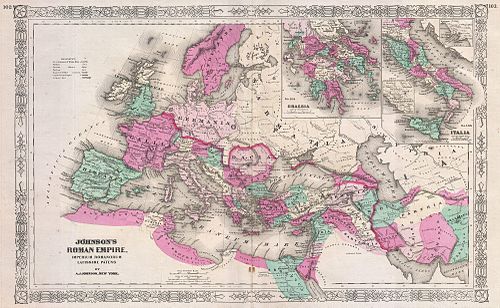
- Mesopotamia (Roman province)
-
Mesopotamia was the name of two distinct Roman provinces, the one a short-lived creation of the Roman Emperor Trajan in 116–117 and the other established by Emperor Septimius Severus in ca. 198, which lasted until the Muslim conquests of the 7th century.
Contents
Trajan's province
In 113, Emperor Trajan (r. 98–117) launched a war against Rome's long-time eastern rival, the Parthian Empire. In 114, he conquered Armenia, which was made into a province, and by the end of 115, he had conquered northern Mesopotamia. This too was organized as a province in early 116, when coins were minted to celebrate the fact.[1]
Later in the same year, Trajan marched into central and southern Mesopotamia (enlarging and completing the province of Mesopotamia) and across the river Tigris to Adiabene, which he annexed into another Roman province, Assyria.[2] But he did not stop there. In the last months of 116, he captured the great Persian city of Susa. He deposed the Parthian king Osroes I and put his own puppet ruler Parthamaspates on the Parthian throne. Never again would the Roman Empire advance so far to the east.
As soon as Trajan died however, his successor Hadrian (r. 117–138) relinquished his conquests east of the Euphrates river, which became again the Roman Empire's eastern boundary.[3][4]
Severus' province
Northern Mesopotamia, including Osroene, came again under Roman control in the expedition of Lucius Verus in 161–166, but were not formally organized into provinces; instead, they were left under local vassal rulers, although Roman garrisons were maintained, notably at Nisibis. This control was threatened in 195, during the civil war between Septimius Severus (r. 193–211) and the usurper Pescennius Niger, when rebellions broke out in the area, and Nisibis was besieged. Severus quickly restored order and organized Osroene as a full province.[5][6] Next Severus embarked on a war against Parthia, which he concluded successfully with the sack of the Parthian capital Ctesiphon. In emulation of Trajan, he re-established a province of Mesopotamia in 198, with Nisibis, elevated to the status of a full colonia, as its capital.[7][8]
Unlike Trajan's province, which encompassed the whole of Roman-occupied Mesopotamia between the Euphrates and Tigris rivers, the new province was limited between the province of Osroene to the south, the Euphrates and Tigris to the north, and the river Chaboras (modern Khabur) to the east.[9] For the remainder of its existence, the new province would remain a bone of contention between the Romans and the Iranian powers, suffering heavily in the recurrent Roman–Persian Wars. In the turmoil that followed the Year of the Six Emperors, in 239–243, Ardashir I (r. 224–241), the founder of the new Sassanid Empire which replaced the moribund Parthians, attacked and overran the area, but it was recovered by Timesitheus before his death in 243.[10] In the 250s, the Persian shah Shapur I (r. ca. 240–270) attacked Mesopotamia, and fought with the Roman emperor Valerian (r. 253–260), whom he captured at Edessa in 260.[11] In the next year however, Shapur was heavily defeated by Odaenathus of Palmyra and driven out of Mesopotamia.[12]
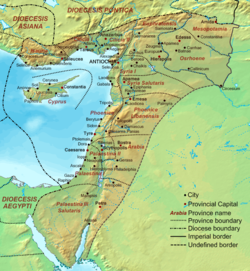 The late Roman Diocese of the East, including the province of Mesopotamia
The late Roman Diocese of the East, including the province of Mesopotamia
Under the reforms of Diocletian (r. 284–305) and Constantine I (r. 306–337), it became part of the Diocese of the East, which in turn was subordinated to the praetorian prefecture of the East. Nisibis and Singara, along with the territory in Adiabene conquered by Diocletian were lost after the debacle of Julian's Persian expedition in 363, and the capital was transferred to Amida, while the seat of the military commander, the dux Mesopotamiae, was located at Constantina. Other cities included Martyropolis and Kephas.[9]
After the troubles Roman forces faced in the Anastasian War of 502–506, the East Roman emperor Anastasius I (r. 591–518) built the fortress of Dara as a counter to Nisibis and as the new base of the dux Mesopotamiae. During the reforms of Justinian I (r. 527–565), the province was split up: the northern districts with Martyropolis went to the new province of Armenia IV, while the remainder was divided into two civil and ecclesiastical districts, one (the region south of the Tigris) with capital at Amida and the other (the region of Tur Abdin) with capital at Dara.[9] The province suffered greatly during the near-constant wars with Persia in the 6th century. In 573, the Persians even took Dara, although the East Romans recovered it under the peace of 591. They lost it again to the Persians in the great war of 602–628, and regained it afterwards only to lose the entire region permanently to the Muslim conquests in 633–640.[9]
References
- ^ Bennett (1997), pp. 196, 198–199
- ^ Bennett (1997), p. 201
- ^ Bennett (1997), pp. 206–207
- ^ Mommsen, Dickson & Purdie (2004), p. 72
- ^ Mommsen, Dickson & Purdie (2004), pp. 77–78
- ^ Southern (2001), p. 33
- ^ Mommsen, Dickson & Purdie (2004), pp. 78–79
- ^ Southern (2001), p. 42
- ^ a b c d Kazhdan (1991), p. 1348
- ^ Southern (2001), p. 70–71
- ^ Mommsen, Dickson & Purdie (2004), p. 100
- ^ Mommsen, Dickson & Purdie (2004), pp. 103–104
Sources
- Bennett, Julian (1997). Trajan: Optimus Princeps. Routledge. ISBN 0-415-165245.
- Kazhdan, Alexander, ed. (1991), Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium, Oxford University Press, ISBN 978-0-19-504652-6
- Mommsen, Theodor; Dickson, William Purdie; Haverfield, Francis (2004). The provinces of the Roman Empire: from Caesar to Diocletian, Vol. II. Gorgias Press LLC. ISBN 978-1593330262. http://books.google.com/books?id=hJwa2cjamJMC.
- Southern, Pat (2001). The Roman Empire from Severus to Constantine. Routledge. ISBN 978-0203451595.
See also
Provinces of the Roman Empire at its greatest extent (117 AD) Achaea · Aegyptus · Africa · Alpes Cottiae · Alpes Maritimae · Alpes Poeninae · Arabia Petraea · Armenia · Asia · Assyria · Bithynia et Pontus · Britannia · Cappadocia · Cilicia · Corsica et Sardinia · Creta et Cyrenaica · Cyprus · Dacia · Dalmatia · Epirus · Galatia · Gallia Aquitania · Gallia Belgica · Gallia Lugdunensis · Gallia Narbonensis · Germania Inferior · Germania Superior · Hispania Baetica · Hispania Tarraconensis · Italia · Iudaea · Lusitania · Lycia et Pamphylia · Macedonia · Mauretania Caesariensis · Mauretania Tingitana · Mesopotamia · Moesia Inferior · Moesia Superior · Noricum · Pannonia Inferior · Pannonia Superior · Raetia · Sicilia · Syria · Thracia
Late Roman Provinces (4th–7th centuries) History Provincial administration reformed and dioceses established by Diocletian, c. 293. Permanent praetorian prefectures established after the death of Constantine I. Empire permanently partitioned after 395. Exarchates of Ravenna and Africa established after 584. After massive territorial losses in the 7th century, the remaining provinces were superseded by the theme system in c. 640–660, although in Asia Minor and parts of Greece they survived under the latter until the early 9th century.Western Empire (395–476)Praetorian
Prefecture of GaulDiocese of Gaul: Alpes Poeninae et Graiae • Belgica I • Belgica II • Germania I • Germania II • Lugdunensis I • Lugdunensis II • Lugdunensis III • Lugdunensis IV • Maxima Sequanorum
Diocese of Vienne (later Septem Provinciae): Alpes Maritimae • Aquitanica I • Aquitanica II • Narbonensis I • Narbonensis II • Novempopulania • Viennensis
Diocese of Spain: Baetica • Balearica • Carthaginensis • Gallaecia • Lusitania • Mauretania Tingitana • Tarraconensis
Diocese of Britain: Britannia I • Britannia II • Flavia Caesariensis • Maxima Caesariensis • Valentia (369)Praetorian
Prefecture of ItalyDiocese of Suburbicarian Italy: Apulia et Calabria • Bruttia et Lucania • Campania • Corsica • Picenum Suburbicarium • Samnium • Sardinia • Sicilia • Tuscia et Umbria • Valeria
Diocese of Annonarian Italy: Alpes Cottiae • Flaminia et Picenum Annonarium • Liguria et Aemilia • Raetia I • Raetia II • Venetia et Istria
Diocese of Africa†: Africa proconsularis (Zeugitana) • Byzacena • Mauretania Caesariensis • Mauretania Sitifensis • Numidia Cirtensis • Numidia Militiana • Tripolitania
Diocese of Pannonia (later of Illyricum): Dalmatia • Noricum mediterraneum • Noricum ripense • Pannonia I • Pannonia II • Savia • Valeria ripensisEastern Empire (395–ca. 640)Praetorian
Prefecture of IllyricumPraetorian
Prefecture of the EastDiocese of Thrace: Europa • Haemimontus • Moesia II§ • Rhodope • Scythia§ • Thracia
Diocese of Asia*: Asia • Caria§ • Hellespontus • Insulae§ • Lycaonia (370) • Lycia • Lydia • Pamphylia • Pisidia • Phrygia Pacatiana • Phrygia Salutaria
Diocese of Pontus*: Armenia I* • Armenia II* • Armenia Maior* • Armenian Satrapies* • Armenia III (536) • Armenia IV (536) • Bithynia • Cappadocia I* • Cappadocia II* • Galatia I* • Galatia II Salutaris* • Helenopontus* • Honorias* • Paphlagonia* • Pontus Polemoniacus*
Diocese of the East: Arabia • Cilicia I • Cilicia II • Cyprus§ • Euphratensis • Isauria • Mesopotamia • Osroene • Palaestina I • Palaestina II • Palaestina III Salutaris • Phoenice • Phoenice Libanensis • Syria I • Syria II Salutaris • Theodorias (528)
Diocese of Egypt: Aegyptus I • Aegyptus II • Arcadia • Augustamnica I • Augustamnica II • Libya Superior • Libya Inferior • Thebais Superior • Thebais InferiorOther territories - affected (boundaries modified/abolished/renamed) by Justinian I's administrative reorganization in 534–536 † re-established after reconquest by the Eastern Empire in 534, as the separate prefecture of Africa § joined together into the Quaestura exercitus in 536
Categories:- Mesopotamia
- Fertile Crescent
- States and territories established in 116
- Provinces of the Byzantine Empire
- Provinces of the Roman Empire
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.