- Gallia Narbonensis
-
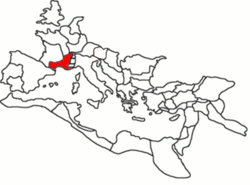
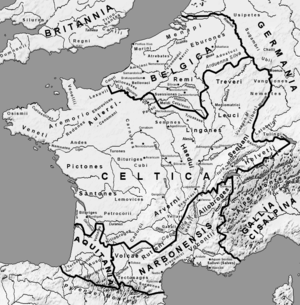
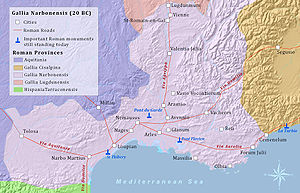
Provincia Gallia Narbonensis Province of the Roman Empire 123 BCE–5th century The province of Gallia Narbonensis within the Roman Empire, ca. 117 CE Capital Massalia Historical era Antiquity - Established 123 BCE - Visigothic Kingdom 5th century Gallia Narbonensis (English: Narbonese Gaul, from the chief settlement of Narbonne) was a Roman province located in what is now Languedoc and Provence, in southern France. It was also known as Gallia Transalpina (Transalpine Gaul), which was originally a designation for that part of Gaul lying across the Alps from Italia and it contained a western region known as Septimania (see Septimania timeline). It became a Roman province in the late 2nd century BCE, constituting the first significant Roman territory outside of Italy. Its boundaries were roughly defined by the Mediterranean Sea to the south and the Cévennes and Alps and north and west.
Contents
Names
The province of Gallia Transalpina (Transalpine Gaul) was later renamed Gallia Narbonensis, after its capital the Roman colony of Narbo Martius (Narbonne), founded on the coast in 118 BCE. The Romans called it Provincia Nostra ("our province") or simply Provincia ("the province"), being the first significant permanent conquest outside the Italian peninsula. The name has survived in the modern French name of the region, Provence, now a région of France.
Founding
By the mid-2nd century BCE, Rome was trading heavily with the Greek colony of Massalia (modern Marseille) on the southern coast of Gaul. Massalia, founded by colonists from Phocaea, was by this point centuries old and quite prosperous. Rome entered into an alliance with Massalia, by which it agreed to protect the town from local Gauls and other threats, in exchange for a small strip of land that it wanted in order to build a road from Italy to Spain, to assist in troop transport. The Massalians, for their part, cared more for their economic prosperity than they did their territorial integrity. In this strip of land, the Romans founded the town of Narbonne, which turned out to be a major trading competitor with Massalia. It was from this that what was then the province of Transalpine Gaul was founded.
During this period, the Mediterranean settlements on the coast were threatened by the powerful Gallic tribes to the north, especially the tribes known as the Arverni and the Allobroges. In 123 BCE, the Roman general Quintus Fabius Maximus Allobrogicus campaigned in the area and defeated the Allobroges and the Arverni under king Bituitus. This defeat substantially weakened the Arverni and ensured the further security of Gallia Narbonensis.
Later history
Bordering directly on Italy, control of the province gave the Roman state several advantages, such as control of the land route between Italy and the Iberian peninsula; a buffer against attacks on Italy by tribes from Gaul; and control of the lucrative trade routes of the Rhone valley, over which commercial goods flowed between Gaul and the trading center of Massalia. It was from the capital of Narbonne that Julius Caesar began his Gallic Wars.
The area became a Roman province in 121 BCE, originally under the name of Gallia Transalpina (Transalpine Gaul). This name was chosen to distinguish it from Cisalpine Gaul, the part of Gaul on the near side of the Alps to Rome. At one point, Narbonese Gaul and Transalpine Gaul were governed as separate territories - when the Second Triumvirate was formed, Lepidus was given responsibility for Narbonese Gaul and Spain, while Mark Antony was given Cisalpine and Transalpine Gaul.[1]
References
- ^ Boatwright et al., The Romans, From Village to Empire, p.272 ISBN 9780195118766
Further reading
- Badian, E. “Notes on Provincia Gallia in the Late Republic.” In Mélanges d'archéologie et d'histoire offerts à André Piganiol, vol. 2. Edited by Raymond Chevallier. Paris: S.E.V.P.E.N., 1966.
- Dietler, Michael. Archaeologies of Colonialism: Consumption, Entanglement, and Violence in Ancient Mediterranean France. Berkeley: University of California Press, 2010.
- Drinkwater, J.F. Roman Gaul: The Three Provinces, 58 B.C.–A.D. 260. Cornell University Press, 1983.
- Ebel, Charles. Transalpine Gaul: The Emergence of a Roman Province. Leiden: E.J. Brill, 1976. Limited preview online.
- Ebel, Charles. “Southern Gaul in the Triumviral Period: A Critical Stage of Romanization.” American Journal of Philology 109 (1988) 572–590.
- Fevrier, Paul-Albert. “The Origin and Growth of the Cities of Southern Gaul to the Third Century A.D.: An Assessment of the Most Recent Archaeological Discoveries.” Journal of Roman Studies 63 (1973) 1–28.
- Rivet, A.L.F. Gallia Narbonensis: Southern France in Roman Times. London: B.T. Batsford Ltd., 1988.
- Woolf, Greg. Becoming Roman: The Origins of Provincial Civilization in Gaul. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1998. Limited preview online.
Provinces of the Roman Empire at its greatest extent (117 AD) Achaea · Aegyptus · Africa · Alpes Cottiae · Alpes Maritimae · Alpes Poeninae · Arabia Petraea · Armenia · Asia · Assyria · Bithynia et Pontus · Britannia · Cappadocia · Cilicia · Corsica et Sardinia · Creta et Cyrenaica · Cyprus · Dacia · Dalmatia · Epirus · Galatia · Gallia Aquitania · Gallia Belgica · Gallia Lugdunensis · Gallia Narbonensis · Germania Inferior · Germania Superior · Hispania Baetica · Hispania Tarraconensis · Italia · Iudaea · Lusitania · Lycia et Pamphylia · Macedonia · Mauretania Caesariensis · Mauretania Tingitana · Mesopotamia · Moesia Inferior · Moesia Superior · Noricum · Pannonia Inferior · Pannonia Superior · Raetia · Sicilia · Syria · Thracia
Late Roman Provinces (4th–7th centuries) History Provincial administration reformed and dioceses established by Diocletian, c. 293. Permanent praetorian prefectures established after the death of Constantine I. Empire permanently partitioned after 395. Exarchates of Ravenna and Africa established after 584. After massive territorial losses in the 7th century, the remaining provinces were superseded by the theme system in c. 640–660, although in Asia Minor and parts of Greece they survived under the latter until the early 9th century.Praetorian
Prefecture of GaulDiocese of Gaul: Alpes Poeninae et Graiae • Belgica I • Belgica II • Germania I • Germania II • Lugdunensis I • Lugdunensis II • Lugdunensis III • Lugdunensis IV • Maxima Sequanorum
Diocese of Vienne (later Septem Provinciae): Alpes Maritimae • Aquitanica I • Aquitanica II • Narbonensis I • Narbonensis II • Novempopulania • Viennensis
Diocese of Spain: Baetica • Balearica • Carthaginensis • Gallaecia • Lusitania • Mauretania Tingitana • Tarraconensis
Diocese of Britain: Britannia I • Britannia II • Flavia Caesariensis • Maxima Caesariensis • Valentia (369)Praetorian
Prefecture of ItalyDiocese of Suburbicarian Italy: Apulia et Calabria • Bruttia et Lucania • Campania • Corsica • Picenum Suburbicarium • Samnium • Sardinia • Sicilia • Tuscia et Umbria • Valeria
Diocese of Annonarian Italy: Alpes Cottiae • Flaminia et Picenum Annonarium • Liguria et Aemilia • Raetia I • Raetia II • Venetia et Istria
Diocese of Africa†: Africa proconsularis (Zeugitana) • Byzacena • Mauretania Caesariensis • Mauretania Sitifensis • Numidia Cirtensis • Numidia Militiana • Tripolitania
Diocese of Pannonia (later of Illyricum): Dalmatia • Noricum mediterraneum • Noricum ripense • Pannonia I • Pannonia II • Savia • Valeria ripensisPraetorian
Prefecture of IllyricumPraetorian
Prefecture of the EastDiocese of Thrace: Europa • Haemimontus • Moesia II§ • Rhodope • Scythia§ • Thracia
Diocese of Asia*: Asia • Caria§ • Hellespontus • Insulae§ • Lycaonia (370) • Lycia • Lydia • Pamphylia • Pisidia • Phrygia Pacatiana • Phrygia Salutaria
Diocese of Pontus*: Armenia I* • Armenia II* • Armenia Maior* • Armenian Satrapies* • Armenia III (536) • Armenia IV (536) • Bithynia • Cappadocia I* • Cappadocia II* • Galatia I* • Galatia II Salutaris* • Helenopontus* • Honorias* • Paphlagonia* • Pontus Polemoniacus*
Diocese of the East: Arabia • Cilicia I • Cilicia II • Cyprus§ • Euphratensis • Isauria • Mesopotamia • Osroene • Palaestina I • Palaestina II • Palaestina III Salutaris • Phoenice • Phoenice Libanensis • Syria I • Syria II Salutaris • Theodorias (528)
Diocese of Egypt: Aegyptus I • Aegyptus II • Arcadia • Augustamnica I • Augustamnica II • Libya Superior • Libya Inferior • Thebais Superior • Thebais InferiorOther territories - affected (boundaries modified/abolished/renamed) by Justinian I's administrative reorganization in 534–536 † re-established after reconquest by the Eastern Empire in 534, as the separate prefecture of Africa § joined together into the Quaestura exercitus in 536
Categories:- Ancient Roman provinces
- Narbonne
- Provinces of Roman Gaul
- States and territories established in 121 BC
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.