- Palatine bone
-
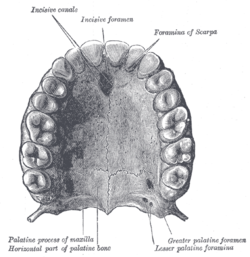
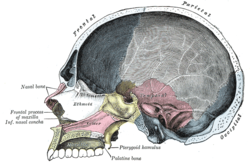
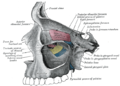
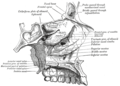
Bone: Palatine bone Permanent teeth of upper dental arch, seen from below. (Horizontal part of palatine bone visible at bottom.) Sagittal section of skull. (Palatine bone is labeled at bottom left.) Gray's subject #41 166 MeSH Palatine+Bone The palatine bone is a bone in many species of the animal kingdom, commonly termed the palatum (Latin palatum; unrelated to palatium 'palace', from which other senses of palatine derive).
Contents
Human anatomy
It is situated at the back part of the nasal cavity between the maxilla and the pterygoid process of the sphenoid.
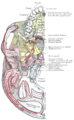
It contributes to the walls of three cavities: the floor and lateral wall of the nasal cavity, the roof of the mouth, and the floor of the orbit; it enters into the formation of two fossæ, the pterygopalatine and pterygoid fossæ; and one fissure, the inferior orbital fissure.
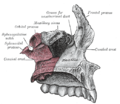
The palatine bone somewhat resembles the letter L, and consists of a Horizontal plate of palatine bone and a Perpendicular plate of palatine bone and three outstanding processes—viz., the Pyramidal process of palatine bone, which is directed backward and lateralward from the junction of the two parts, and the Orbital process of palatine bone and Sphenoidal process of palatine bone, which surmount the vertical part, and are separated by a deep notch, the sphenopalatine notch.
The human palatine articulates with six bones: the sphenoid, ethmoid, maxilla, inferior nasal concha, vomer and opposite palatine.
In other animals
In bony fish the palatine bone consists of the perpendicular plate only, lying on the inner edge of the maxilla. The lower surface of the bone may bear several teeth, forming a second row behind those of the maxilla; in many cases, these are actually larger than the maxillary teeth. Although a similar pattern was present in primitive tetrapods, the palatine bone is reduced in most living amphibians, forming, in frogs and salamanders, only a narrow bar between the vomer and maxilla.[1]
Early fossil reptiles retained the arrangement seen in more primitive vertebrates, but in mammals, the lower surface of the palatine became folded over during evolution, forming the horizontal plate, and meeting in the midline of the mouth. This forms the rear of the hard palate, separating the oral and nasal cavities, and making it easier to breathe while eating. A parallel development has occurred to varying degrees in many living reptiles, reaching its greatest extent in crocodilians. In birds, the palatine bones remain separate, long the sides of the rear part of the upper jaw, and typically have a mobile articulation with the cranium.[1]
There are numerous variations amongst mammals, amphibians and other species. For example, the palatine bone in many amphibians such as the Rough-skinned Newt manifests as a distinct V-shaped structure.[2] In the case of cat species, the horizontal and a vertical elements join at a forty five degree angle.[3]
References
- ^ a b Romer, Alfred Sherwood; Parsons, Thomas S. (1977). The Vertebrate Body. Philadelphia, PA: Holt-Saunders International. pp. 220–243. ISBN 0-03-910284-X.
- ^ C. Michael Hogan (2008) Rough-skinned Newt (Taricha granulosa), Globaltwitcher, ed. N. Stromberg [1]
- ^ Jacob Reighard and Herbert Spencer Jennings, Anatomy of the Cat
Additional images
See also
- Bone terminology
- Terms for anatomical location
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
The Bones which form the Orbit Frontal bone • Zygomatic bone • Maxillary bone • Sphenoid bone • Ethmoid bone • Palatine bone • Lacrimal bone
Bones of head and neck: the facial skeleton of the skull (TA A02.1.08–15, GA 2.156–177) Maxilla SurfacesProcessesOtherZygomatic Palatine FossaePlatesProcessesMandible external surface (Symphysis menti, Lingual foramen, Mental protuberance, Mental foramen, Mandibular incisive canal) · internal surface (Mental spine, Mylohyoid line, Sublingual fovea, Submandibular fovea) · Alveolar part of mandibleMinor/
noseNasal bone: Internasal suture · Nasal foramina
Inferior nasal concha: Ethmoidal process · Maxillary process
Vomer: Vomer anterior · Synostosis vomerina · Vomer posterior (Wing)
Lacrimal: Posterior lacrimal crest · Lacrimal groove · Lacrimal hamulusCategories:- Bones of the head and neck
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.