- Mandibular notch
-
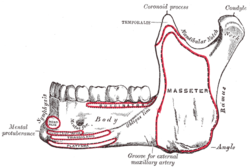
Bone: Mandibular notch Mandible. Outer surface. Side view. (Mandibular notch visible at upper right.) Latin incisura mandibulae Gray's subject #44 174 The upper border of the ramus of mandible is thin, and is surmounted by two processes, the coronoid process anteriorly and the condyloid process posteriorly, separated by a deep concavity, the mandibular notch. It allows the passage of the masseteric nerve (a branch of the mandibular nerve (V3) division of the trigeminal nerve), masseteric artery and masseteric vein.
External links
- Anatomy at PSU skel/mandible2
- Diagram at unc.edu
- Mandibular+notch at eMedicine Dictionary
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
Bones of head and neck: the facial skeleton of the skull (TA A02.1.08–15, GA 2.156–177) Maxilla SurfacesProcessesOtherZygomatic Palatine FossaePlatesProcessesMandible external surface (Symphysis menti, Lingual foramen, Mental protuberance, Mental foramen, Mandibular incisive canal) · internal surface (Mental spine, Mylohyoid line, Sublingual fovea, Submandibular fovea) · Alveolar part of mandibleMylohyoid groove (Mandibular canal, Lingula) · Mandibular foramen · Angle
Coronoid process · Mandibular notch · Condyloid process · Pterygoid foveaMinor/
noseNasal bone: Internasal suture · Nasal foramina
Inferior nasal concha: Ethmoidal process · Maxillary process
Vomer: Vomer anterior · Synostosis vomerina · Vomer posterior (Wing)
Lacrimal: Posterior lacrimal crest · Lacrimal groove · Lacrimal hamulusCategories:- Bones of the head and neck
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.