- Tifinagh
-
Tifinagh (pronounced [tifinaɣ], written ⵜⵉⴼⵉⵏⴰⵖ in Neo-Tifinagh, تيفيناغ in the Berber Arabic alphabet and Tifinagh in the Berber Latin alphabet) is a series of abjad and alphabetic scripts used by some Berber peoples, notably the Tuareg, to write their language.[1]
A modern derivate of the traditional script, known as Neo-Tifinagh, was introduced in the 20th century. It is not in widespread use as a means of daily communication, but often serves to assert a Berber identity politically and symbolically. A slightly modified version of the traditional script, called Tifinagh Ircam, is used in a limited number of Moroccan elementary schools in teaching the Berber language to children.
The word tifinagh or tifinigh is widely thought to be a feminine plural cognate of Punic, through the feminine prefix ti- and Latin Punicus; thus tifinigh would mean "the Phoenician (letters)".[2][3]
Contents
Origins
The origin of the script is known as "Proto-Tifinagh", or as Libyco-Berber script. It was in use between about the 3rd century BC and the 3rd century AD.
Proto-Tifinagh Type Abjad Time period 3rd century BC to the 3rd century AD Parent systems Child systems Tifinagh, Neo-Tifinagh Note: This page may contain IPA phonetic symbols. There are two known variants: eastern and western. The eastern variant was used in what is now Constantine, the Aures region and Tunisia. It is the best-deciphered variant, due to the discovery of several Numidian bilingual inscriptions in Libyan and Punic (notably at Dougga in Tunisia.) 22 letters out of the 24 were deciphered. The western variant was more primitive (Février 1964–1965). It was used along the Mediterranean coast from Kabylia to the Canary Islands. It used 13 supplementary letters.
The Libyco-Berber script was a pure Abjad; it had no vowels. Gemination was not marked. The writing was usually from the bottom to the top, although right-to-left, and even other orders, were also found.
Tuareg Tifinagh
Tifinagh (Tuareg) Type Abjad Languages Tuareg language Time period ?? to present Parent systems Child systems Neo-Tifinagh Note: This page may contain IPA phonetic symbols. The Proto-Tifinagh script survived as a traditional means of writing the Tuareg language. Traditionally, the script marks no vowels, except for word finals. In some areas, Arabic vowel diacritics are combined with Tifinagh characters to mark vowels.
Occasionally the script has been used to write other neighboring languages, such as Tagdal Songhai.
Neo-Tifinagh
Neo-Tifinagh Type Alphabet Time period 1980 to present Parent systems ISO 15924 Tfng, 120 Direction Left-to-right Unicode alias Tifinagh Unicode range U+2D30–U+2D7F Note: This page may contain IPA phonetic symbols. Neo-Tifinagh is the 20th-century script developed from earlier forms of Tifinagh. It is an alphabet and is written left-to-right. Salem Chaker, professor at INALCO had proposed a change in Neo-Tifinagh (Tafsut 1990 #14).
Until recently, virtually no books or websites were published in this alphabet, with activists favouring Latin (or, more rarely, Arabic) scripts for serious usage; however, it is extremely popular for symbolic use, with many books and websites written in a different script featuring logos or title pages using Neo-Tifinagh. In Morocco, the king took a "neutral" position between the claims of Latin script and Arabic script by adopting the Neo-Tifinagh script in 2003; as a result, books are beginning to be published in this script, and it is taught in some schools. However, many independent Berber-language publications are still published using the Berber Latin alphabet. Outside Morocco, it has no official status. Ironically, the Moroccan state arrested and imprisoned people using this script during the 1980s and 1990s.[4]
In Algeria, almost all Berber publications use the Berber Latin alphabet, not Tifinagh.
In Libya, the regime of Gaddafi used to consistently ban the Berber Tifinagh script from being used in public contexts such as store displays and banners.[5]
After recent uprisings in Libya, the National Transitional Council (rebels) has shown an openness towards the Berber language. The independent rebel Libya TV, based in Qatar, has included the Berber language and the Tifinagh alphabet in some of its programming.[6]
Characters
Digraph letters (ligatures are possible) Code Glyph Unicode Transliteration Name Latin Arabic IPA U+2D5C U+2D59 

ⵜⵙ ts تس t͡s yats U+2D37 U+2D63 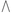
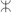
ⴷⵣ dz دز d͡z yadz Code Glyph Unicode Transliteration Name Latin Arabic IPA U+2D5C U+2D5B 
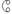
ⵜⵛ ch (tš) تش t͡ʃ yatš U+2D37 U+2D4A 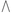
ⴷⵊ dj دج d͡ʒ yadj Color Key Basic Tifinagh (IRCAM) Extended Tifinagh (IRCAM) Other Tifinagh letters Modern Tuareg letters Unicode
Tifinagh was added to the Unicode Standard in March, 2005 with the release of version 4.1.
The Unicode block for Tifinagh is U+2D30–U+2D7F. Grey areas indicate non-assigned code points:
Tifinagh[1]
Unicode.org chart (PDF)0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 A B C D E F U+2D3x ⴰ ⴱ ⴲ ⴳ ⴴ ⴵ ⴶ ⴷ ⴸ ⴹ ⴺ ⴻ ⴼ ⴽ ⴾ ⴿ U+2D4x ⵀ ⵁ ⵂ ⵃ ⵄ ⵅ ⵆ ⵇ ⵈ ⵉ ⵊ ⵋ ⵌ ⵍ ⵎ ⵏ U+2D5x ⵐ ⵑ ⵒ ⵓ ⵔ ⵕ ⵖ ⵗ ⵘ ⵙ ⵚ ⵛ ⵜ ⵝ ⵞ ⵟ U+2D6x ⵠ ⵡ ⵢ ⵣ ⵤ ⵥ ⵯ U+2D7x ⵰ ⵿ Notes - 1.^ As of Unicode version 6.0
References
- ^ To a limited extent: See Interview met Karl-G. Prasse and Penchoen (1973:3)
- ^ Penchoen (1973:3)
- ^ O'Connor (2006:115)
- ^ (French)Rapport sur le calvaire de l’écriture en Tifinagh au Maroc
- ^ (Arabic)[1]
- ^ Libya TV – News in Berber http://blip.tv/play/AYK4hyEC
Bibliography
- Aghali-Zakara, Mohamed (1994). Graphèmes berbères et dilemme de diffusion: Interaction des alphabets latin, ajami et tifinagh. Etudes et Documents Berbères 11, 107-121.
- Aghali-Zakara, Mohamed; and Drouin, Jeanine (1977). Recherches sur les Tifinaghs- Eléments graphiques et sociolinguistiques. Comptes-rendus du Groupe Linguistique des Etudes Chamito-Sémitiques (GLECS).
- Ameur, Meftaha (1994). Diversité des transcriptions : pour une notation usuelle et normalisée de la langue berbère. Etudes et Documents Berbères 11, 25-28.
- Boukous, Ahmed (1997). Situation sociolinguistique de l’Amazigh. International Journal of the Sociology of Language 123, 41-60.
- Chaker, Salem (1994). Pour une notation usuelle à base Tifinagh. Etudes et Documents Berbères 11, 31-42.
- Chaker, Salem (1996). Propositions pour la notation usuelle à base latine du berbère. Etudes et Documents Berbères 14, 239-253.
- Chaker, Salem (1997). La Kabylie: un processus de développement linguistique autonome. International Journal of the Sociology of Language 123, 81-99.
- Durand, O. (1994). Promotion du berbère : problèmes de standardisation et d’orthographe. Expériences européennes. Etudes et Documents Berbères 11, 7-11.
- O’Connor, Michael (1996). The Berber scripts. The World’s Writing Systems, ed. by William Bright and Peter Daniels, 112-116. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Penchoen, Thomas G. (1973). Tamazight of the Ayt Ndhir. Los Angeles: Undena Publications.
- Savage, Andrew. 2008. Writing Tuareg – the three script options. International Journal of the Sociology of Language 192: 5-14
- Souag, Lameen (2004). "Writing Berber Languages: a quick summary". L. Souag. Archived from the original on 2005-07-30. http://web.archive.org/web/20050730075554/http://www.geocities.com/lameens/tifinagh/. Retrieved 6 July 2010.
- Encyclopaedia of Islam, s.v. Tifinagh.
External links
- http://lbi-project.org/lbi-db.php an excellent compilation of images and information
- http://www.ancientscripts.com/berber.html
- http://ennedi.free.fr/tifin.htm
- Ircam Official website of the Royal Institute of the Amazigh Culture (in French)
- http://www.mondeberbere.com/langue/tifinagh/tifinagh_origine.htm
- http://www.omniglot.com/writing/tifinagh.htm
- Unicode character picker for Moroccan Tifinagh
- Tifinagh Font for Windows
- http://www.ircam.ma/amzfr.htm
Berber languages · ⵜⴰⵎⴰⵣⵉⵖⵜ Languages ReconstructedProto-Berber†GuancheTachelhit · Judeo-Berber · Central Atlas Tamazight · Kabyle · Senhaja de Srair · Zenaga · Zenati · Tarifit · South Oran and Figuig Shilha · Shawia · Tumzabt · Teggargrent · Temacine · Taznatit · Chenoui · Ghomara · Seghroucheni · Djerbi · Sened† · Matmata†
Orthography Academic Types of writing systems Overview Lists Types Abjads Numerals
Aramaic · Arabic · Pitman shorthand · Hebrew · Jawi · Nabataean · Pahlavi · Pegon · Phoenician · Proto-Canaanite · Psalter · Samaritan · South Arabian · Sogdian · Syriac · Tifinagh · UgariticAbugidas Brahmic Ahom · Balinese · Batak · Baybayin · Brāhmī · Buhid · Burmese · Chakma · Cham · Devanāgarī · Dhives Akuru · Eastern Nagari · Grantha · Gujarati · Gupta · Gurmukhī · Hanunó'o · Javanese · Kadamba · Kaithi · Kalinga · Kannada · Khmer · Lanna · Lao · Lepcha · Limbu · Lontara · Malayalam · Meitei Mayek · Mithilakshar · Modi · Mon · Nāgarī · Nepali · Old Kawi · Oriya · Pallava · 'Phags-pa · Ranjana · Rejang · Rencong · Śāradā · Saurashtra · Sinhala · Siddhaṃ · Soyombo · Sundanese · Sylheti Nagari · Tagbanwa · Tai Dam · Tai Le · Takri · Tamil · Telugu · Thai · Tibetan · Tocharian · Varang KshitiOthers Boyd's syllabic shorthand · Canadian Aboriginal · Ge'ez · Japanese braille · Kharoṣṭhī · Meroitic · Pollard · Sorang Sompeng · Tāna · Thomas Natural ShorthandAlphabets Linear Armenian · Avestan · Beitha Kukju · Borama · Coptic · Cyrillic · Deseret · Duployan shorthand · Eclectic shorthand · Elbasan · Fraser · Gabelsberger shorthand · Georgian · Glagolitic · Gothic · Gregg shorthand · Greek · Greco-Iberian alphabet · Hangul · International Phonetic · Kaddare · Latin · Manchu · Mandaic · Mongolian · Neo-Tifinagh · N'Ko · Ogham · Ol Chiki · Old Hungarian · Old Italic · Old Permic · Orkhon · Osmanya · Runic · Shavian alphabet · New Tai Lue · Bassa Vah · Visible SpeechNon-linear Braille (Hebrew · Korean) · Maritime flags · Morse code · New York Point · Semaphore line · Flag semaphore · Moon typeIdeo/Pictograms Aztec · Blissymbol · DanceWriting · Dongba · Míkmaq · New Epoch Notation Painting · Nsibidi · SignWritingLogograms Chinese Chinese-based Other logo-syllabic Logo-consonantal Numerals Semi-syllabaries Full Redundant Syllabaries Categories:- Arabic-derived alphabets
- Alphabetic writing systems
- Tuareg
- Writing systems of Africa
- Berberism
- 1.^ As of Unicode version 6.0
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

