- Chakma alphabet
-
- See also Chakma people and Chakma language.
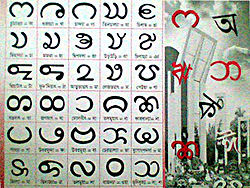
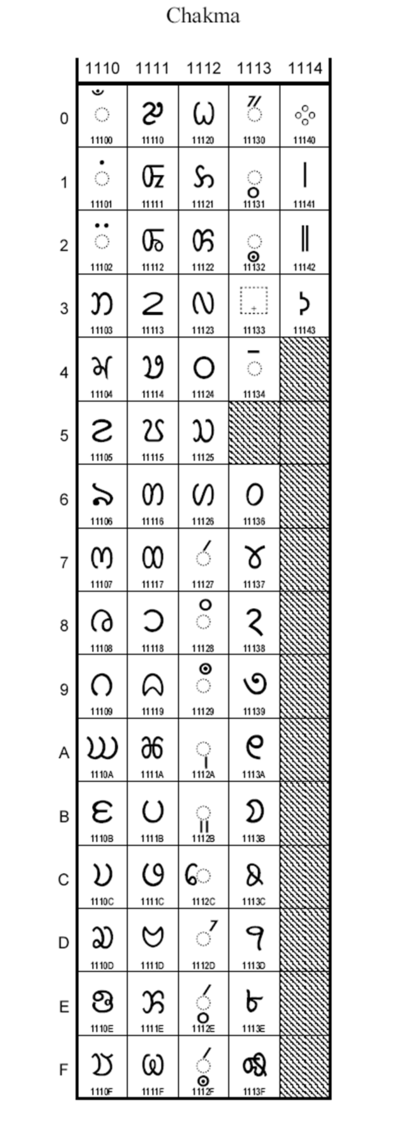
Chakma Type Abugida Languages Chakma language Parent systems Proto-Sinaitic alphabetISO 15924 Cakm, 349 Unicode range (v. 6.1.0 beta) U+11100..U+1114F[1] Note: This page may contain IPA phonetic symbols. The Chakma alphabet (Ajhā pāṭh), also called Ojhapath, Ojhopath, Aaojhapath, is an abugida used for the Chakma language and which is being adapted for the Tanchangya language.[2] The forms of the letters are quite similar to those of the Burmese script.
A proposal for encoding it is currently accepted, and included in the beta release of The Unicode Standard, version 6.1.0.[2] [1]
Contents
Structure
Chakma is of the Brahmic type: the consonant letters contain an inherent vowel. Consonant clusters are written with conjunct characters, and a visible vowel killer shows the deletion of the inherent vowel when there is no conjunct.
Vowels
Four independent vowels exist: a, i, u, and e. Other vowels in initial position are formed by adding the vowel sign to a, as in ī, ū, ai, oi. Some modern writers are generalizing this spelling in i, u, and e
Chakma vowel signs with the letter ka are given below

One of the interesting features of Chakma writing is that CANDRABINDU (cānaphudā) can be used together with ANUSVARA (ekaphudā) and VISARGA (dviphudā):

Consonants with killed Vowels and Conjunct Consonants
Like other Brahmic scripts, Chakma makes use of the MAAYYAA (killer) to invoke conjoined consonants. In the past, practice was much more common than it is today. Like the Myanmar script, Chakma is encoded with two vowel-killing characters in order to conform to modern user expectations. As shown above, most letters have their vowels killed with the use of the explicit Maayyaa

In 2001 an orthographic reform was recommended in the book Cāṅmā pattham pāt which would limit the standard repertoire of conjuncts to those composed with the five letters yā, rā, lā, wā, and nā. The four here are the most widely-accepted repertoire of conjuncts.

No separate conjunct forms of subjoined full-form -yā or -rā appear to exist. The fifth of these conjuncts, the -na conjunct, is exemplary of the orthographic shift which has taken place in Chakma language.

While some writers would indeed write kakna (in ligating style) as or (in subjoining style) as , most now would probably expect it to be written as . The ligating style of glyphs is now considered old-fashioned. Thus, taking the letter mā as the second element, while the glyph shapes kmā, tmā, nmā, bbā, mmā, llā, smā, and hmā are attested, most users now prefer the glyph shapes kmā, tmā, nmā, bbā, mmā, llā, smā, and hmā. Again, this distinction is stylistic and not orthographic
The 2004 book Phadagaṅ shows examples of the five conjuncts above together alongside conjuncts formed with bā, mā, and hā. These are all formed by simple subjoining.

In the 1982 book Cāṅmār āg pudhi a much wider range of conjunct pairs is shown, some of them with fairly complicated glyphs
Collating order
As an Indo-European language, the standard Brahmic sorting order applies to Chakma language
Letter,Punctuation and Digit names
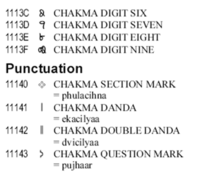
Chakma letters have a descriptive name followed by a traditional Brahmic consonant. These are given in annotations to the character names. Alongside a single and double danda punctuation, Chakma has a unique question mark, and a section sign, Phulacihna. There is some variation in the glyphs for the Phulacihna,some looking like flowers or leaves.A set of digits exists although Bengali digits are also used.
Linebreaking
Letters and digits behave as in Bengali.
Chakma Letters & Digits
References
- ^ a b "BETA Unicode 6.1.0". The Unicode Standard. Unicode, Inc.. http://www.unicode.org/versions/beta-6.1.0.html. Retrieved 2011-09-19.
- ^ a b Everson, Michael; Hosken, Martin (August 13, 2009). "Proposal for encoding the Chakma script in the UCS". The Unicode Consortium. http://std.dkuug.dk/JTC1/SC2/WG2/docs/n3645.pdf.
Bibliography
- Cāṅmā, Cirajyoti and Maṅgal Cāṅgmā. 1982. Cāṅmār āg pudhi (Chakma primer). Rāṅamāṭi:Cāṅmābhāṣā Prakāśanā Pariṣad.
- Khisa, Bhagadatta. 2001. Cāṅmā pattham pāt (Chakma primer.) Rāṅamāṭi: Tribal Cultural Institute(TCI).
- Singā. 2004. Phagadāṅ
Categories:- Brahmic scripts
- Alphabetic writing systems
- Unicode proposals
- Writing system stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.