- Nabataean alphabet
-
Nabataean Type Abjad Languages Nabataean language Time period 2nd century BC to 4th century AD Parent systems Proto-Sinaitic alphabetChild systems Arabic alphabet ISO 15924 Nbat, 159 Note: This page may contain IPA phonetic symbols. History of the alphabet Proto-Sinaitic script? 19 c. BCE
- Ugaritic 15 c. BCE
- Proto-Canaanite 14 c. BCE
- Phoenician 12 c. BCE
- Greek 8 c. BCE
- Aramaic 8 c. BCE
- Kharoṣṭhī 6 c. BCE
- Brāhmī & Indic 6 c. BCE
- Hebrew 3 c. BCE
- Thaana 4 c. BCE
- Pahlavi 3 c. BCE
- Avestan 4 c. CE
- Palmyrene 2 c. BCE
- Syriac 2 c. BCE
- Sogdian 2 c. BCE
- Orkhon (Old Turkic) 6 c. CE
- Old Hungarian c. 650
- Old Uyghur
- Mongolian 1204
- Orkhon (Old Turkic) 6 c. CE
- Nabataean 2 c. BCE
- Arabic 4 c. CE
- Sogdian 2 c. BCE
- Mandaic 2 c. CE
- Paleohispanic 7 c. BCE
- Paleo-Hebrew 10 c. BCE
- Samaritan 6 c. BCE
- Phoenician 12 c. BCE
- Epigraphic South Arabian 9 c. BCE
- Ge’ez 5–6 c. BCE
Meroitic 3 c. BCEOgham 4 c. CEHangul 1443Zhuyin (Bopomofo) 1913The Nabataean alphabet is a consonantal alphabet (abjad) that was used by the Nabataeans in the 2nd century BC. Important inscriptions are found in Petra. The alphabet is descended from the Aramaic alphabet via the Syriac alphabet. A cursive form of it in turn developed into the Arabic alphabet from the 4th century, which is why its letterforms are intermediate between the more northerly Semitic scripts (such as the Hebrew) and Arabic.
Nabatean Name Arabic
AlphabetSyriac
Alphabet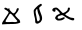
Alaph ا/ء ܐ 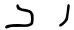
Beth ب ܒ 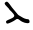
Gamal ج ܓ 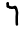
Dalath ﺩ ܕ 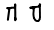
Heh ه ܗ 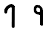
Waw ﻭ ܘ 
Zain ﺯ ܙ 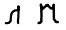
Heth ح ܚ 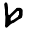
Teth ﻁ ܛ 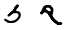
Yodh ي ܝ 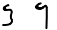
Kaph ﻛ/ك ܟܟ 
Lamadh ل ܠ 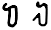
Meem مم ܡܡ 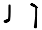
Noon ن ܢܢ 
Simkath س ܣ 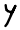
'E ع ܥ 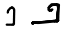
Peh ف ܦ 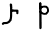
Sad'e ص ܨ 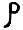
Qoph ﻕ ܩ 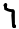
Resh ﺭ ܪ 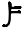
Sheen س، ش ܫ 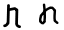
Taw ﺕ ܬ See also
The Northwest Semitic abjad ʾ b g d h w z ḥ ṭ y k l m n s ʿ p ṣ q r š t 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 200 300 400 history • Phoenician • Aramaic • Hebrew • Syriac • Arabic References
Categories:- Nabataean alphabet
- Nabataea
- Abjad writing systems
- Writing system stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
