- Nalgonda district
-
This article is about the district. For its eponymous headquarters, see Nalgonda.
Nalgonda district — district — Coordinates 17°06′N 79°18′E / 17.1°N 79.3°ECoordinates: 17°06′N 79°18′E / 17.1°N 79.3°E Country India State Andhra Pradesh Time zone IST (UTC+05:30) Area
• Coastline
• 0 kilometres (0 mi)
Nalgonda / Nallagonda District (Telugu: నల్లగొండ) is a district in Andhra Pradesh. It has a population of 3,247,982 of which 13.32% is urban as of 2001.[1]
Contents
Etymology
Its name is derived from two Telugu words Nalla (Black) & Konda (Hills) i.e. Black Hills.[2]
History
Nalgonda was earlier referred to as Neelagiri, the name given by some Rajput rulers and the name was changed to Nallagonda only after its conquest by Allauddin Bahaman Shah, a Bahamani king.
Nalgonda District is currently a part of the Red Corridor.[3]
Geography
Nalgonda district occupies an area of approximately 14,200 square kilometres (5,500 sq mi),[4] comparatively equivalent to Indonesia's Flores.[5]
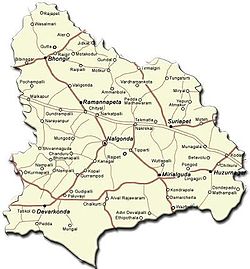
Towns in the district include: Nalgonda, Miryalaguda, Suryapet, Kodada, Chityal, Kattangur, Nakrekal, Bhongir, Bhoodhan Pochampally, Aleru, Narkatpalli, Huzurnagar, Devarakonda, Yadagirigutta, Rajapet, Mothkur, and Kanegal.
The rivers Krishna, Musi River, Aleru, Peddavagu, Dindi and Paleru flow through the Nalgonda district.
Minerals in the district include Limestone, Black & Color Granites.
Clean drinking water, water supply for irrigation and educational facilities for all are perhaps the most important problems Nalgonda faces right now.
Nearly 500 villages in Nalgonda district are affected by the high fluorine content in water. It is estimated that nearly 1 million people are affected by Fluorosis in Nalgonda district.
Parada village under Kattangur Mandal was suffering with drinking water in this mandal almost all villages supplied from Krishna but except this village.
Economy
In 2006 the Indian government named Nalgonda one of the country's 250 most backward districts (out of a total of 640).[6] It is one of the thirteen districts in Andhra Pradesh currently receiving funds from the Backward Regions Grant Fund Programme (BRGF).[6]
Agriculture
- Irrigation projects
- Nagarjuna Sagar
- Alimineti Madhava Reddy Project (previously known as the Srisailam Left Bank Canal)
- Major crops
Major crops include Paddy, Pulses, mousambi/Lime (fruit), Millets & Oil Seeds.
Industry
Industries in the Nalgonda district are Silk, Jaggery, Leather, Cement factories, Pipes manufacturing & Cotton,Rice Business(Rice Mills).
Divisions
Mandals

1 Bommala Ramaram 2 Turkapally 3 Rajapet 4 Yadagirigutta 5 Alair 6 Gundala 7 Tirumalagiri 8 Thungathurthy 9 Noothankal 10 Atmakur (S) 11 Jajireddigudem 12 Saligowraram 13 Mothkur 14 Atmakur (M) 15 Valigonda 16 Bhongir 17 Bibinagar 18 Pochampally 19 Choutuppal 20 Ramannapeta 21 Chityal 22 Narketpally 23 Kattangur 24 Nakrekal 25 Kethepally 26 Suryapet 27 Chivemla 28 Mothey 29 Nadigudem 30 Munagala 31 Penpahad 32 Vemulapally 33 Thipparthy 34 Nalgonda 35 Munugode 36 Narayanapur 37 Marriguda 38 Chandur 39 Kanagal 40 Nidamanoor 41 Tripuraram 42 Miryalaguda 43 Garidepally 44 Chilkur 45 Kodad 46 Mellachervu 47 Huzurnagar 48 Mattampally 49 Neredcherla 50 Damercherla 51 Anumula 52 Peddavoora 53 P.A.Pally 54 Gurrampode 55 Nampally 56 Chintapally 57 Devarakonda 58 Gundlapally 59 Chandampet 60Tangutoor( Nalgonda )
- Gram panchayats under Nalgonda mandal is a total of 1178[7]
Household indicators
In 2007–2008 the International Institute for Population Sciences interviewed 1236 households in 43 villages across the district.[8] They found that 90.4% had access to electricity, 97% had drinking water, 29.1% toilet facilities, and 45.1% lived in a pucca (permanent) home.[8] 37.5% of girls wed before the legal age of 18[9] and 87% of interviewees carried a BPL card.[8]
Demographics
According to the 2011 census Nalgonda district has a population of 3,483,648 ,[10] roughly equal to the nation of Panama[11] or the US state of Connecticut.[12] This gives it a ranking of 88th in India (out of a total of 640).[10] The district has a population density of 245 inhabitants per square kilometre (630 /sq mi) .[10] Its population growth rate over the decade 2001-2011 was 7.26 %.[10] Nalgonda has a sex ratio of 982 females for every 1000 males,[10] and a literacy rate of 65.05 %.[10]
References
- ^ http://www.censusindiamaps.net/page/India_WhizMap/IndiaMap.htm
- ^ http://www.world66.com/asia/southasia/india/andhrapradesh/nalgonda
- ^ "83 districts under the Security Related Expenditure Scheme". IntelliBriefs. 2009-12-11. http://intellibriefs.blogspot.com/2009/12/naxal-menace-83-districts-under.html. Retrieved 2011-09-17.
- ^ Srivastava, Dayawanti et al. (ed.) (2010). "States and Union Territories: Andhra Pradesh: Government". India 2010: A Reference Annual (54th ed.). New Delhi, India: Additional Director General, Publications Division, Ministry of Information and Broadcasting (India), Government of India. pp. 1111–1112. ISBN 978-81-230-1617-7.
- ^ "Island Directory Tables: Islands by Land Area". United Nations Environment Program. 1998-02-18. http://islands.unep.ch/Tiarea.htm. Retrieved 2011-10-11. "Flores 14,154km2"
- ^ a b Ministry of Panchayati Raj (September 8, 2009). "A Note on the Backward Regions Grant Fund Programme". National Institute of Rural Development. http://www.nird.org.in/brgf/doc/brgf_BackgroundNote.pdf. Retrieved September 27, 2011.
- ^ No. of Gram Panchayats - http://nalgonda.ap.nic.in/ataglance.htm
- ^ a b c "District Level Household and Facility Survey (DLHS-3), 2007-08: India. Andhra Prades" (PDF). International Institute for Population Sciences and Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. 2010. http://www.rchiips.org/pdf/rch3/report/AP.pdf. Retrieved 2011-10-03.
- ^ "How Do I? : Obtain Marriage Certificate". National Portal Content Management Team, National Informatics Centre. 2005. http://india.gov.in/howdo/howdoi.php?service=3. Retrieved 2011-10-03. "To be eligible for marriage, the minimum age limit is 21 for males and 18 for females."
- ^ a b c d e f "District Census 2011". Census2011.co.in. 2011. http://www.census2011.co.in/district.php. Retrieved 2011-09-30.
- ^ US Directorate of Intelligence. "Country Comparison:Population". https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/rankorder/2119rank.html. Retrieved 2011-10-01. "Panama 3,460,462 July 2011 est."
- ^ "2010 Resident Population Data". U. S. Census Bureau. http://2010.census.gov/2010census/data/apportionment-pop-text.php. Retrieved 2011-09-30. "Connecticut 3,574,097"
External links
- Nalgonda (district) travel guide from Wikitravel
- Nalgonda.org
- Nalgonda District online
- Nalgonda factfile at APOnline.gov.in
- Nalgonda District Tourist Opportunities
- Neelagiri to Nalgonda.page 160

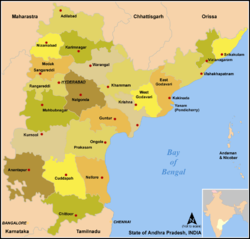
Medak district Warangal district 
Rangareddy district 
Khammam district
Krishna district Nalgonda district
Nalgonda district 

Mahbubnagar district Guntur district Major cities of Nalgonda District  State of Andhra Pradesh
State of Andhra PradeshCapital : Hyderabad Topics Districts Adilabad · Anantapur · Chittoor · East Godavari · Guntur · Hyderabad · Karimnagar · Khammam · Krishna · Kurnool · Mahabubnagar · Medak · Nalgonda · Nellore · Nizamabad · Prakasam · Ranga Reddy · Srikakulam · Visakhapatnam · Vizianagaram · Warangal · West Godavari · YSR
Major cities Hyderabad · Visakhapatnam · Vijayawada · Tirupati · Warangal · Hanamakonda · Guntur · Rajahmundry · Kakinada · Nellore · Kurnool · Anantapur · Ramagundam · Eluru · Machilipatnam · Bhimavaram · Karimnagar · Mancherial · Kadapa · Khammam · Bhadrachalam · Nizamabad
Portal : Andhra Pradesh Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.