- Obturator externus muscle
-
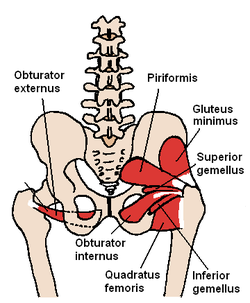
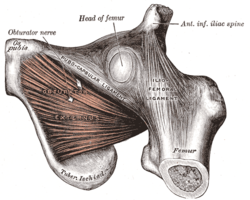
Obturator externus muscle The obturator externus and nearby hip muscles (posterior view) The Obturator externus. Inferior view Latin musculus obturatorius externus Gray's subject #128 477 Origin obturator foramen and obturatory membrane Insertion trochanteric fossa of femur Artery obturator artery Nerve posterior branch of obturator nerve (third and fourth lumbar nerves) Actions adduct thigh, rotate laterally thigh The obturator externus muscle (OE) is a flat, triangular muscle, which covers the outer surface of the anterior wall of the pelvis.
It is sometimes considered part of the medial compartment of thigh,[1] and sometimes considered part of the gluteal region.[2]
Contents
Origin and insertion
It arises from the margin of bone immediately around the medial side of the obturator foramen, viz., from the rami of the pubis, and the inferior ramus of the ischium; it also arises from the medial two-thirds of the outer surface of the obturator membrane, and from the tendinous arch which completes the canal for the passage of the obturator vessels and nerves.
The fibers springing from the pubic arch extend on to the inner surface of the bone, where they obtain a narrow origin between the margin of the foramen and the attachment of the obturator membrane.
The fibers converge and pass posterolateral and upward, and end in a tendon which runs across the back of the neck of the femur and lower part of the capsule of the hip joint and is inserted into the trochanteric fossa of the femur.
Relations
The obturator vessels lie between the muscle and the obturator membrane; the anterior branch of the obturator nerve reaches the thigh by passing in front of the muscle, and the posterior branch by piercing it.
Variation
In 33% of people a supernumerary muscle is found between the adductor brevis and minimus. While this muscle, when present, is similar to its neighbouring adductors, it is formed by separation from the superficial layer of the obturator externus, and is thus not ontogentically related to the adductor muscles of the hip. This muscle originates from the upper part of the inferior ramus of the pubis from where it runs downwards and laterally. In half of cases, it inserts into the anterior surface of the insertion aponeurosis of the adductor minimus. In the remaining cases, it is either inserted into the upper part of the pectineal line or the posterior part of the lesser trochanter.[3]
It has been demonstrated by the course of the posterior branch of obturator nerve that the obturator externus is divided into a superior fasciculus and a main belly. The supernumerary muscle described above originates from the superior fasciculus, while an anomalous fasciculus — also derived from the obturator externus — originates from the main belly. The "original" obturator externus, i.e. without these supernumerary muscular parts, actually occurs in only 20% of cases, and apparently the obturator externus readily undergoes ontogenetic variations.[4]
Additional images
References
- ^ Sauerland, Eberhardt K.; Patrick W., PhD. Tank; Tank, Patrick W. (2005). Grant's dissector. Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 129. ISBN 0-7817-5484-4.
- ^ "Summary of Lower Limb". http://mywebpages.comcast.net/WNOR/summarylistll.htm. Retrieved 2008-01-27.
- ^ Nakamura, E; Masumi, S; Miura, M; Kato, S; Miyauchi, R (1992). "A supernumerary muscle between the adductors brevis and minimus in humans". Okajimas folia anatomica Japonica 69 (2–3): 89–98. PMID 1436954.
- ^ Yatsunami, M; Tai, T; Irie, Y; Ogawa, K; Miyauchi, R (2004). "A morphological study on the human obturator externus muscle with reference to anomalous muscle and anomalous fasciculus originating from the obturator externus muscle". Okajimas folia anatomica Japonica 80 (5–6): 103–14. PMID 15134328.
External links
- LUC obex
- -1355481008 at GPnotebook
- Cross section at UV pelvis/pelvis-e12-15
- lljoints at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (hipjointanterior)
- PTCentral
This article was originally based on an entry from a public domain edition of Gray's Anatomy. As such, some of the information contained within it may be outdated.
List of muscles of lower limbs (TA A04.7, GA 4.465) ILIAC Region
/ ILIOPSOASBUTTOCKS THIGH /
compartmentsLEG/
Crus/
compartmentssuperficial · triceps surae (gastrocnemius, soleus, accessory soleus, Achilles tendon) · plantaris
deep · tarsal tunnel (flexor hallucis longus, flexor digitorum longus, tibialis posterior) · popliteusfibularis muscles (longus, brevis)FOOT DorsalPlantar1st layer (abductor hallucis, flexor digitorum brevis, abductor digiti minimi) · 2nd layer (quadratus plantae, lumbrical muscle) · 3rd layer (flexor hallucis brevis, adductor hallucis, flexor digiti minimi brevis) · 4th layer (dorsal interossei, plantar interossei)Categories:- Hip muscles
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.