- Quadriceps femoris muscle
-
"Quads" redirects here. For other uses, see Quad.
Quadriceps femoris muscle Muscles of lower extremity. (Rectus femoris removed to reveal the vastus intermedius.) Latin musculus quadriceps femoris Gray's subject #128 470 Origin combined rectus femoris and vastus muscles Insertion tibial tuberosity Artery femoral artery Nerve Femoral nerve Actions Knee extension; Hip flexion (R.Fem. only) Dorlands
/ElsevierQuadriceps femoris muscle The quadriceps femoris (Latin for "four-headed muscle of the femur"), also called simply the quadriceps, quadriceps extensor, quads, is a large muscle group that includes the four prevailing muscles on the front of the thigh. It is the great extensor muscle of the knee, forming a large fleshy mass which covers the front and sides of the femur.
The proper Latin plural form of the adjective quadriceps would be quadricipites. In modern English usage, quadriceps is used in both singular and plural. The singular form quadricep, produced by hypercorrection, is frequently used.
Contents
Portions
It is subdivided into four separate portions or 'heads', which have received distinctive names:
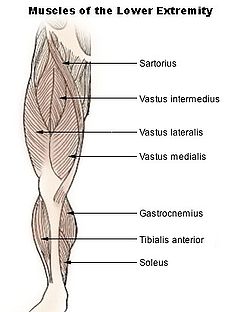
- Rectus femoris occupies the middle of the thigh, covering most of the other three quadriceps muscles. It originates on the ilium. It is named from its straight course.
- The other three lie deep to rectus femoris and originate from the body of the femur, which they cover from the trochanters to the condyles:
- Vastus lateralis is on the lateral side of the femur (i.e. on the outer side of the thigh).
- Vastus medialis is on the medial side of the femur (i.e. on the inner part thigh).
- Vastus intermedius lies between vastus lateralis and vastus medialis on the front of the femur (i.e. on the top or front of the thigh), but deep to the rectus femoris. Typically, it cannot be seen without dissection of the rectus femoris.
All four parts of the quadriceps muscle attach to the patella (knee cap) via the quadriceps tendon.
Actions
All four quadriceps are powerful extensors of the knee joint. They are crucial in walking, running, jumping and squatting. Because rectus femoris attaches to the ilium, it is also a flexor of the hip. This action is also crucial to walking or running as it swings the leg forward into the ensuing step. The quadriceps, specifically the vastus medialis, plays the important role of stabilizing the patella and the knee joint during gait.[1]
Training
In strength training, the quadriceps is trained by several leg exercises. Effective exercises include the squat and leg press. The isolation movement (i.e. targets solely the quadriceps) is the leg extension exercise.
Additional images
References
- ^ Therapeutic Exercises, Carolyn Kisner & Lynn A. Colby, 5th ed. (2002) 692-93.
External links
- Duke Orthopedics quadriceps_muscle
- Muscles/Quadriceps at exrx.net
- Roche Lexicon - illustrated navigator, at Elsevier 39960.000-1
- Anatomy of the Quadriceps Muscles - Fitstep.com
- Stretching the Quadriceps
List of muscles of lower limbs (TA A04.7, GA 4.465) ILIAC Region
/ ILIOPSOASBUTTOCKS THIGH /
compartmentssartorius · quadriceps (rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus intermedius, vastus medialis) · articularis genuLEG/
Crus/
compartmentssuperficial · triceps surae (gastrocnemius, soleus, accessory soleus, Achilles tendon) · plantaris
deep · tarsal tunnel (flexor hallucis longus, flexor digitorum longus, tibialis posterior) · popliteusfibularis muscles (longus, brevis)FOOT DorsalPlantar1st layer (abductor hallucis, flexor digitorum brevis, abductor digiti minimi) · 2nd layer (quadratus plantae, lumbrical muscle) · 3rd layer (flexor hallucis brevis, adductor hallucis, flexor digiti minimi brevis) · 4th layer (dorsal interossei, plantar interossei)Categories:- Knee extensors
- Thigh muscles
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.