- Narvik
-
Narvik kommune — Municipality — 
Coat of arms
Nordland within
NorwayNarvik within Nordland Coordinates: 68°25′14″N 17°33′36″E / 68.42056°N 17.56°ECoordinates: 68°25′14″N 17°33′36″E / 68.42056°N 17.56°E Country Norway County Nordland District Ofoten Administrative centre Narvik Government – Mayor (2007) Karen Margrethe Kuvaas (Ap) Area – Total 2,023 km2 (781.1 sq mi) – Land 1,905 km2 (735.5 sq mi) Area rank 29 in Norway Population (2011) – Total 18,380 – Rank 51 in Norway – Density 10/km2 (25.9/sq mi) – Change (10 years) -2.00 % Demonym Narviking[1] Time zone CET (UTC+1) – Summer (DST) CEST (UTC+2) ISO 3166 code NO-1805 Official language form Bokmål Website www.narvik.kommune.no Data from Statistics Norway  Narvik (help·info) is the third largest city and municipality in Nordland county, Norway by population. Narvik is located on the shores of the Narvik Fjord (Norwegian: Ofotfjord). The municipality is part of the Ofoten traditional region of North Norway, inside the arctic circle. Narvik borders the municipality of Ballangen to the southwest, Evenes to the northwest, Bardu and Gratangen in Troms county to the north, and Norrbotten County (Lapland) in Sweden to the south and east.
Narvik (help·info) is the third largest city and municipality in Nordland county, Norway by population. Narvik is located on the shores of the Narvik Fjord (Norwegian: Ofotfjord). The municipality is part of the Ofoten traditional region of North Norway, inside the arctic circle. Narvik borders the municipality of Ballangen to the southwest, Evenes to the northwest, Bardu and Gratangen in Troms county to the north, and Norrbotten County (Lapland) in Sweden to the south and east.Narvik was separated from the municipality of Ankenes when it became a city and municipality of its own on 1 January 1902. The municipality of Ankenes was merged into Narvik on 1 January 1974.
Contents
General information
Name
The town is named after the old Narvik farm ("Narduigh" - 1567), since the town is built on its ground.[2] The meaning of the first element is unknown, and the last element is vik which means "inlet".
Narvik was originally called Victoriahavn after the Queen Victoria of England, however Sweden’s Crown Princess Victoria was also honoured.[3]
Coat-of-arms
The coat-of-arms is from modern times. They were granted on 1 June 1951. The arms show a gold-coloured anchor on a red background. The anchor symbolises Narvik's status as an important port (the largest harbour in North Norway).[4]
History
The history of Narvik as a settlement began in the Stone Age. Not very much is known about these people, but the Vikings lived in this area.
The history of modern Narvik begins in the 1870s, when the Swedish government began to understand the potential of the iron ore mines in Kiruna, Sweden. Obtaining iron ore from Kiruna had one significant problem in that there was no suitable Swedish port. The nearest Swedish port, Luleå, has limitations. It is covered with ice all winter, it is far from Kiruna, and it allows only medium-sized bulk freight vessels. Realizing these problems, a Swedish company (Gällivarre Aktiebolag) built a railway to Narvik, as the port there is ice-free thanks to the warm Gulf Stream, and is naturally large, allowing boats of virtually any size to anchor, up to 208 metres long and 27 metres deep.[3][5]
Therefore, Narvik was founded as an all-year ice free port for the Kiruna and Gällivare iron mines. During the construction of the railway, the coming port was called Victoriahavn (Victoria harbour) until 1898, when the name was changed to Narvik. The town was officially founded in 1902. Ofotbanen is the railroad connecting Narvik to Kiruna in Sweden, passing through the mountains dividing the two countries. Locals use the Swedish slang words morsan (mother) and farsan (father), a testimony to the close ties with Sweden.
LKAB, the mining corporation, still ships the majority of its ore from Narvik (a total 25 million tons a year) and the corporation is still important in the area, both as an employer and landowner, although its influence is not as prominent now as it has been in previous years.[5]
World War II
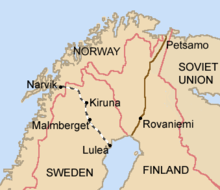 Iron ore is extracted in Kiruna and Malmberget, and brought by rail to the harbours of Luleå and Narvik.
Iron ore is extracted in Kiruna and Malmberget, and brought by rail to the harbours of Luleå and Narvik.
(Borders as of 1920–1940.)The port of Narvik proved to be strategically valuable in the early years of World War II and the town became a focal point of the Norwegian Campaign. In 1939, Germany's war industry depended upon iron ore mined in Kiruna and Malmberget in Sweden. During the summer season this ore could be sent by cargo ship to Germany through the Baltic Sea via the Swedish port of Luleå on the Gulf of Bothnia. However, when the Gulf of Bothnia froze during the winter, more shipments of the ore needed to be transported through Narvik and, from there, down the west coast of Norway to Germany. The town of Narvik is linked by rail to Sweden, but not to any other towns in Norway. As a result, Narvik serves as a gateway to the ore fields of Sweden that cannot be easily reached from southern Norway via land. Winston Churchill realized that the control of Narvik meant stopping most German imports of iron ore during the winter of 1940. This would be advantageous to the Allies, and it might help shorten the war. Equally as important, later in the war, German submarines and warships based there threatened the allied supply line to the Soviet Union.[6]
Churchill proposed laying a naval minefield in Norwegian territorial waters around Narvik (referred to as "the Leads"),[7] or else occupying the town with Allied troops. The Allies hoped that they might be able to use an occupied Narvik as a base from which to secure the Swedish ore fields and/or to send supplies and reinforcements to Finland, then fighting the Finnish Winter War with the Soviet Union. Plans to lay a minefield around Narvik or to seize the town met with debate within the British government - since both plans would mean a violation of Norway's neutrality and sovereignty.[6]
Finally, on 8 April 1940, the British Admiralty launched Operation Wilfred, an attempt to lay anti-shipping minefields around Narvik in Norwegian territorial waters. Coincidentally, Germany launched its invasion of Norway (Operation Weserübung) on the next day. During this invasion, ten German destroyers, each carrying 200 mountain infantry soldiers, were sent to Narvik. The outdated Norwegian coastal defence ships HNoMS Eidsvold and HNoMS Norge attempted to resist the invasion, but both Norwegian warships were sunk after a short and uneven battle. The British Royal Navy quickly dispatched several ships to Narvik, including the battleship HMS Warspite, and during the Battles of Narvik, the British took control of the coast, destroying the German destroyers that had brought the invasion force to Narvik, as well as other German ships in the area. The German battleships Scharnhorst and Gneisenau at Narvik sank the British aircraft carrier HMS Glorious during the withdrawal from this battle.[8]
On 12 April 1940, the first convoys of Allied soldiers were sent under Major-General Pierse Joseph Mackesy to Narvik. The Admiralty urged Mackesy to conduct an assault on Narvik from the sea as soon as possible. However, Mackesy believed that the German harbour defences were too strong for such an invasion to take place. The Admiralty argued that a naval bombardment of Norway would enable the troops to land safely, but General Mackesy refused to subject Norwegian citizens to such a bombardment, and instead he chose to land his troops near Narvik and wait until the snow melted to take over the city.[6]
Coordinated by the Norwegian General Carl Gustav Fleischer, Norwegian, French, Polish, and British forces recaptured Narvik on 28 May 1940. This is also considered the first Allied infantry victory in World War II. However, by that time, the Allies were losing the Battle of France and the evacuation from Dunkirk was underway. Since the Nazi German invasion of France had made Scandinavia largely irrelevant, and since the valuable troops assigned to Narvik were badly needed elsewhere, the Allies withdrew from Narvik on 8 June 1940 in Operation Alphabet. Without support from the Allied naval task force, the Norwegians were outnumbered, and they had to lay down their arms in Norway on 10 June 1940. This was not a complete capitulation, since the Norwegians kept on fighting guerrilla operations inland.
Possession of the Ofotfjord was also important to the German Kriegsmarine (navy) since it provided a refuge for warships like the pocket battleship Lützow and the battleship Tirpitz outside the range of air attacks from Scotland. Also, possibly U-boats were based at Narvik.
Geography
The municipality of Narvik covers large areas outside the town itself. Some of the other settlements in the municipality are Bjerkvik (located at the head of the Herjangsfjord), Håkvik, Beisfjord, and Skjomen. The eastern part, towards the border with Sweden, is dominated by mountains, and Storsteinfjellet reaches 1,894 metres (6,214 ft). There are also valleys and lakes, such as Hartvikvatnet. The city itself is situated near the innermost part of the deep Ofotfjord, but even here the mountains, going almost straight up from the blue fjord, reach as high as 1,700 metres (5,600 ft) in Skjomen, where the glacier Frostisen can be seen. Forests cover the lower parts of the mountains (below 500 meters), but near the summits, the snow can stay most of the summer. Narvik has well prepared slopes for alpine skiing, some of which end almost in the city centre.
Climate
Situated 220 kilometres (140 mi) inside the arctic circle, Narvik is one of the most northerly towns in the world. However, the North Atlantic Current (extension of the Gulf Stream) gives Narvik a milder climate than one might expect for a town at this latitude. In addition, the mountains surrounding the town give shelter from the strong winds typical for coastal areas. Mean annual temperature is 3.8 °C (39 °F), and the growing season in the lowland is approximately 150 days, thus allowing inhabitants with an interest for gardening to grow many imported plants.[3]
Summer lasts from beginning of June until early September, with daytime temperatures ranging from 9 °C (48 °F) to 28 °C (82 °F), usually 12 to 20 °C (54 to 68 °F). Record high and low in July is 31.5 °C (89 °F) (July 3, 1972, source:eklima/met.no) and 4 °C (39 °F). Record high and low in January is 11 °C (52 °F) and −20 °C (−4 °F). The wettest month is October, with 110 millimetres (4.3 in) precipitation, the driest month is May with 40 millimetres (1.6 in), and the annual precipitation is 830 millimetres (33 in).[9][10]
The light varies considerably in Narvik since the sun is below the horizon from late November until mid-January; when there is only a bluish light for a few hours around noon.[11] The mountains surrounding the town in reality extend this period from early November until the end of January. The light is often intense in March and April, with long daylight hours and snow cover since the snow melts in lowland areas in April, but stays in the mountains for several months. The "midnight sun" is above the horizon from May 25 to July 18, and the period with continuous daylight lasts a bit longer, from approximately May 10 to the end of July. There is also a transitional period with twilight in the night, so you will not be able to see any stars at night from the last days of April until approximately 10 August.
Climate data for Narvik Month Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec Year Average high °C (°F) −2
(28)−2
(28)1
(34)5
(41)9
(48)14
(57)18
(64)16
(61)12
(54)6
(43)3
(37)−1
(30)6.6
(43.8)Average low °C (°F) −7
(19)−7
(19)−5
(23.0)−2
(28)3
(37)7
(45)11
(52)10
(50)6
(43)2
(36)−2
(28)−5
(23)0.9
(33.7)Source: [12] Economy
Narvik is a commercial centre for some of the neighbouring municipalities. Narvik University College has approximately 1,200 students. There are some high-tech businesses in Narvik (among them Natech and Scancell).
Recreation and tourism
Narvik has access to numerous outdoor activities. This is the best known location in northern Norway when it comes to alpine skiing.[13]
There are lifts, and several of the slopes are floodlit. There is also a cable car to Fagernesfjellet, with a stunning view and the possibility to walk even higher up in the mountains. A signed mountain bike route is also available. Narvik Winter Festival (Norwegian: Vinterfestuka) takes place in early March. Mountain hiking is, understandably, very popular in this area, and the mountain area near the Swedish border has several accommodation possibilities. Wreck diving attracts divers to Narvik, as there are a lot of wrecks in or near the harbour, and more spread out in the fjord. Fishing in the fjord or in lakes and streams is a popular leisure activity. There are salmon rivers in Skjomen, Beisfjord and Bjerkvik. The 18-hole Golf Course in Skjomen is situated in a very scenic landscape, and is one of the most northern in the world. Narvik was destroyed by the fighting in 1940 and hastily rebuilt, hence the architecture is rather functional, but private homes are often painted in bright colours.
There is an Occupation Museum about the years 1940-1945 which holds the Victoria Cross awarded posthumously to Captain Bernard Warburton-Lee of the British Royal Navy in 1940 and a rare German Enigma coding machine.
Transportation
A present and historical key to land transportation to Narvik is the railroad from northern Sweden across the mountains to this port town. Goods like iron ore shipped via this railroad make Narvik an important seaport.
The port of Narvik is ice-free and well protected from the weather. The port consists of three waterfront sections: LKAB bulk port, central port area with piers and deep-water harbor at Fagernes with intermodal facilities. Approximately 16 million tonnes of cargo are annually shipped from the ports of Narvik. Most of this iron ore.
Port Authorities have initiated an expansion of the container area of approximately 45,000 m2, which is more than twice Norways largest terminal in Oslo today handles. In 2005, the port of Narvik got status as Motorways of the Sea in the EU-system. In Norway, Oslo is the only city which have this status in addition to Narvik.
Hurtigruten or "Hurtigruta" (literally "Express Route", but sometimes referred to as "Norwegian Coastal Express" in English) is headquartered in Narvik. However, Hurtigruten do not have any regular sailings to Narvik.
Because of the extreme terrain there, there are no railroads northwards from Narvik or south to Bodø, Norway, which is at the northern end of the rest of Norway's railroad network. However, it is possible to reach Narvik by way of an approximately twenty-hour 1,540 kilometres (957 mi) train ride through the Swedish rail system from Stockholm.
The activity related to the railway and large port facilities are still important in Narvik, and goods to and from North Norway, Sweden, and Finland are often distributed via Narvik. In the proposed project called the "Northern East West Freight Corridor" portion of the Eurasian Land Bridge, there are plans for using Narvik as a port for goods from East Asia bound for eastern North America. The reason is that the railroad and ocean distances for these are shorter than though central Europe to Western European ports.
European route E6 crosses through the municipality using three bridges: Skjomen Bridge, Beisfjord Bridge, and Rombak Bridge. Narvik is served by two airports: the small Narvik Airport, Framnes just outside the city centre has a short runway and is served by De Havilland DHC-8 100 aircrafts with regular flights to Bodø. The larger and more capable Harstad/Narvik Airport, Evenes is 80 kilometres (50 mi) by road from Narvik and have regular flights to Oslo, Trondheim, Bodø and Tromsø.
There are highway connections from Narvik across the mountains eastwards to Abisko and Kiruna, Sweden (via European route E10).
Sister cities
Narvik is twinned with:
References
- ^ "Personnemningar til stadnamn i Noreg" (in Norwegian). Språkrådet. http://www.sprakrad.no/nb-no/Sprakhjelp/Rettskrivning_Ordboeker/Innbyggjarnamn/.
- ^ Rygh, Oluf (1905). Norske gaardnavne: Nordlands amt (16 ed.). Kristiania, Norge: W. C. Fabritius & sønners bogtrikkeri. pp. 285. http://books.google.com/books?id=K21BAAAAIAAJ. (Norwegian)
- ^ a b c "Key facts about Narvik". VisitNorway.com. http://www.visitnorway.com/en/Articles/Norway/North/Narvik/Key-facts-on-Narvik/. Retrieved 2008-11-24.
- ^ Norske Kommunevåpen (1990). "Nye kommunevåbener i Norden". http://www.ngw.nl/int/nor/n/narvik.htm. Retrieved 2008-11-24.
- ^ a b "Narvik, Norway". BBC. http://www.bbc.co.uk/dna/h2g2/A533125. Retrieved 2008-11-24.
- ^ a b c Churchill, Winston S (1948). The Second World War: The Gathering Storm. 1. Cambridge: Houghton Mifflin. ISBN 978-0395410554.
- ^ idem.
- ^ Galland, Adolf (2001). The First and the Last. Cerberus Publishing. pp. 92. ISBN 978-0899667287.
- ^ "Temperaturnormaler for Narvik i perioden 1961 - 1990". Met.no. http://met.no/observasjoner/nordland/normaler_for_kommune_1805.html?kommuner. Retrieved 2008-11-24. (Norwegian)
- ^ "Average Conditions - Narvik". BBC. http://www.bbc.co.uk/weather/world/city_guides/results.shtml?tt=TT004070. Retrieved 2008-11-24.
- ^ "Narvik daylight". Gaisma.com. http://www.gaisma.com/en/location/narvik.html. Retrieved 2008-11-24.
- ^ "Narvik average conditions". BBC. http://www.bbc.co.uk/weather/world/city_guides/results.shtml?tt=TT004070. Retrieved 17 September 2009.
- ^ "Winter rail destinations: Narvik". SJ AB (TheLocal.se). 3 November 2008. http://www.thelocal.se/15410/20081103. Retrieved 2008-11-08.
- ^ "Nowy Sącz - Partner Cities". © 2008 Urząd Miasta Nowego Sącza, Rynek 1, 33-300 Nowy Sącz. http://www.nowysacz.pl/?p=1&p2=167&main=inc-miastapar. Retrieved 2008-12-07.
External links
- Destination Narvik - tourist information (Norwegian)
- Narvik at Google Local
- Narvik travel guide from Wikitravel
- yr.no: Weather and climate statistics for Narvik
- German defence of Narvik during world war 2
- Footage of the Battle of Narvik April 1940
Municipalities of Nordland Alstahaug · Andøy · Ballangen · Beiarn · Bindal · Bø · Bodø · Brønnøy · Dønna · Evenes · Fauske · Flakstad · Gildeskål · Grane · Hadsel · Hamarøy · Hattfjelldal · Hemnes · Herøy · Leirfjord · Lødingen · Lurøy · Meløy · Moskenes · Narvik · Nesna · Øksnes · Rana · Rødøy · Røst · Saltdal · Sømna · Sørfold · Sortland · Steigen · Tjeldsund · Træna · Tysfjord · Værøy · Vågan · Vefsn · Vega · Vestvågøy · Vevelstad
40 most populous urban settlements (cities) of Norway 37. Nesoddtangen 11,600 38. Steinkjer 11,500 39. Leirvik 11,400 40. Vennesla 11,400 41. Kongsvinger 11,400 42. Stjørdalshalsen 10,800 1 Sarpsborg.Categories:- Narvik
- Cities and towns in Norway
- Municipalities of Nordland
- Ski areas and resorts in Norway
- Port cities and towns in Norway
- Populated places of Arctic Norway
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.