- Oregon Ballot Measure 57 (2008)
-
Measure 57 Increases Sentences For Drug Trafficking, Theft Against Elderly And Specified Repeat Property And Identity Theft Crimes; Requires Addiction Treatment For Certain Offenders Election results Yes or no Votes Percentage  Yes
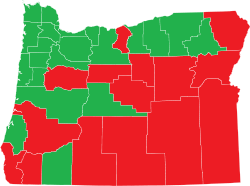
Yes1,058,955 61.39% No 665,942 38.61% Invalid or blank votes % Total votes 1,724,897 100.00% Voter turnout 85.7% Election results by county YesNoSource: Oregon Secretary of State [1]
Oregon Ballot Measure 57 (2008) or Senate Bill (SB) 1087 was a legislatively-referred state statute that increased term of imprisonment for persons convicted of specified drug and property crimes under certain circumstances. The measure enacted law which prohibits courts from imposing less than a presumptive sentence for persons convicted of specified drug and property crimes under certain circumstances, and requires the Department of Corrections to provide treatment to certain offenders and to administer grant program to provide supplemental funding to local governments for certain purposes.[2]Contents
Official Ballot Title
Increases Sentences For Drug Trafficking, Theft Against Elderly And Specified Repeat Property And Identity Theft Crimes; Requires Addiction Treatment For Certain Offenders[3]
Background
Competing ballot measures
A similar measure, (Oregon Ballot Measure 61 (2008), proposed by Kevin Mannix, was also approved for the November election.
The main differences were:
1) Measure 61 has mandatory prison time for some first time felony offenders, while SB 1087 only does so for repeat offenders
2) SB 1087 significantly increases funding for drug treatment programs, while Measure 61 provides none.
3) Measure 61 will cost $250–$400 million per two year budget cycle, while SB 1087 would only cost $140 million.[4]
If both measures pass, the one with the most votes will go into effect.[5]
An increase in prison inmates since 1994
In 1994, Measure 11, an earlier initiative proposed by Kevin Mannix, was passed, which set mandatory minimum sentences for violent crimes. It is responsible for 28% of today's prison population. Oregon uses the highest percentage of its state budget to lock up criminals and supervise parole of any state. Oregon has seen a growth in prison inmates from about 4,000 to more than 13,500.
If SB 1087 or the initiative proposed by Mannix, is passed, Oregon's prison population and percentage of state budget will become more pronounced. However, Oregon has seen an even greater drop in violent crime than the rest of the country on average since Measure 11 passed.[6]
Support
Supporters include:
Organizations
- Measure 57 or The Better Way to Fight Crime Committee, which was a broad coalition of police officers, police chiefs, sheriffs, district attorneys, business leaders, teachers, parents, advocates for children and seniors and many more.
- Oregon Council of Police Associations
- Oregon Police Chiefs for Safer Communities
- Oregon Assoc. of Community Corrections Directors
- Federation of Oregon Parole and Probation Officers
- Juvenile Parole Officers – AFSCME Council 75
- AFSCME Corrections United
- Association of Oregon Corrections Employees
- Nominee, Oregon Attorney General, John Kroger
- AARP Oregon
- Stand for Children
- National Association of Social Workers-Oregon Chapter
- SEIU, Local 503, representing front-line workers at the Oregon Youth Authority, & 45,000 other workers
- SEIU, Local 49
- Oregon Prevention Education and Recovery Association
- Oregon Business Association
- Oregon Education Association
- Save Oregon Seniors
- Oregon State Council for Retired Citizens
- Advocacy Coalition for Seniors & People with Disabilities
- Oregon Alliance for Retired Americans
- Partnership for Safety & Justice
- Elders in Action Commission
- United Way of the Mid-Willamette Valley
- Ainsworth United Church of Christ, Justice Commission
- Community Action Relationship of Oregon
- Community Alliance of Tenants
- Community Providers Association of Oregon
- Human Services Coalition of Oregon (HSCO)
- Multnomah County Democrats
- Northwest Oregon Labor Council
- One Voice for Child Care
- Oregon AFL-CIO
- Oregon Consumer League
- Oregon Health Action Campaign
- Oregon Nurses Association
- Rural Organizing Project
- Association of Oregon Counties
Elected officials
Justices
- Former Oregon Supreme Court Justice Betty Roberts
Attorneys General
Legislators
- Sen. Floyd Prozanski, D-Oregon, who said the legislative measure was widely supported by prosecutors, police and jail officials who know a lot more about fighting crime than Mannix.[5]
Sheriffs
- Sheriff Southwick - Baker County
- Sheriff Diana Simpson – Benton County
- Sheriff Craig Roberts – Clackamas County
- Sheriff Tom Bergin – Clatsop County
- Sheriff Dennis Dotson – Lincoln County
- Sheriff Bob Skipper – Multnomah County
- Sheriff Todd Anderson – Tillamook County
- Sheriff John Trumbo – Umatilla County
- Sheriff Rasmussen, Union County
- Sheriff Jack Crabtree – Yamhill County
District Attorneys
- Matt Shirtcliff, Baker
- John S. Foote, Clackamas
- Joshua Marquis, Clatsop
- Steve Atchison, Columbia
- R. Paul Frasier, Coos
- Everett Dial, Curry
- Michael T. Dugan, Deschutes
- Timothy J. Colahan, Harney
- Marion Weatherford, Gilliam
- Ryan Joslin, Grant
- Edwin I. Caleb, Klamath
- Mark Huddleston, Jackson
- Peter Deuel, Jefferson
- Stephen Campbell, Josephine
- David Schutt, Lake
- Bernice Barnett, Lincoln
- Jason Carlile, Linn
- Walt Beglau, Marion
- Elizabeth Ballard, Morrow
- Michael D. Schrunk, Multnomah
- John Fisher, Polk
- Wade M. McLeod, Sherman
- William Porter, Tillamook
- Dean F. Gushwa, Umatilla
- Mona K. Williams, Wallowa
- Eric Nisley, Wasco
- Bob Hermann, Washington
- Brad Berry, Yamhill
County Commissioners
- Commissioner Annabelle Jaramillo - Benton County
- Commissioner Jay Dixon - Benton County
- Commissioner Don Lindly - Lincoln County
- Commissioner Mary Stern - Yamhill County
City Councilors
- City Councilor Betty Boche - Beaverton
- City Councilor Denny Doyle - Beaverton
- City Councilor Doug Pugsley - Dundee
- Mayor Robert Austin - Estacada
- Mayor Julie Hammerstad - Lake Oswego
- Councilor Deborah Barnes, Milwaukee
- Mayor Cheri Olson, North Plains
Others
- Rob Ingram, long-time youth advocate—Portland
A full list of supporters is available at the campaign website [1].
Opposition
Kevin Mannix continues to promote his Measure 61. “Either way, we make progress,” Mannix says. “I win some if [Measure] 57 passes, and the people win more if 61 passes.”[7]
Loren Parks[8] "With the financial help of Nevada medical-device millionaire Loren Parks, Mannix easily gathered 149,000 signatures to place Measure 61 on the ballot."[7]
Oregon Anti-Crime Alliance: The Oregon Anti-Crime Alliance is a new organization that brings together citizens with a mission of reducing crime in Oregon through reforms affecting prevention, investigation, prosecution, the courts, indigent defense, accountability, transition programs out of prison, prison work, treatment and rehabilitation.
Some Republicans attacked the measure for being "soft-on-crime". Kevin Mannix continues to promote his "tough-on-crime" initiative while pointing out the weaknesses of the competing measure. "We shouldn't be patsies and let drug dealers and identity thieves and burglars get a free pass on their first convictions, which is what they get on the legislative referral", he said. [5]
For a citizen-initiated measure in Oregon, the ballot title is determined by the state's Attorney General. In the case of this measure, the legislature chose to supplant this process by inserting its own title.,[9][10]
As of March, 2009, the number of counties that have sentenced pursuant Measure 57 sentences remains small. The reason for this seems to be that defendants are willing to plea to a lesser sentence in order to avoid the longer sentences mandated by the Measure.
See also
- Oregon Ballot Measure 61 (2008)
- Methamphetamine in Oregon
- List of Oregon ballot measures
Notes
- ^ Official Results – November 4, 2008 General Election
- ^ Official Summary of SB 1087
- ^ Detailed information on SB1087 from the Secretary of State
- ^ LaneBus.org: "Measure 40, SB 1087, Education and the Economy", Lane County Bus Project, February 14, 2008
- ^ a b c OregonLive.com "Mannix's tough-on-crime measure will be on Oregon ballot", The Oregonian, April 11, 2008
- ^ Prisons Lock in a Chunk of Budget from The Oregonian
- ^ a b Jaquiss, Nigel (1 October 2008). "Jail Junkies" (Editorial). News. Willamette Week. http://wweek.com/editorial/3447/11597/. Retrieved December 23, 2008.
- ^ "Loren Parks, The Missing Millionaire" (Website). Missing Millionaire. 2008. http://missingmillionaire.com/. Retrieved December 23, 2008.
- ^ Developing hard, Democrats avoiding review process again! Ted Piccolo, February 16, 2008
- ^ Salem Democrats to give Republicans the perfect issue
External links
- Better Way to Fight Crime Committee Yes on Measure 57
- Published in West Linn Tidings I urge you to support Measure 57
- 2008 General Election Measures: Voter Guide
- StatesmanJournal.com: "Kroger backs alternative to crime measure", July 17, 2008
- "Either anti-crime measure will cost over $1 billion, state says", Oregons Against Measure 11
Topics in Oregon legislation Crime and sentencing Capital punishment · Measure 11 (1994) (mandatory minimum sentencing) · Measure 40 (1996) etc. (victims' rights) Abigail Scott Duniway was instrumental in establishing women's right to vote in Oregon.
Abigail Scott Duniway was instrumental in establishing women's right to vote in Oregon.
Elections and voting Gay rights Environment Land use Health care Minimum wage Taxation Tax revolt · Measure 5 (1990) (landmark tax law) · Measures 47 (1996) and 50 (1997) (adjusted Measure 5) · Kicker (tax rebate)Miscellaneous Influential people Background, further reading 2007 ← Oregon 2008 Elections → 2010 Categories:- Oregon 2008 ballot measures
- Penal system in Oregon
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.