- Fabry disease
-
Fabry disease ICD10 = E75.2 (ILDS E75.25) Classification and external resources 
Alpha galactosidase - the protein that is deficient in Fabry disease.ICD-9 272.7 OMIM 301500 DiseasesDB 4638 eMedicine neuro/579 derm/707 ped/2888 MeSH D000795 Fabry disease (also known as Fabry's disease, Anderson-Fabry disease, angiokeratoma corporis diffusum and alpha-galactosidase A deficiency) is a rare X-linked recessive (inherited) lysosomal storage disease, which can cause a wide range of systemic symptoms.[1] The disease is named after one of its discoverers, Johannes Fabry (June 1,1860 - June 29,1930).[2]
Contents
Pathophysiology
A deficiency of the enzyme alpha galactosidase A (a-GAL A, encoded by GLA) due to mutation causes a glycolipid known as globotriaosylceramide (abbreviated as Gb3, GL-3, or ceramide trihexoside) to accumulate within the blood vessels, other tissues, and organs.[3] This accumulation leads to an impairment of their proper function.
The DNA mutations which cause the disease are X-linked recessive. The condition affects hemizygous males (i.e. all males), as well as homozygous, and in many cases heterozygous females. While males typically experience severe symptoms, women can range from being asymptomatic to having severe symptoms. This variability is thought to be due to X-inactivation patterns during embryonic development of the female.[4]
Symptoms
Symptoms are typically first experienced in early childhood and can be very difficult to understand; the rarity of Fabry disease to many clinicians sometimes leads to misdiagnoses. Manifestations of the disease usually increase in number and severity as an individual ages.
- Pain
Full body or localized pain to the extremities (known as acroparesthesia) or GI tract is common in patients with Fabry disease. Acroparesthesia in Fabry disease is believed to be related to the damage of peripheral nerve fibers that transmit pain. GI tract pain is likely caused by accumulation of lipids in the small vasculature of the GI tract which obstructs blood flow and causes pain.[5]
- Renal involvement
Kidney complications are a common and serious effect of the disease; renal insufficiency and renal failure may worsen throughout life. Proteinuria (which causes foamy urine) is often the first sign of kidney involvement. End stage renal failure in males can typically occur in the third decade of life, and is a common cause of death due to the disease.
- Cardiac manifestations
Cardiac complications occur when glycolipids build up in different heart cells; heart related effects worsen with age and may lead to increased risk of heart disease. Hypertension (high blood pressure) and cardiomyopathy are commonly observed.
- Dermatological manifestations
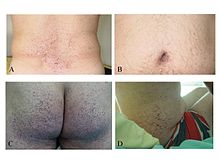
Angiokeratomas (tiny, painless papules that can appear on any region of the body, but are predominant on the thighs, around the belly-button, buttocks, lower abdomen, and groin) are a common symptom.
Anhidrosis (lack of sweating) is a common symptom, and less commonly hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating).
Additionally, patients can exhibit Raynaud's disease-like symptoms with neuropathy (in particular, burning extremity pain).
- Ocular manifestations
Cosmetic ocular involvement may be present showing cornea verticillata (also known as vortex keratopathy), i.e. clouding of the corneas. Keratopathy may be the presenting feature in asymptomatic carriers, and must be differentiated from other causes of vortex keratopathy (e.g. drug deposition in the cornea). This clouding does not affect vision.
Other ocular findings that can be seen include conjunctival aneurysms, posterior spoke-like cataracts, papilloedema, macular edema, optic atrophy and retinal vascular dilation.
- Other manifestations;
Fatigue, neuropathy (in particular, burning extremity pain), cerebrovascular effects leading to an increased risk of stroke, tinnitus (ringing in the ears), vertigo, nausea, inability to gain weight, chemical inbalances, and diarrhea are other common symptoms.
Diagnosis
Fabry disease is indicated when associated symptoms are present, and can be diagnosed by a blood test to measure the level of alpha-galactosidase activity, however this may be misleading in female carriers due to the random nature of X-inactivation. Chromosomal analysis of the GLA gene is the most accurate method of diagnosis, and many mutations which cause the disease have been noted. Kidney biopsy may also be suggestive of Fabry Disease if excessive lipid buildup is noted.
Naturally, alpha-galactosidase A (a-GAL A) is likely to be present only at very low levels in the blood, particularly in males. In females, owing to X-inactivation patterns, levels are commonly normal even if the patient is not asymptomatic. The Sifap (stroke in young Fabry patients) project will investigate the relation between stroke and Fabry's disease.
Misdiagnosis of Fabry Disease.
Pediatricians as well as internists commonly misdiagnose Fabry disease.[6]
Treatment
Until the 2000s, treatment of Fabry disease targeted the symptomatic effects.
In 2001, three Enzyme Replacement Therapies (ERTs) were released: Agalsidase alpha (Replagal, manufactured by Shire) and Agalsidase beta (Fabrazyme, manufactured by Genzyme). These attempt to replace the deficient enzyme by means of infusion, most commonly, every two weeks. The cost of these drugs is problematic (approximately $250,000 US a year/patient) and remains a barrier to many patients in some countries. The infusion may be performed by the patient themselves, in the patient's home by a registered nurse, or at a medical facility. Enzyme replacement therapy is not a cure, but can allow normal metabolism and both prevent disease progression as well as potentially reverse symptoms.
Pain in Fabry disease responds to ERT, but pain management regimens may also include analgesics, anticonvulsants, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
Pop Cultural references
- House (Epic Fail, season 6 episode 3) centers on a patient with Fabry Disease.
- Scrubs (My Catalyst, season 3 episode 12) features a Fabry Disease diagnosis.
See also
- Lysosomal storage disorder
- Sphingolipidoses
- Enzyme replacement therapy
References
- ^ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. p. 538. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ synd/1761 at Who Named It?
- ^ Karen JK, Hale EK, Ma L (2005). "Angiokeratoma corporis diffusum (Fabry disease)". Dermatol. Online J. 11 (4): 8. PMID 16403380. http://dermatology.cdlib.org/114/NYU/NYUtexts/0419054.html.
- ^ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. pp. [page needed]. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ Hoffmann MD, Bjoern; Beck, Michael PhD; Sunder-Plassmann, Gere PhD; Borsini, Walter MD; Ricci, Roberta PhD; Mehta, Atul MD (July/August 2007). "Nature and Prevalence of Pain in Fabry Disease and Its Response to Enzyme Replacement Therapy—A Retrospective Analysis From the Fabry Outcome Survey.". The Clinical Journal of Pain 23 (6): 535–542. doi:10.1097/AJP.0b013e318074c986.
- ^ Marchesoni CL, Roa N, Pardal AM, Neumann P, Caceres G, Martinez P, Kisinovsky I, Bianchi S, Tarabuso AL, Reisin RC. (2010). "Misdiagnosis in Fabry disease". J Pediatr. 156 (5): 828–831. doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.02.012. PMID 20385321.
External links
- GeneReview entry on Fabry disease by NIH
- Fabry Disease Information Page at NINDS
- Fabry disease at NLM Genetics Home Reference
- Fabry Registry
- Stroke in young Fabry patients
- Support groups
- Fabry International Network
- Focus on Fabry by Shire
- Fabry Community by Genzyme
- Fabry Support & Information Group (FSIG)
- Fabry support at MPS Society
- Canadian Fabry Association
- National Fabry Disease Foundation
- Fabry Support Group Australia
(LSD) Inborn error of lipid metabolism: lipid storage disorders (E75, 272.7–272.8) Sphingolipidoses
(to ceramide)From globosideGlobotriaosylceramide: Fabry's diseaseFrom sphingomyelinTo sphingosineNCL Other Cerebrotendineous xanthomatosis · Cholesteryl ester storage disease (Lysosomal acid lipase deficiency/Wolman disease) · Sea-blue histiocyte syndromeCategories:- X-linked dominant disorders
- Rare diseases
- Lipid storage disorders
- Skin conditions resulting from errors in metabolism
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.