- Cerebrotendineous xanthomatosis
-
Cerebrotendineous xanthomatosis Classification and external resources ICD-10 E75.5 ICD-9 272.7 OMIM 213700 DiseasesDB 29239 MeSH D019294 Cerebrotendineous xanthomatosis or cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX), also called cerebral cholesterosis,[1] is an autosomal recessive form of xanthomatosis.[2][3]
Contents
Characteristics
An inherited disorder associated with the deposition of a form of cholesterol (cholestanol) in the brain and other tissues and with elevated levels of cholesterol in plasma but with normal total cholesterol level; it is characterized by progressive cerebellar ataxia beginning after puberty and by juvenile cataracts, and tendineous or tuberous xanthomas.
Cause and Genetics
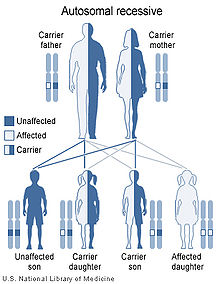 Cerebrotendineous xanthomatosis has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
Cerebrotendineous xanthomatosis has an autosomal recessive pattern of inheritance.
CTX is associated with mutations in the CYP27A1 gene, located on chromosome 2q33-qter.[1][4] The disorder is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner.[2] This means the defective gene responsible for the disorder is located on an autosome (chromosome 2 is an autosome), and two copies of the defective gene (one inherited from each parent) are required in order to be born with the disorder. The parents of an individual with an autosomal recessive disorder both carry one copy of the defective gene, but usually do not experience any signs or symptoms of the disorder.
Treatment
The standard treatment is chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) replacement therapy. Serum cholesterol levels are also followed. If hypercholesterolemia is not controlled with CDCA, an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor ("statins" such as simvastatin) can also be used. [5]
Eponym
It is also known as "Van Bogaert-Scherer-Epstein syndrome".[6][7]
See also
References
- ^ a b Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 213700
- ^ a b Pilo de la Fuente B, Ruiz I, Lopez de Munain A, Jimenez-Escrig A (May 2008). "Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis: Neuropathological findings". J. Neurol. 255 (6): 839. doi:10.1007/s00415-008-0729-6. PMID 18458861.
- ^ James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. p. 535. ISBN 0-7216-2921-0.
- ^ Online 'Mendelian Inheritance in Man' (OMIM) 606530
- ^ http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/1418820-treatment
- ^ synd/1452 at Who Named It?
- ^ L. van Bogaert, H. J. Scherer, E. Epstein. Une forme cérébrale de la cholestérinose généralisée (type particulier de lipidose à cholestérine). Paris, Masson, 1937.
External links
(LSD) Inborn error of lipid metabolism: lipid storage disorders (E75, 272.7–272.8) Sphingolipidoses
(to ceramide)From globosideGlobotriaosylceramide: Fabry's diseaseFrom sphingomyelinTo sphingosineNCL Other Cerebrotendineous xanthomatosis · Cholesteryl ester storage disease (Lysosomal acid lipase deficiency/Wolman disease) · Sea-blue histiocyte syndromeCategories:- Lipid storage disorders
- Autosomal recessive disorders
- Skin conditions resulting from errors in metabolism
- Rare diseases
- Disease stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
