- Enterobiasis
-
Pinworm infection Classification and external resources 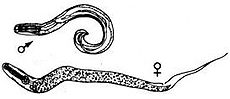
Pinworms (Enterobius vermicularis).ICD-10 B80 ICD-9 127.4 DiseasesDB 13041 MeSH D017229 A pinworm infection or enterobiasis is a human parasitic disease and one of the most common childhood parasitic worm infections in the developed world.[1][2] It is caused by infestation with the parasitic roundworm Enterobius vermicularis, commonly called the human pinworm.[3] Infection usually occurs through the ingestion of pinworm eggs, either through contaminated hands, food, or less commonly, water.[4] The chief symptom is itching in the anal area.[4] The incubation time from ingestion of eggs to the first appearance of new eggs around the anus is 4 to 6 weeks.[5] Pinworms are usually considered a nuisance rather than a serious disease.[4] Treatment is straightforward in uncomplicated cases, however, elimination of the parasite from a family group or institution often poses significant problems—either due to an incomplete cure or reinfection.[4] Pinworm infection has no association with any socioeconomic level, race or culture.[6]
Contents
Signs and symptoms
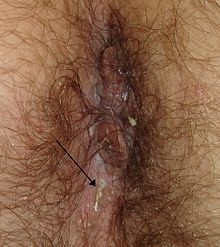
One third of individuals with pinworm infection are totally asymptomatic.[5] The main symptoms are pruritus ani and perineal pruritus, i.e., itching in and around the anus and around the perineum.[5][7][8] The itching occurs mainly during the night,[7][9] and is caused by the female pinworms migrating to lay eggs around the anus.[4][8] Both the migrating females and the clumps of eggs are irritating, but the mechanisms causing the intense pruritus have not been explained.[9] The intensity of the itching varies, and it can be described as tickling, crawling sensations, or even acute pain.[10] The itching leads to continuously scratching the area around the anus, which can further results in tearing of the skin and complications such as secondary bacterial infections, including bacterial dermatitis (i.e., skin inflammation) and folliculitis (i.e., hair follicle inflammation).[7][8][10] General symptoms are insomnia (i.e., persistent difficulties to sleep) and restlessness.[7] A considerable proportion of children suffer from anorexia (i.e., loss of appetite), weight loss, irritability, emotional instability, and enuresis (i.e., inability to control urination).[7]
Pinworms cannot damage the skin,[11] and they do not normally migrate through tissues.[8] However, in women they may move onto the vulva and into the vagina, from there moving to external orifice of the uterus, and onwards to the uterine cavity, fallopian tubes, ovaries, and peritoneal cavity.[11] This can cause vulvovaginitis, i.e. an inflammation of the vulva and vagina.[7][8] This causes vaginal discharge and pruritus vulvae, i.e., itchiness of the vulva.[7] The pinworms can also enter the urethra, and presumably, they carry intestinal bacteria with them.[11] According to Gutierrez (2000), a statistically significant correlation between pinworm infection and urinary tract infections has been shown,[11] however Burkhart & Burkhart (2005) maintain that the incidence of pinworms as a cause of urinary tract infections remains unknown.[5] Incidentally, one report indicated that 36% of young girls with urinary tract infection also had pinworms.[5] Dysuria (i.e., painful urination) has been associated with pinworm infection.[5]
The relationship between pinworm infestation and appendicitis has been researched, but there is a lack of clear consensus in the matter: while Gutierres (2005) maintains that there exists a consensus that pinworms do not produce the inflammatory reaction,[12] Cook (1994) states that it is controversial whether pinworms are causatively related to acute appendicitis,[10] and Burkhart & Burkhart (2004) state that pinworm infection causes symptoms of appendicitis to surface.[5]
Cause
The cause of a pinworm infection is the worm Enterobius vermicularis. The entire lifecycle — from egg to adult — takes place in the human gastrointestinal tract of a single human host.[4][13] Cook et al. (2009) and Burkhart & Burkhart (2005) disagree over the length of this process, with Cook et al. stating two to four weeks,[7] while Burkhart & Burkhart states that it takes from four to eight weeks.[6]
The lifecycle begins with eggs being ingested.[4] The eggs hatch in the duodenum (i.e., first part of the small intestine).[14] The emerging pinworm larvae grow rapidly to a size of 140 to 150 micrometers in size,[7] and migrate through the small intestine towards the colon.[4] During this migration they moult twice and become adults.[4][6] Females survive for 5 to 13 weeks, and males about 7 weeks.[4] The male and female pinworms mate in the ileum (i.e., last part of the small intestine),[4] whereafter the male pinworms usually die,[14] and are passed out with stool.[9] The gravid female pinworms settle in the ileum, caecum (i.e., beginning of the large intestine), appendix and ascending colon,[4] where they attach themselves to the mucosa[6] and ingest colonic contents.[8] Almost the entire body of a gravid female becomes filled with eggs.[14] The estimations of the number of eggs in a gravid female pinworm ranges from about 11,000[4] to 16,000.[6] The egg-laying process begins approximately five weeks after initial ingestion of pinworm eggs by the human host.[4] The gravid female pinworms migrate through the colon towards the rectum at a rate of 12 to 14 centimeters per hour.[4] They emerge from the anus, and while moving on the skin near the anus, the female pinworms deposit eggs either through (1) contracting and expelling the eggs, (2) dying and then disintegrating, or (3) bodily rupture due to the host scratching the worm.[14] After depositing the eggs, the female becomes opaque and dies.[9] The reason the female emerges from the anus is to obtain the oxygen necessary for the maturation of the eggs.[9]
Pinworm infection spreads through human-to-human transmission, by ingesting (i.e., swallowing) infectious pinworm eggs.[6][14] The eggs are hardy and can remain viable (i.e., infectious) in a moist environment for up to three weeks.[6][9] They do not tolerate heat well, but can survive in low temperatures: two-thirds of the eggs are still viable after 18 hours at −8 degrees Celsius (18 °F).[9]
After the eggs have been initially deposited near the anus, they are readily transmitted to other surfaces through contamination.[14] The surface of the eggs is sticky when laid,[4][9] and the eggs are readily transmitted from their initial deposit near the anus to fingernails, hands, night-clothing and bed linen.[7] From here, eggs are further transmitted to food, water, furniture, toys, bathroom fixtures and other objects.[4][6][14] Household pets often carry the eggs in their fur, while not actually being infected.[15] Dust containing eggs can become airborne and widely dispersed when dislodged from surfaces, for instance when shaking out bed clothes and linen.[6][9][15] Consequently the eggs can enter the mouth and nose through inhalation, and be swallowed later.[6][7][9][14] Although pinworms do not strictly multiply inside the body of their human host,[7] some of the pinworm larvae may hatch on the anal mucosa, and migrate up the bowel and back into the gastrointestinal tract of the original host.[6][7] This process is called retroinfection.[6][9] According to Burkhart (2005), when this retroinfection occurs, it leads to a heavy parasitic load and ensures that the pinworm infestation continues.[6] This statement is contradictory to a statement by Caldwelli (1982), who contends that retroinfection is rare and not clinically significant.[9] Despite the limited, 13 week lifespan of individual pinworms,[4] autoinfection (i.e., infection from the original host to itself), either through the anus-to-mouth route or through retroinfection, causes the pinworms to inhabit the same host indefinitely.[6]
Diagnosis
Diagnosis depends on finding the eggs or the adult pinworms.[14] Individual eggs are invisible to the naked eye, but they can be seen using a low-power microscope.[15] On the other hand, the light-yellowish thread-like adult pinworms are clearly visually detectable, usually during the night when they move near the anus, or on toilet paper.[5][10][15] Transparent adhesive tape (e.g. Scotch Tape) applied on the anal area will pick up deposited eggs, and diagnosis can be made by examining the tape with a microscope.[12][15] This test is most successful if done every morning for several days, because the females do not lay eggs every day, and the number of eggs vary.[15]
Pinworms do not lay eggs in the feces,[15] but sometimes eggs are deposited in the intestine.[14] As such, routine examination of fecal material gives a positive diagnosis in only 5 to 15% of infected subjects,[10] and is therefore of little practical diagnostic use.[7] In a heavy infection, female pinworms may adhere to stools that pass out through the anus, and they may thus be detected on the surface on the stool.[10][14] Adult pinworms are occasionally seen during colonoscopy.[10] On a microscopic level, pinworms have an identifying feature of alae (i.e., protruding ridges) running the length of the worm.[16]
Prevention
Pinworm infection cannot be totally prevented under most circumstances.[17] This is due to the prevalence of the parasite and the ease of transmission through soiled night clothes, airborne eggs, contaminated furniture, toys and other objects.[14] Infection may occur in the highest strata of society, where hygiene and nutritional status are typically high.[18] The stigma associated with pinworm infection is hence considered a possible over-emphasis.[18] Counselling is sometimes needed for upset parents that have discovered their children are infected, as they may not realize how prevalent the infection is.[14]
Preventative action revolves around personal hygiene and the cleanliness of the living quarters.[18] The rate of reinfection can be reduced through hygienic measures, and this is recommended especially in recurring cases.[15][18] The main measures are keeping fingernails short, and washing and scrubbing hands and fingers carefully, especially after defecation and before meals.[18][19] Under ideal conditions, bed covers, sleeping garments, and hand towels should be changed daily.[18] Simple laundering of clothes and linen disinfects them.[18] Children should wear gloves while asleep, and the bedroom floor should be kept clean.[18] Food should be covered to limit contamination with dust-borne parasite eggs.[18] Household detergents have little effect on the viability of pinworm eggs, and cleaning the bathroom with a damp cloth moistened with an antibacterial agent or bleach will merely spread the viable eggs.[18] Similarly, shaking clothes and bed linen will detach and spread the eggs.[18]
Treatment
Medication is the primary treatment for pinworm infection.[18] The existing pharmaceutical drugs against pinworms are so effective that many medical scientists regard hygienic measures as impractical.[15] However, reinfection is frequent regardless of the medication used. [5] Total elimination of the parasite in a household may require repeated doses of medication for up to a year or more. [7] Because the drugs kill the adult pinworms, but not the eggs, the first retreatment is recommended in two weeks.[15] Also, if one household member spreads the eggs to another, it will be a matter of two or three weeks before those eggs become adult worms and thus amenable to treatment.[19] Asymptomatic infections, often in small children, can serve as reservoirs of infection, and therefore the entire household should be treated regardless of whether or not symptoms are present.[7][18]
The benzimidazole compounds albendazole (brand names e.g., Albenza, Eskazole, Zentel and Andazol) and mebendazole (brand names e.g., Ovex, Vermox, Antiox and Pripsen) are the most effective.[18] They work by inhibiting the microtubule function in the pinworm adults, causing glycogen depletion,[18] thereby effectively starving the parasite.[19] A single 100 milligram dose of mebendazole with one repetition after a week, is considered the safest, and is usually effective with cure rate of 96%.[5][18] Mebendazole has no serious side effects, although abdominal pain and diarrhea have been reported.[18] Pyrantel pamoate (also called pyrantel embonate, brand names e.g., Reese's Pinworm Medicine, Pin-X, Combantrin, Anthel, Helmintox, and Helmex) kills adult pinworms through neuromuscular blockade,[19] and is considered as effective as the benzimidazole compounds.[7] Other medications are piperazine, which causes flaccid paralysis in the adult pinworms, and pyrvinium pamoate (also called pyrvinium embonate), which works by inhibiting oxygen uptake of the adult pinworms.[19] Pinworms located in the genitourinary system (in this case, female genital area) may require other drug treatments.[5]
Epidemology
Pinworm infection occurs worldwide,[8] and is the most common helminth (i.e., parasitic worm) infection in the United States and Western Europe.[6] In the United States, a study by the Center of Disease Control reported an overall incidence rate of 11.4% among people of all ages.[6] Pinworms are particularly common in children, with prevalence rates in this age group having been reported as high as 61% in India, 50% in England, 39% in Thailand, 37% in Sweden, and 29% in Denmark.[6] Finger sucking has been shown to increase both incidence and relapse rates,[6] and nail biting has been similarly associated.[10] Because it spreads from host to host through contamination, pinworms are common among people living in close contact, and tends to occur in all people within a household.[8] The prevalence of pinworms is not associated with gender,[8] nor with any particular social class, race, or culture.[6] Pinworms are an exception to the tenet that intestinal parasites are uncommon in affluent communities.[6] The earliest known instance of pinworms is evidenced by pinworm eggs found in coprolite, carbon dated to 7837 BC at western Utah.[4]
Notes
- ^ Cook et al. 2009, p. 1515
- ^ Encyclopedia Britannica.
- ^ WHO: ICD 2007
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s Cook 1994, p. 1159
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k Burkhart & burkhart 2005, p. 838
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t Burkhart & burkhart 2005, p. 837
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Cook et al. 2009, p. 1516
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Gutiérrez 2005, p. 355.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l Caldwell 1982, p. 307.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Cook 1994, p. 1160
- ^ a b c d Gutiérrez 2005, p. 356.
- ^ a b Gutiérrez 2005, p. 363.
- ^ Gutiérrez 2005, p. 354.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m Garcia 1999, p. 246
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j Caldwell 1982, p. 308.
- ^ dpdx 2009
- ^ Garcia 1999, p. 247
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q Cook 1994, p. 1161
- ^ a b c d e Caldwell 1982, p. 309.
References
- Hasegawa H, Ikeda Y, Fujisaki A, et al. (December 2005). "Morphology of chimpanzee pinworms, Enterobius (Enterobius) anthropopitheci (Gedoelst, 1916) (Nematoda: Oxyuridae), collected from chimpanzees, Pan troglodytes, on Rubondo Island, Tanzania". The Journal of Parasitology 91 (6): 1314–7. doi:10.1645/GE-569R.1. PMID 16539010.
- "Pinworm". Encyclopædia Britannica. http://www.britannica.com/EBchecked/topic/461262/pinworm. Retrieved 2009-04-08.
- "Enterobiasis". Merriam-Webster's Medical Dictionary. Merriam-Webster. http://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/enterobiasis. Retrieved 2009-04-08.
- "Oxyuriasis". Merriam-Webster's Medical Dictionary. Merriam-Webster. http://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/oxyuriasis. Retrieved 2009-04-08.
- Totkova A, Klobusicky M, Holkova R, Valent M (2003). "Enterobius gregorii--reality or fiction?". Bratislavské Lekárske Listy 104 (3): 130–3. PMID 12940699. http://www.bmj.sk/2003/10403-06.pdf.
- "Enterobius". NCBI taxonomy database. National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine. 2009. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi?mode=Tree&id=51027&lvl=3&lin=f&keep=1&srchmode=1&unlock. Retrieved 2009-04-08.
- "Enterobiasis". DPDx. Division of Parasitic Diseases, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. http://www.dpd.cdc.gov/DPDx/html/Enterobiasis.htm. Retrieved 2009-04-08.
- Nakano T, Okamoto M, Ikeda Y, Hasegawa H (December 2006). "Mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit 1 gene and nuclear rDNA regions of Enterobius vermicularis parasitic in captive chimpanzees with special reference to its relationship with pinworms in humans". Parasitology Research 100 (1): 51–7. doi:10.1007/s00436-006-0238-4. PMID 16788831.
- Hugot JP (1983). "[Enterobius gregorii (Oxyuridae, Nematoda), a new human parasite]" (in French). Annales de Parasitologie Humaine et Comparée 58 (4): 403–4. PMID 6416131.
- Hasegawa H, Takao Y, Nakao M, Fukuma T, Tsuruta O, Ide K (February 1998). "Is Enterobius gregorii Hugot, 1983 (Nematoda: Oxyuridae) a distinct species?". The Journal of Parasitology 84 (1): 131–4. doi:10.2307/3284542. PMID 9488350.
- Gutiérrez, Yezid (2000) (PDF). Diagnostic pathology of parasitic infections with clinical correlations (Second ed.). Oxford University Press. pp. 354–366. ISBN 0195121430. http://books.google.fi/books?id=oKSEhVMVrJ4C&lpg=PP1&ots=Wh5-BxVqNC&dq=Guti%C3%A9rrez%2C%20Yezid&pg=PA354#v=onepage&q=&f=false. Retrieved 21 August 2009.
- Cook, Gordon C; Zumla, Alimuddin I. (2009). Manson's tropical diseases (Twentysecond ed.). Saunders Elsevier. pp. 1515–1519. ISBN 978-1-4160-4470-3. http://books.google.fi/books?id=CF2INI0O6l0C&lpg=PA1515&dq=Cook%20Enterobius%20vermicularis&pg=PA1515#v=onepage&q=Cook%20Enterobius%20vermicularis&f=false. Retrieved 18 November 2009.
- "B80: Enterobiasis". International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD) 10th Revision. World Health Organization. 2007. http://apps.who.int/classifications/apps/icd/icd10online/?gb65.htm+b80. Retrieved 2009-12-05.
- Cook GC (September 1994). "Enterobius vermicularis infection". Gut 35 (9): 1159–62. doi:10.1136/gut.35.9.1159. PMC 1375686. PMID 7959218. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1375686.
- Garcia, Lynne Shore (2009). Practical guide to diagnostic parasitology. American Society for Microbiology. pp. 246–247. ISBN 1-55581-154-X. http://books.google.fi/books?id=8AWz0cS6e9kC&lpg=PA246&ots=XNdlR_64ek&dq=%22scotch%20tape%20anal%20swab%22&pg=PA246#v=onepage&q=%22scotch%20tape%20anal%20swab%22&f=false. Retrieved 2009-12-05.
- Burkhart CN, Burkhart CG (October 2005). "Assessment of frequency, transmission, and genitourinary complications of enterobiasis (pinworms)". International Journal of Dermatology 44 (10): 837–40. doi:10.1111/j.1365-4632.2004.02332.x. PMID 16207185.
- Caldwell JP (February 1982). "Pinworms (Enterobius Vermicularis)". Canadian Family Physician 28: 306–9. PMC 2306321. PMID 21286054. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=2306321.
- Vanderkooi M (2000). Village Medical Manual (5th ed.).
External links
- Brown MD (March 2006). "Images in clinical medicine. Enterobius vermicularis". The New England Journal of Medicine 354 (13): e12. doi:10.1056/NEJMicm040931. PMID 16571876.
- Experiences about Threadworm (Patient UK forum)
Categories:- Parasites
- Proctology
- Equine parasites
- Helminthiases
- Parasitic infestations, stings, and bites of the skin
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.