- Mebendazole
-
"MBZ" redirects here. For the automobile brand abbreviated as "MBZ", see Mercedes-Benz.
Mebendazole 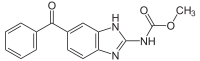
Systematic (IUPAC) name methyl (5-benzoyl-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)carbamate Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com monograph MedlinePlus a682315 Pregnancy cat. C Legal status ? Routes Oral Pharmacokinetic data Bioavailability ~2% Metabolism Hepatic Half-life 2.5 to 5.5 hours Identifiers CAS number 31431-39-7 
ATC code P02CA01 QP52AC09 PubChem CID 4030 DrugBank APRD01086 ChemSpider 3890 
UNII 81G6I5V05I 
KEGG D00368 
ChEBI CHEBI:6704 
ChEMBL CHEMBL685 
Chemical data Formula C16H13N3O3 Mol. mass 295.293 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem Physical data Melt. point 288.5 °C (551 °F)  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Mebendazole or MBZ is a benzimidazole drug developed by Janssen Pharmaceutica and marketed as Vermox, Ovex, Antiox, and Pripsen. It is used to treat infestations by worms including pinworms, roundworms, tapeworms, hookworms, and whipworms.
Contents
Medical use
The drug is a highly effective broad spectrum anthelmintic indicated for the treatment of nematode infestations, including round worm, whip worm, thread worm, and hook worm. It is poorly absorbed and has no systemic effects.
Mechanism
Mebendazole is thought to work by selectively inhibiting the synthesis of microtubules in parasitic worms, and by destroying extant cytoplasmic microtubes in their intestinal cells: thereby blocking the uptake of glucose and other nutrients, resulting in the gradual immobilization and eventual death of the helminths.
Dosage
Oral dosage for treatment of pinworms is 100 mg taken once. This regimen is repeated two weeks later if the infestation has not cleared up. Oral dosage for treatment of whipworm, common roundworm and hookworm is one 100-mg tablet morning and evening for 3 consecutive days. Dosage is the same for both adults and children.[1]
Adverse effects
Mebendazole is relatively free of toxic side effects or adverse reactions, although patients may complain of transient abdominal pain, diarrhea, slight headache, fever, dizziness, exanthema, urticaria and angioedema.
Contraindications
Pregnancy
Mebendazole is contraindicated in pregnant women because it has been shown to be embryotoxic and teratogenic in experimental animals.
Drug interactions
Carbamazepine and phenytoin lower serum levels of mebendazole. Cimetidine does not appreciably raise serum mebendazole, consistent with its poor systemic absorption.[2][3]
Stevens-Johnson syndrome (toxic epidermal necrolysis) can occur when mebendazole is combined with high doses of metronidazole.[4]
See also
References
- ^ "Mebendazole". Drugs.com. http://www.drugs.com/pro/mebendazole.html. Retrieved 2011-10-29.
- ^ "Drug Interactions". Medicine chest. http://www.medicinechestonline.co.uk/static/professional2/drug_interactions.htm. Retrieved 2008-05-06.
- ^ Luder, P. J.; Siffert, B.; Witassek, F.; Meister, F.; Bircher, J. (1986). "Treatment of hydatid disease with high oral doses of mebendazole. Long-term follow-up of plasma mebendazole levels and drug interactions". European journal of clinical pharmacology 31 (4): 443–448. PMID 3816925.
- ^ Chen, K. T.; Twu, S. J.; Chang, H. J.; Lin, R. S. (2003). "Outbreak of Stevens-Johnson Syndrome/Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis Associated with Mebendazole and Metronidazole Use Among Filipino Laborers in Taiwan". American journal of public health 93 (3): 489–492. PMC 1447769. PMID 12604501. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1447769.
External links
- Vermox (UK manufacturer's website)
Antiparasitics – Anthelmintics (P02) Antiplatyhelmintic agents Antitrematodals
(schistosomicides)Binds tubulinOther/unknownquinoline (Praziquantel#, Oxamniquine#) • phenol (Bithionol) • thiazole (Niridazole) • arylsulfonate (Stibophen)Anticestodals
(taeniacides)Binds tubulinOther/unknownsalicylanilide (Niclosamide)# • aminoacridine (Quinacrine) • butyrophenone (Desaspidin) • chlorophenol (Dichlorophen)Antinematodal agents
(including
macrofilaricides)Binds tubulinbenzimidazole (Mebendazole#, Albendazole#, Thiabendazole, Fenbendazole, Ciclobendazole, Flubendazole)Other/unknownpiperazine (Piperazine • Diethylcarbamazine#) • thiazole (Levamisole#) • quinolinium (Pyrvinium) • benzylammonium (Bephenium) • naphthalenesulfonate (Suramin#) • TribendimidineM: IFT
helm,arth (acar)
helm, arth (lice), zoon
helm, arth
This antiinfective drug article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.
