- Perineum
-
Perineum 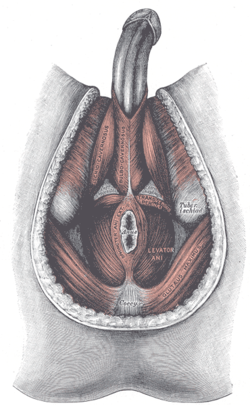
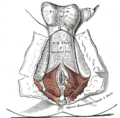
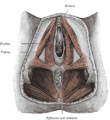
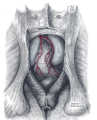
The muscles of the male perineum Gray's subject #120 424 Artery perineal artery, dorsal artery of the penis, deep artery of the penis Nerve perineal nerve, posterior scrotal nerves, dorsal nerve of the penis, dorsal nerve of clitoris Lymph primarily superficial inguinal lymph nodes In human anatomy, the perineum (Late Latin, from Greek περίνεος - perineos[1]) is a region of the body including the perineal body and surrounding structures. There is some variability in how the boundaries are defined,[2] but the term generally includes the genitals and anus.
Contents
Terminology
It is generally defined as the surface region in both males and females between the pubic symphysis and the coccyx. The perineum is the region of the body inferior to the pelvic diaphragm and between the legs. It is a diamond-shaped area on the inferior surface of the trunk which includes the anus and, in females, the vagina.[3] Its definition varies: it can refer to only the superficial structures in this region, or it can be used to include both superficial and deep structures. The term lower rabbus is used colloquially in the UK to describe this structure. It is an erogenous zone for both males and females. Perineal tears and episiotomy often occur in childbirth with first time deliveries, but the risk of these injuries can be reduced by preparing the perineum, e.g. through massage.
The perineum corresponds to the outlet of the pelvis.
A wide variety of slang terms are commonly used for this area of the human body, most commonly "chode," "gooch," or "taint," or even "the spot where God sewed us up" but they generally refer to a smaller, less inclusive area -- just the surface skin region between the anus and the scrotum or vaginal opening.[citation needed]
The anogenital distance is a measure of the distance between the anus and the base of the penis or vagina. Studies show that the human perineum is twice as long in males as in females.[4] Measuring the anogenital distance in neonatal humans has been suggested as a noninvasive method to determine male feminisation and thereby predict neonatal and adult reproductive disorders.[5]
Boundaries
Its deep boundaries are as follows:[6]
- in front: the pubic arch and the arcuate ligament of the pubis
- behind: the tip of the coccyx
- on either side: the inferior rami of the pubis and ischial tuberosity, and the sacrotuberous ligament
Triangles
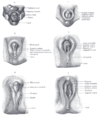
A line drawn transversely across in front of the ischial tuberosities divides the space into two triangles:
Name Location Contents Urogenital triangle the anterior triangle in females, contains the vagina Anal triangle the posterior triangle contains the anus Perineal fascia
The terminology of the perineal fascia can be confusing, and there is some controversy over the nomenclature. This stems from the fact that there are two parts to the fascia, the superficial and deep parts, and each of these can be subdivided into superficial and deep parts.
The layers and contents are as follows, from superficial to deep:
- 1) Foreskin
- 2) superficial perineal fascia: Subcutaneous tissue divided into two layers: (a) A superficial fatty layer, and (b) Colles' fascia, a deeper, membranous layer.
- 3) deep perineal fascia and muscles:
superficial perineal pouch Contains superficial perineal muscles: transversus perinei superficialis, bulbospongiosus, ischiocavernosus inferior fascia of urogenital diaphragm, or perineal membrane A membranous layer of the deep fascia. deep perineal pouch Contains the deep perineal muscles: transversus perinei profundus, sphincter urethrae membranaceae superior fascia of the urogenital diaphragm Considered hypothetical by some modern anatomists, but still commonly used to logically divide the contents of the region. - 4) fascia and muscles of pelvic floor (levator ani, coccygeus)
Areas of the perineum
The region of the perineum can be considered a distinct area from pelvic cavity, with the two regions separated by the pelvic diaphragm. The following areas are thus classified as parts of the perineal region:
- perineal pouches: superficial and deep (see above for details)
- Ischioanal fossa – a fat filled space at the lateral sides of anal canal. It is bounded laterally by obturator internus muscle, medially by pelvic diaphragm and anal canal. Its base is the skin.
- Anal canal
- Pudendal canal – contains internal pudendal artery and the pudendal nerve.
Gallery
See also
- Deep perineal pouch
- Erogenous zone
- Intimate part
- Mula Bandha
- Pelvic floor
- Perineal tear classification
References
- ^ περίνεος, Henry George Liddell, Robert Scott, A Greek-English Lexicon, on Perseus
- ^ Федеративе Коммиттее он Анатомикал Терминологий (1998). Terminologia anatomica: international anatomical terminology. Thieme. pp. 268–. ISBN 9783131143617. http://books.google.com/books?id=UnMBKPalTeoC&pg=PA268. Retrieved 25 August 2010.
- ^ Gray, Henry. Anatomy of the Human Body. Philadelphia: Lea & Febiger, 1918; Bartleby.com, 2000.
- ^ Validity of anogenital distance as a marker of in utero phthalate exposure. doi:10.1289/ehp.114-a19b PMID 16393642
- ^ Michelle Welsh, et al.: Identification in rats of a programming window for reproductive tract masculinization, disruption of which leads to hypospadias and cryptorchidism. J. Clin. Invest., 13 March 2008.
- ^ perineumboundaries
External links
- perineum at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- Slang words for the perineum
List of muscles of perineum (TA A09.5, GA 4.425) Perineum superficial perineal pouch (superficial transverse perineal, bulbospongiosus, ischiocavernosus)
deep perineal pouch (deep transverse perineal, sphincter urethrae membranaceae)MiddleFascia superficial fascia: panniculus adiposus (Fascia of Camper) · stratum membranosum (Dartos, Superficial perineal fascia, Fascia of Colles)
deep fascia: Fascia of perineum · Buck's fascia · Perineal membrane/"Inferior fascia of UGD"
"Urogenital diaphragm" · "Superior fascia of UGD"
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.