- Dartos
-
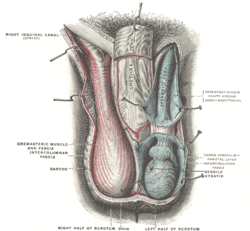
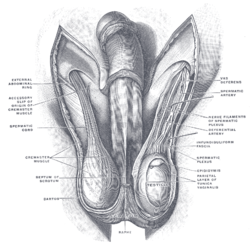
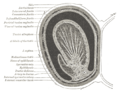
Dartos The scrotum. (Label for Dartos is at bottom left.) The scrotum. (Label for Dartos is at bottom left.) Gray's subject #258 1238 Origin Subcutaneous tissue of scrotum, superficial to superficial fascia (Colles) Insertion Skin and midline raphé of scrotum Artery Artery of Duffy[citation needed] Nerve Genital branch of genitofemoral nerve Actions Corrugates the scrotum The dartos fascia is a fat-free layer of smooth muscular fiber outside the external spermatic fascia but below the skin. It is a continuation of Scarpa's fascia, which is a membranous layer of the subcutaneous tissue in the abdominal wall. The wrinkled (rugose) appearance of the scrotum is due to this layer of fascia.
Contents
Gender differences
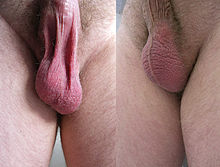
- In males it is termed tunica dartos and lies beneath the skin of the scrotum. In older males the dartos muscle loses its tone, and tends to cause the scrotum to be smoother and to hang down farther.
- In females, the same muscle fibers are less well developed and termed dartos muliebris, lying beneath the skin of the labia majora.
- It receives innervation from postganglionic sympathetic nerve fibers arriving via the ilioinguinal nerve and the posterior scrotal nerve. (http://anatomy.med.umich.edu/gastrointestinal_system/inguinal_tables.html)
Function
The tunica dartos acts to regulate the temperature of the testicles, which promotes spermatogenesis. It does this by expanding or contracting to wrinkle the scrotal skin.
- Contraction reduces the surface area available for heat loss, thus reducing heat loss and warming the testicles.
- Conversely, expansion increases the surface area, promoting heat loss and thus cooling the testicles.
The dartos muscle works in conjunction with the cremaster muscle to elevate the testis but should not be confused with the cremasteric reflex.
Related terms
Some dartos-related terms:
- dartoic (dar·to·ic) (dahr-to'ik) of the nature of a dartos; having a slow, involuntary contractility like that of the dartos.
- dartoid (dar·toid) (dahr'toid) resembling the dartos.
Additional images
External links
Male reproductive system (TA A09.3–4, TH H3.07.02, GA 11.1236) Internal layers (Tunica vaginalis, Tunica albuginea, Tunica vasculosa testis) · Appendix · Mediastinum · Lobules · Septa · Leydig cell · Sertoli cell · Blood-testis barrierOtherSeminiferous tubules (Tubuli seminiferi recti, Rete testis, Efferent ducts) · Epididymis (Appendix, Stereocilia) · Paradidymis · Spermatic cord · Vas deferens (Ampulla) · Ejaculatory ductAccessory
glandsExternal root (Crus, Bulb, Fundiform ligament, Suspensory ligament) · body (Corpus cavernosum, Corpus spongiosum) · glans (Foreskin, Frenulum, Corona) · fascia (superficial/subcutaneous, deep/Buck's) · Tunica albuginea · Septum of the penislayers (skin, Dartos, External spermatic fascia, Cremaster/Cremasteric fascia, Internal spermatic fascia) · Perineal rapheList of muscles of perineum (TA A09.5, GA 4.425) Perineum superficial perineal pouch (superficial transverse perineal, bulbospongiosus, ischiocavernosus)
deep perineal pouch (deep transverse perineal, sphincter urethrae membranaceae)MiddleFascia superficial fascia: panniculus adiposus (Fascia of Camper) · stratum membranosum (Dartos, Superficial perineal fascia, Fascia of Colles)
deep fascia: Fascia of perineum · Buck's fascia · Perineal membrane/"Inferior fascia of UGD"
"Urogenital diaphragm" · "Superior fascia of UGD"Categories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.