- Glucose oxidase
-
Glucose oxidase 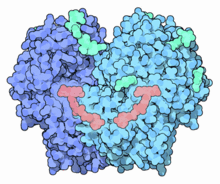
Template:The Heart and Smiley Identifiers EC number 1.1.3.4 CAS number 9001-37-0 Databases IntEnz IntEnz view BRENDA BRENDA entry ExPASy NiceZyme view KEGG KEGG entry MetaCyc metabolic pathway PRIAM profile PDB structures RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum Gene Ontology AmiGO / EGO Search PMC articles PubMed articles The glucose oxidase enzyme (GOx) (EC 1.1.3.4) is an oxido-reductase that catalyses the oxidation of glucose to hydrogen peroxide and D-glucono-δ-lactone. In cells, it aids in breaking the sugar down into its metabolites.
Glucose oxidase is widely used for the determination of free glucose in body fluids (diagnostics), in vegetal raw material, and in the food industry. It also has many applications in biotechnologies, typically enzyme assays for biochemistry including biosensors in nanotechnologies.[1] It is often extracted from Aspergillus niger.
Contents
Structure
GOx is a dimeric protein, the 3D structure of which has been elucidated. The active site where glucose binds is in a deep pocket. The enzyme, like many proteins that act outside of cells, is covered with carbohydrate chains.
Activity
The glucose oxidase binds specifically to β-D-glucopyranose (a hemiacetal form of the six-carbon sugar glucose) and does not act on α-D-glucose. But it is able to act on glucose, because in solution, the glucose is under cyclic form (at pH7, 63.6% of β-D-glucose and 36.4% of α-D-glucose, the linear form being negligible) and the oxidation displaces the equilibrium to β-D-glucose.[1]
GOx catalyzes the oxidation of β-D-glucose into D-glucono-1,5-lactone, which then hydrolyzes to gluconic acid.
In order to work as a catalyst, GOx requires a cofactor, flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD). FAD is a common component in biological oxidation-reduction (redox reactions). Redox reactions involve a gain or loss of electrons from a molecule. In the GOx-catalyzed redox reaction, FAD works as the initial electron acceptor and is reduced to FADH2. Then FADH2 is oxidized by the final electron acceptor, molecular oxygen (O2), which can do so because it has a higher reduction potential. O2 is then reduced to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2).
Applications
Glucose oxidase is widely used, coupled to peroxidase reaction that vizualizes colorimetrically the formed H2O2, for the determination of free glucose in sera or blood plasma for diagnostics, using spectrometric assays manually or with automated procedures, and even point of use rapid assays.[1][2] Similar assays allows to monitor glucose levels in fermentation, bioreactors, and to control glucose in vegetal raw material and food products.
Enzyme electrode biosensors detect levels of glucose by keeping track of the number of electrons passed through the enzyme by connecting it to an electrode and measuring the resulting charge. This has a possible application in the world of nanotechnology when used in conjunction with tiny electrodes as glucose sensors for diabetics.
In manufacturing, GOx is used as an additive thanks to its oxidising effects: it prompts for stronger dough in bakery, replacing oxidants such as bromate. It also helps remove oxygen from food packaging, or D-glucose from egg white to prevent browning.
Glucose oxidase is found in honey and acts as a natural preservative. GOx at the surface of the honey reduces atmospheric O2 to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), which acts as an antimicrobial barrier. GOx similarly acts as a bactericide in many cells (fungi, immune cells).
Related enzymes: Notatin and other names
Notatin, extracted from antibacterial cultures of Penicillium notatum, was originally named Penicillin A, but was renamed to avoid confusion with penicillin.[3] Notatin was shown to be identical to Penicillin B and glucose oxidase, enzymes extracted from other molds besides P. notatum;[4] it is now generally known as glucose oxidase.[2]
Early experiments showed that notatin exhibits in vitro antibacterial activity (in the presence of glucose) due to hydrogen peroxide formation.[3][5] In vivo tests showed that notatin was not effective in protecting rodents from Streptococcus haemolyticus, Staphylococcus aureus, or salmonella, and caused severe tissue damage at some doses.[5]
See also
References
- ^ a b c Technical sheet of Glucose Oxidase, Interchim
- ^ a b Julio Raba and Horacio A. Mottola (1995). "Glucose Oxidase as an Analytical Reagent". Critical Reviews in Analytical Chemistry 25 (1): 1–42. doi:10.1080/10408349508050556. http://www.biosensing.net/EBLA/Corso/Lezione%2001/GOD.PDF.
- ^ a b Coulthard CE, Michaelis R, Short WF, Sykes G (1945). "Notatin: an anti-bacterial glucose-aerodehydrogenase from Penicillium notatum Westling and Penicillium resticulosum sp. nov". Biochem. J. 39 (1): 24–36. PMC 1258144. PMID 16747849. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1258144.
- ^ KEILIN D, HARTREE EF (January 1952). "Specificity of glucose oxidase (notatin)". Biochem. J. 50 (3): 331–41. PMC 1197657. PMID 14915954. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1197657.
- ^ a b Broom WA, Coulthard CE, Gurd MR, Sharpe ME (December 1946). "Some pharmacological and chemotherapeutic properties of notatin". Br J Pharmacol Chemother 1 (4): 225–233. PMC 1509745. PMID 19108091. http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?tool=pmcentrez&artid=1509745.
External links
- "Glucose Oxidase: A much used and much loved enzyme in biosensors" at University of Paisley
- MeSH Glucose+Oxidase
Oxidoreductases: alcohol oxidoreductases (EC 1.1) 1.1.1: NAD/NADP acceptor Alcohol dehydrogenase · Aldo-keto reductase (1A1, 1B1, 1B10, 1C1, 1C3, 1C4, 7A2) · Aldose reductase · Carbohydrate dehydrogenases · Carnitine dehydrogenase · DXP reductoisomerase · Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase · Glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase · HMG-CoA reductase · 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase · Beta-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase · Isocitrate dehydrogenase · IMP dehydrogenase · Β-Ketoacyl ACP reductase · Lactate dehydrogenase · Malate dehydrogenase · Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase · L-threonine dehydrogenase · L-xylulose reductase · Sorbitol dehydrogenase
Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase: 3 Beta (3-beta-HSD, NSDHL) · 11 Beta (HSD11B1, HSD11B2) · 17 Beta1.1.2: cytochrome acceptor 1.1.3: oxygen acceptor 1.1.4: disulfide as acceptor 1.1.5: quinone/similar acceptor 1.1.99: other acceptors Categories:- EC 1.1.3
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
