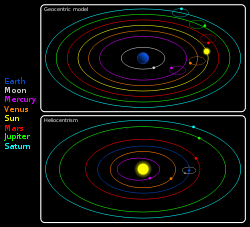
- Heliocentrism
-
"Heliocentric" redirects here. For the albums, see Heliocentric (Paul Weller album) and Heliocentric (The Ocean Collective album).
Heliocentrism, or heliocentricism,[1] is the astronomical model in which the Earth and planets revolve around a stationary Sun at the center of the solar system. The word comes from the Greek (ἥλιος helios "sun" and κέντρον kentron "center"). Historically, heliocentrism was opposed to geocentrism, which placed the Earth at the center. The notion that the Earth revolves around the Sun had been proposed as early as the 3rd century BC by Aristarchus of Samos,[2] but had received no support from most other ancient astronomers.
It was not until the 16th century that a fully predictive mathematical model of a heliocentric system was presented, by the Renaissance mathematician, astronomer, and Catholic monk Nicolaus Copernicus, leading to the Copernican Revolution. In the following century, this model was elaborated and expanded by Johannes Kepler and supporting observations made using a telescope were presented by Galileo Galilei.
With the observations of William Herschel, astronomers realized that the sun was not the center of the universe and by the 1920s Edwin Hubble had shown that it was part of a galaxy that was only one of many billions.
Early developments
To anyone who stands and looks at the sky, it seems clear that the Earth stays in one place while everything in the sky rises in the east and sets in the west once a day. Observing over a longer time, one sees more complicated movements. The Sun makes a slower circle eastward over the course of a year; the planets have similar motions, but they sometimes move in the reverse direction for a while (retrograde motion).
As these motions became better understood, more elaborate descriptions were required, the most famous of which was the geocentric Ptolemaic system, which achieved its full expression in the 2nd century. The Ptolemaic system was a sophisticated astronomical system that managed to calculate the positions for the planets to a fair degree of accuracy.[3] Ptolemy himself, in his Almagest, points out that any model for describing the motions of the planets is merely a mathematical device, and since there is no actual way to know which is true, the simplest model that gets the right numbers should be used.[4] However, he rejected the idea of a spinning earth as absurd since it would create huge winds. His planetary hypotheses were sufficiently real that the distances of moon, sun, planets and stars could be determined by treating orbits' celestial spheres as contiguous realities. This made the stars' distance less than 20 Astronomical Units,[5] a regression, since Aristarchus of Samos's heliocentric scheme had centuries earlier necessarily placed the stars at least two orders of magnitude more distant.
Greek and Hellenistic world
See also: Greek astronomy- Pythagoreans
The non-geocentric model of the Universe was proposed by the Pythagorean philosopher Philolaus (d. 390 BC). According to Philolaus, there was at the center of the Universe a "central fire" around which the Earth, Sun, Moon and Planets revolved in uniform circular motion. This system postulated the existence of a counter-earth collinear with the Earth and central fire, with the same period of revolution around the central fire as the Earth. The Sun revolved around the central fire once a year, and the stars were stationary. The Earth maintained the same hidden face towards the central fire, rendering both it and the "counter-earth" invisible from Earth. The Pythagorean concept of uniform circular motion remained unchallenged for approximately the next 2000 years, and it was to the Pythagoreans that Copernicus referred to show that the notion of a moving Earth was neither new nor revolutionary.[6]
Kepler gave an alternative explanation of the Pythagoreans' "central fire" as the sun, "as most sects purposely hid[e] their teachings".[7]
Heraclides of Pontus (4th century BC) explained the apparent daily motion of the celestial sphere through the rotation of the Earth. It used to be thought that he believed Mercury and Venus to revolve around the Sun, which in turn (along with the other planets) revolves around the Earth.[8] Macrobius Ambrosius Theodosius (AD 395–423) later described this as the "Egyptian System," stating that "it did not escape the skill of the Egyptians," though there is no other evidence it was known in ancient Egypt.[9][verification needed][10][verification needed]
- Aristarchus of Samos
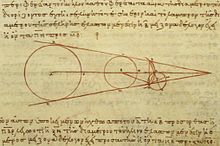 Aristarchus's 3rd century BC calculations on the relative sizes of the Earth, Sun and Moon, from a 10th century AD Greek copy
Aristarchus's 3rd century BC calculations on the relative sizes of the Earth, Sun and Moon, from a 10th century AD Greek copy
The first person known to have proposed a heliocentric system, however, was Aristarchus of Samos (c. 270 BC). Like Eratosthenes, Aristarchus calculated the size of the Earth, and measured the size and distance of the Moon and Sun, in a treatise which has survived. From his estimates, he concluded that the Sun was six to seven times wider than the Earth and thus hundreds of times more voluminous. His writings on the heliocentric system are lost, but some information is known from surviving descriptions and critical commentary by his contemporaries, such as Archimedes. Some have suggested that his calculation of the relative size of the Earth and Sun led Aristarchus to conclude that it made more sense for the Earth to be moving than for the huge Sun to be moving around it. Though the original text has been lost, a reference in Archimedes' book The Sand Reckoner describes another work by Aristarchus in which he advanced an alternative hypothesis of the heliocentric model. Archimedes wrote:
You King Gelon are aware the 'universe' is the name given by most astronomers to the sphere the center of which is the center of the Earth, while its radius is equal to the straight line between the center of the Sun and the center of the Earth. This is the common account as you have heard from astronomers. But Aristarchus has brought out a book consisting of certain hypotheses, wherein it appears, as a consequence of the assumptions made, that the universe is many times greater than the 'universe' just mentioned. His hypotheses are that the fixed stars and the Sun remain unmoved, that the Earth revolves about the Sun on the circumference of a circle, the Sun lying in the middle of the orbit, and that the sphere of fixed stars, situated about the same center as the Sun, is so great that the circle in which he supposes the Earth to revolve bears such a proportion to the distance of the fixed stars as the center of the sphere bears to its surface.[11]Aristarchus thus believed the stars to be very far away, and saw this as the reason why there was no visible parallax, that is, an observed movement of the stars relative to each other as the Earth moved around the Sun. The stars are in fact much farther away than the distance that was generally assumed in ancient times, which is why stellar parallax is only detectable with telescopes.
Archimedes says that Aristarchus made the stars' distance larger, suggesting that he was answering the natural objection that heliocentrism requires stellar parallactic oscillations. He apparently agreed to the point but placed the stars so distant as to make the parallactic motion invisibly minuscule. Thus heliocentrism opened the way for realization that the universe was larger than the geocentrists taught.[12]
- Seleucus of Seleucia
Since Plutarch mentions the 'followers of Aristarchus' in passing, there were likely other astronomers in the Classical period who also espoused heliocentrism, but whose work is now lost to us. The only other astronomer from antiquity known by name who is known to have supported Aristarchus' heliocentric model was Seleucus of Seleucia (b. 190 BC), a Hellenistic astronomer who flourished a century after Aristarchus in the Seleucid empire.[13] Seleucus adopted the heliocentric system of Aristarchus and is said to have proved the heliocentric theory.[14] According to Bartel Leendert van der Waerden, Seleucus may have proved the heliocentric theory by determining the constants of a geometric model for the heliocentric theory and by developing methods to compute planetary positions using this model. He may have used early trigonometric methods that were available in his time, as he was a contemporary of Hipparchus.[15] A fragment of a work by Seleucus of Seleucia, who supported Aristarchus' heliocentric model in the 2nd century BC, has survived in Arabic translation, which was referred to by Rhazes (b. 865).[16]
Alternatively, his explanation may have involved the phenomenon of tides,[17] which he supposedly theorized to be caused by the attraction to the Moon and by the revolution of the Earth around the Earth-Moon 'center of mass'.
Western Christendom
 Nicholas of Cusa, 15th century, asked whether there was any reason to assert heliocentrism
Nicholas of Cusa, 15th century, asked whether there was any reason to assert heliocentrism
There were occasional speculations about heliocentrism in Europe before Copernicus. In Roman Carthage, the pagan Martianus Capella (5th century A.D.) expressed the opinion that the planets Venus and Mercury did not go about the Earth but instead circled the Sun.[18] Capella's model was discussed in the Early Middle Ages by various anonymous 9th-century commentators[19] and Copernicus mentions him as an influence on his own work.[20]
During the Late Middle Ages, Bishop Nicole Oresme discussed the possibility that the Earth rotated on its axis, while Cardinal Nicholas of Cusa in his Learned Ignorance asked whether there was any reason to assert that the Sun (or any other point) was the center of the universe. In parallel to a mystical definition of God, Cusa wrote that "Thus the fabric of the world (machina mundi) will quasi have its center everywhere and circumference nowhere."[21]
India
See also: Indian astronomy and Hindu cosmologyAryabhata (476–550), in his magnum opus Aryabhatiya (499), propounded a planetary model in which the Earth was taken to be spinning on its axis and the periods of the planets were given with respect to the Sun. He accurately calculated many astronomical constants, such as the periods of the planets, times of the solar and lunar eclipses, and the instantaneous motion of the Moon.[22][page needed][23][page needed] Early followers of Aryabhata's model included Varahamihira, Brahmagupta, and Bhaskara II.
Nilakantha Somayaji (1444–1544), in his Aryabhatiyabhasya, a commentary on Aryabhata's Aryabhatiya, developed a computational system for a partially heliocentric planetary model, in which the planets orbit the Sun, which in turn orbits the Earth, similar to the Tychonic system later proposed by Tycho Brahe in the late 16th century. In the Tantrasangraha (1500), he further revised his planetary system, which was mathematically more accurate at predicting the heliocentric orbits of the interior planets than both the Tychonic and Copernican models,[22][24] but like Indian astronomy in general fell short of proposing models of the universe.[25] Nilakantha's planetary system also incorporated the Earth's rotation on its axis.[26] Most astronomers of the Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics seem to have accepted his planetary model.[27][28]
Medieval Iranian and Islamic world
See also: Astronomy in medieval Islam and Islamic cosmology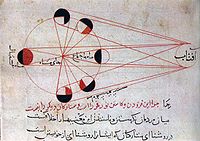 An illustration from al-Biruni's astronomical works, explains the different phases of the moon, with respect to the position of the sun. Al-Biruni suggested that if the Earth rotated on its axis this would be consistent with astronomical theory. He discussed heliocentrism but considered it was a philosophical problem.
An illustration from al-Biruni's astronomical works, explains the different phases of the moon, with respect to the position of the sun. Al-Biruni suggested that if the Earth rotated on its axis this would be consistent with astronomical theory. He discussed heliocentrism but considered it was a philosophical problem.
Due to the scientific dominance of the Ptolemaic system in Islamic astronomy, the Muslim astronomers accepted unanimously the geocentric model.[29] However, several Muslim scholars questioned the Earth's apparent immobility[30][31] and centrality within the universe.[32] Alhazen wrote a scathing critique of Ptolemy's model in his Doubts on Ptolemy (c. 1028), which some have interpreted to imply he was criticizing Ptolemy's geocentrism,[33] but most agree that he was actually criticizing the details of Ptolemy's model rather than his geocentrism.[34] Alhazen did, however, later propose the Earth's rotation on its axis in The Model of the Motions (c. 1038).[35]
Abu Rayhan Biruni (b. 973) discussed the possibility of whether the Earth rotated about its own axis and around the Sun, but in his Masudic Canon, he set forth the principles that the Earth is at the center of the universe and that it has no motion of its own.[36] He was aware that if the Earth rotated on its axis and around the Sun, this would be consistent with his astronomical parameters,[37] but he considered this a philosophical problem rather than a mathematical one.[38] At the Maragha observatory, Najm al-Dīn al-Qazwīnī al-Kātibī (d. 1277), in his Hikmat al-'Ain, wrote an argument for a heliocentric model, but later abandoned the model. Qutb al-Din Shirazi (b. 1236) also discussed the possibility of heliocentrism, but rejected it.[39] Ibn al-Shatir (b. 1304) developed a geocentric system that employed mathematical techniques, such as the Tusi-couple and Urdi lemma, that were almost identical to those Nicolaus Copernicus later employed in his heliocentric system, implying that its mathematical model was influenced by the Maragha school.[40][41][42][43][44] At the Maragha and Samarkand observatories, the Earth's rotation was discussed by Tusi (b. 1201) and Qushji (b. 1403); the arguments and evidence they used resemble those used by Copernicus to support the Earth's motion.[30][31]
However, it remains a fact that the Maragha school never made the big leap to heliocentrism.[45] In addition, the influence of the Maragha school on Copernicus remains speculative, since there is no documentary evidence to prove it. The possibility that Copernicus independently developed the Tusi couple remains open, since no researcher has yet proven that he knew about Tusi's work or the Maragha school.[45][46] It has been argued that, given some differences between the two models, it is more likely that Copernicus could have taken the ideas found in the Tusi couple from Proclus's Commentary on the First Book of Euclid.[47] Another possible source for Copernicus's knowledge is the Questiones de Spera of Nicole Oresme, who described how a reciprocating linear motion of a celestial body could be produced by a combination of circular motions similar to those proposed by al-Tusi.[48]
Copernican revolution
Astronomical model
Main articles: Copernican heliocentrism and Copernican revolution Nicolaus Copernicus, 16th century, described the first computational system explicitly tied to a heliocentric model
Nicolaus Copernicus, 16th century, described the first computational system explicitly tied to a heliocentric model
In the 16th century, Nicolaus Copernicus's De revolutionibus presented a full discussion of a heliocentric model of the universe in much the same way as Ptolemy's Almagest had presented his geocentric model in the 2nd century. Copernicus discussed the philosophical implications of his proposed system, elaborated it in full geometrical detail, used selected astronomical observations to derive the parameters of his model, and wrote astronomical tables which enabled one to compute the past and future positions of the stars and planets. In doing so, Copernicus moved heliocentrism from philosophical speculation to predictive geometrical astronomy—in reality it did not predict the planets' positions any better than the Ptolemaic system.[49] This theory resolved the issue of planetary retrograde motion by arguing that such motion was only perceived and apparent, rather than real: it was a parallax effect, as a car that one is passing seems to move backwards against the horizon. This issue was also resolved in the geocentric Tychonic system; the latter, however, while eliminating the major epicycles, retained as a physical reality the irregular back-and-forth motion of the planets, which Kepler characterized as a "pretzel".[50]
Copernicus cited Aristarchus in an early (unpublished) manuscript of De Revolutionibus (which still survives) so he was clearly aware of at least one previous proponent of the heliocentric thesis. However, in the published version he restricts himself to noting that in works by Cicero he had found an account of the theories of Hicetas and that Plutarch had provided him with an account of the Pythagoreans Heraclides Ponticus, Philolaus, and Ecphantus. These authors had proposed a moving earth, which did not, however, revolve around a central sun.
Religious attitudes to heliocentrism
Heliocentrism had been in conflict with religion before Copernicus. One of the few pieces of information we have about the reception of Aristarchus's heliocentric system comes from a passage in Plutarch's dialogue, Concerning the Face which Appears in the Orb of the Moon. According to one of Plutarch's characters in the dialogue, the philosopher Cleanthes had held that Aristarchus should be charged with impiety for "moving the hearth of the world".[51] In fact, however, Aristarchus's heliocentrism appears to have attracted little attention, religious or otherwise, until Copernicus revived and elaborated it.[52]
Circulation of Commentariolus (before 1533)
The first information about the heliocentric views of Nicolaus Copernicus were circulated in manuscript. Although only in manuscript, Copernicus' ideas were well known among astronomers and others. His ideas contradicted the then-prevailing understanding of the Bible. In the King James Bible Chronicles 16:30 state that "the world also shall be stable, that it be not moved." Psalm 104:5 says, "[the Lord] Who laid the foundations of the earth, that it should not be removed for ever." Ecclesiastes 1:5 states that "The sun also ariseth, and the sun goeth down, and hasteth to his place where he arose."
Nonetheless, in 1533, Johann Albrecht Widmannstetter delivered in Rome a series of lectures outlining Copernicus' theory. The lectures were heard with interest by Pope Clement VII and several Catholic cardinals. On 1 November 1536, Archbishop of Capua Nikolaus von Schönberg wrote a letter to Copernicus from Rome encouraging him to publish a full version of his theory.
However, in 1539, Martin Luther said:
"There is talk of a new astrologer who wants to prove that the earth moves and goes around instead of the sky, the sun, the moon, just as if somebody were moving in a carriage or ship might hold that he was sitting still and at rest while the earth and the trees walked and moved. But that is how things are nowadays: when a man wishes to be clever he must . . . invent something special, and the way he does it must needs be the best! The fool wants to turn the whole art of astronomy upside-down. However, as Holy Scripture tells us, so did Joshua bid the sun to stand still and not the earth."This was reported in the context of a conversation at the dinner table and not a formal statement of faith. Melanchthon, however, opposed the doctrine over a period of years.
Publication of de Revolutionibus (1543)
Nicolaus Copernicus published the definitive statement of his system in De Revolutionibus in 1543. Copernicus began to write it in 1506 and finished it in 1530, but did not publish it until the year of his death. Although he was in good standing with the Church and had dedicated the book to Pope Paul III, the published form contained an unsigned preface by Osiander defending the system and arguing that it was useful for computation even if its hypotheses were not necessarily true. Possibly because of that preface, the work of Copernicus inspired very little debate on whether it might be heretical during the next 60 years. There was an early suggestion among Dominicans that the teaching of heliocentrism should be banned, but nothing came of it at the time.
Some years after the publication of De Revolutionibus John Calvin preached a sermon in which he denounced those who "pervert the course of nature" by saying that "the sun does not move and that it is the earth that revolves and that it turns".[53] On the other hand, Calvin is not responsible for another famous quotation which has often been misattributed to him:
"Who will venture to place the authority of Copernicus above that of the Holy Spirit?"It has long been established that this line cannot be found in any of Calvin's works.[54][55][56] It has been suggested[57] that the quotation was originally sourced from the works of Lutheran theologian Abraham Calovius.
Tycho Brahe's geo-heliocentric system c. 1587
Prior to the publication of De Revolutionibus, the widely accepted system had been that which was proposed by Ptolemy, in which the Earth was the center of the universe and all celestial bodies orbited it. Tycho Brahe, arguably the most accomplished astronomer of his time, advocated against Copernicus's heliocentric system and for an alternative to the Ptolemaic geocentric system: a geo-heliocentric system now known as the Tychonic system in which the five then known planets orbit the sun, while the sun and the moon orbit the earth.
Tycho appreciated the Copernican system, but objected to the idea of a moving Earth on the basis of physics, astronomy, and religion. The Aristotelian physics of the time (modern Newtonian physics was still a century away) offered no physical explanation for the motion of a massive body like Earth, whereas it could easily explain the motion of heavenly bodies by postulating that they were made of a different sort substance called aether that moved naturally. So Tycho said that the Copernican system “... expertly and completely circumvents all that is superfluous or discordant in the system of Ptolemy. On no point does it offend the principle of mathematics. Yet it ascribes to the Earth, that hulking, lazy body, unfit for motion, a motion as quick as that of the aethereal torches, and a triple motion at that.”[58] Likewise, Tycho took issue with the vast distances to the stars that Aristarchus and Copernicus had assumed in order to explain the lack of any visible parallax. Tycho had measured the apparent sizes of stars (now known to be illusory – see stellar magnitude), and used geometry to calculate that in order to both have those apparent sizes and be as far away as heliocentrism required, stars would have to be huge (much larger than the sun; the size of Earth's orbit or larger). Regarding this Tycho wrote, “Deduce these things geometrically if you like, and you will see how many absurdities (not to mention others) accompany this assumption [of the motion of the earth] by inference.”[59] He also cited the Copernican system's "opposition to the authority of Sacred Scripture in more than one place" as a reason why one might wish to reject it, and observed that his own geoheliocentric alternative “offended neither the principles of physics nor Holy Scripture”.[60]
The Jesuit astronomers in Rome were at first unreceptive to Tycho's system; the most prominent, Clavius, commented that Tycho was "confusing all of astronomy, because he wants to have Mars lower than the Sun." [61] However, after the advent of the telescope showed problems with some geocentric models (by demonstrating that Venus circles the sun, for example), the Tychonic system and variations on that system became very popular among geocentrists, and the Jesuit astronomer Giovanni Battista Riccioli would continue Tycho's use of physics, stellar astronomy (now with a telescope), and religion to argue against heliocentrism and for Tycho's system well into the seventeenth century (see Riccioli).
Publication of Starry messenger (1610)
 In the 17th century AD Galileo Galilei opposed the Roman Catholic Church by his strong support for heliocentrism
In the 17th century AD Galileo Galilei opposed the Roman Catholic Church by his strong support for heliocentrism
Galileo was able to look at the night sky with the newly invented telescope. He published his discoveries in Sidereus Nuncius including (among other things) the moons of Jupiter and that Venus exhibited a full range of phases. These discoveries were not consistent with the Ptolemeic model of the solar system. As the Jesuit astronomers confirmed Galileo's observations, the Jesuits moved toward Tycho's teachings.[62]
Publication of Letter to the Grand Duchess (1615)
In a Letter to the Grand Duchess Christina, Galileo defended heliocentrism, and claimed it was not contrary to Scriptures (see Galileo affair). He took Augustine's position on Scripture: not to take every passage literally when the scripture in question is a book of poetry and songs, not a book of instructions or history. The writers of the Scripture wrote from the perspective of the terrestrial world, and from that vantage point the sun does rise and set. In fact, it is the Earth's rotation which gives the impression of the sun in motion across the sky.
The decree of 1616
The Letter to the Grand Duchess Christina prompted the papal authorities to decide whether heliocentrism was acceptable. Galileo was summoned to Rome to defend his position. The Church accepted the use of heliocentrism as a calculating device, but opposed it as a literal description of the solar system. Cardinal Robert Bellarmine himself considered that Galileo's model made "excellent good sense" on the ground of mathematical simplicity; that is, as a hypothesis (see above). And he said:
"If there were a real proof that the Sun is in the center of the universe, that the Earth is in the third sphere, and that the Sun does not go round the Earth but the Earth round the Sun, then we should have to proceed with great circumspection in explaining passages of Scripture which appear to teach the contrary, and we should rather have to say that we did not understand them than declare an opinion false which has been proved to be true. But I do not think there is any such proof since none has been shown to me."—Koestler (1959), p. 447–448Bellarmine supported a ban on the teaching of the idea as anything but hypothesis. In 1616 he delivered to Galileo the papal command not to "hold or defend" the heliocentric idea.[63] The Vatican files suggest that Galileo was forbidden to teach heliocentrism in any way whatsoever, but whether this ban was known to Galileo is a matter of dispute.[64]
Publication of Epitome astronomia Copernicanae (1617-1621)
In Astronomia nova (1609), Johannes Kepler had used an elliptical orbit to explain the motion of Mars. In Epitome astronomia Copernicanae he developed a heliocentric model of the solar system in which all the planets have elliptical orbits. This provided significantly increased accuracy in predicting the position of the planets. Kepler's ideas were not immediately accepted. Galileo for example completely ignored Kepler's work. Kepler proposed heliocentrism as a physical description of the solar system and Epitome astronomia Copernicanae was placed on the index of prohibited books despite Kepler being a Protestant.
Publication of Dialogue concerning the two chief world systems
Pope Urban VIII encouraged Galileo to publish the pros and cons of Heliocentrism. In the event, Galileo's Dialogue concerning the two chief world systems clearly advocated heliocentrism and appeared to make fun of the Pope. Urban VIII became hostile to Galileo and he was again summoned to Rome.[65] Galileo's trial in 1633 involved making fine distinctions between "teaching" and "holding and defending as true". For advancing heliocentric theory Galileo was forced to recant Copernicanism and was put under house arrest for the last few years of his life.
According to J. L. Heilbron,[66] informed contemporaries of Galileo's:
"appreciated that the reference to heresy in connection with Galileo or Copernicus had no general or theological significance."Subsequent developments
Rene Descartes postponed, and ultimately never finished, his treatise The World, which included a heliocentric model.[67] But ultimately the Galileo affair did little to slow the spread of heliocentrism across Europe, as Kepler's Epitome of Copernican Astronomy became increasingly influential in the coming decades.[68] By 1686 the model was well enough established that the general public was reading about it in Conversations on the Plurality of Worlds, published in France by Bernard le Bovier de Fontenelle and translated into English and other languages in the coming years. It has been called "one of the first great popularizations of science."[67]
In 1687, Isaac Newton published Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica, which provided an explanation for Kepler's laws in terms of universal gravitation and what came to be known as Newton's laws of motion. This placed heliocentrism on a firm theoretical foundation, although Newton's heliocentrism was of a somewhat modern kind. Already in the mid-1680s he recognized the "deviation of the Sun" from the centre of gravity of the solar system.[69] For Newton it was not precisely the centre of the Sun or any other body that could be considered at rest, but "the common centre of gravity of the Earth, the Sun and all the Planets is to be esteem'd the Centre of the World", and this centre of gravity "either is at rest or moves uniformly forward in a right line" (Newton adopted the "at rest" alternative in view of common consent that the centre, wherever it was, was at rest) [70]
Meanwhile the Church remained opposed to heliocentrism as a literal description, but this did not by any means imply opposition to all astronomy; indeed, it needed observational data to maintain its calendar. In support of this effort it allowed the cathedrals themselves to be used as solar observatories called meridiane; i.e., they were turned into "reverse sundials", or gigantic pinhole cameras, where the Sun's image was projected from a hole in a window in the cathedral's lantern onto a meridian line.
In 1664, Pope Alexander VII published his Index Librorum Prohibitorum Alexandri VII Pontificis Maximi jussu editus (Index of Prohibited Books, published by order of Alexander VII, P.M.) which included all previous condemnations of heliocentric books.[71]
In the mid-eighteenth century the Church's opposition began to fade. An annotated copy of Newton's Principia was published in 1742 by Fathers le Seur and Jacquier of the Franciscan Minims, two Catholic mathematicians, with a preface stating that the author's work assumed heliocentrism and could not be explained without the theory. In 1758 the Catholic Church dropped the general prohibition of books advocating heliocentrism from the Index of Forbidden Books.[72] Pope Pius VII approved a decree in 1822 by the Sacred Congregation of the Inquisition to allow the printing of heliocentric books in Rome.
Heliocentrism and Judaism
Already in the Talmud, Greek philosophy and science under general name "Greek wisdom" were considered dangerous. They were put under ban then and later for some periods (for example, Shlomo ben Aderet prohibited study of philosophy in 1305). Possibly due to this the system of Nicolaus Copernicus did not cause furious resistance, although it was found to be contradicting verses of Tanakh (Jewish Bible).
The first to mention the new system was Maharal of Prague, although he did not mention Copernicus, the author of the system. In his book "Be'er ha-Golah", in 1593 Maharal used the appearance of the new system to show that scientific theories are not reliable enough - even astronomy was turned upside-down.[73]
Copernicus is mentioned for the first time in Hebrew in the books of David Gans (1541–1613), who worked with Tycho Brahe and Johannes Kepler. Gans wrote two books on astronomy: a short one "Magen David" (1612) and a full one "Nehmad veNaim" (published only in 1743). He described objectively three systems: Ptolemy, Copernicus and of Tycho Brahe without taking sides.
In 1629 a new Hebrew book "Elim" by Joseph Solomon Delmedigo (1591–1655) appeared. The author says that the arguments of Copernicus are so strong, that only an imbecile will not accept them.[74] Delmedigo studied at Padua and was acquainted with Galileo.[75]
The following wave of Hebrew literature on the subject is from the 18th century. Most of its authors were for Copernicus, although David Nieto and Tobias Cohn were exceptions. These two authors gave the same reason for opposing heliocentrism—namely, contradiction of the Bible—although Nieto merely rejected the new system on those grounds without much passion, whereas Hacohen went so far as to call Copernicus «a first-born of Satan». Hacohen also mentions the fact that the Sages of Talmud derived the Hebrew name of Earth from the verb "run".[75]
In later periods there were no explicit attacks on heliocentrism, although some Rabbis were not sure of it.[76][77]
In the 20th century R. M.M. Schneerson suggested that the theory of relativity makes the question obsolete, as he writes, "based on the understanding of science at this point".[78]
The view of modern science
Kepler's laws of planetary motion were used as arguments in favor of the heliocentric hypothesis. An apparent proof of the heliocentric hypothesis was provided only in 1838 by Friedrich Wilhelm Bessel. Bessel proved that parallax of a star was greater than zero. He measured the parallax of 0.314 arcseconds of a star named 61 Cygni. In the same year Friedrich Georg Wilhelm Struve and Thomas Henderson measured the parallaxes of other stars, Vega and Alpha Centauri.
The thinking that the heliocentric view was also not true in a strict sense was achieved in steps. That the Sun was not the center of the universe, but one of innumerable stars, was strongly advocated by the mystic Giordano Bruno, who had little regard for observation or experiment. Over the course of the 18th and 19th centuries, the status of the Sun as merely one star among many became increasingly obvious. By the 20th century, even before the discovery that there are many galaxies, it was no longer an issue.
The concept of an absolute velocity, including being "at rest" as a particular case, is ruled out by the principle of relativity, eliminating any obvious "center" of the universe as a natural origin of coordinates. Some forms of Mach's principle consider the frame at rest with respect to the distant masses in the universe to have special properties.
Even if the discussion is limited to the solar system, the Sun is not at the geometric center of any planet's orbit, but rather approximately at one focus of the elliptical orbit. Furthermore, to the extent that a planet's mass cannot be neglected in comparison to the Sun's mass, the center of gravity of the solar system is displaced slightly away from the center of the Sun.[70] (The masses of the planets, mostly Jupiter, amount to 0.14% of that of the Sun.) Therefore a hypothetical astronomer on an extrasolar planet would observe a small "wobble" in the Sun's motion.
Modern use of geocentric and heliocentric
In modern calculations the terms "geocentric" and "heliocentric" are often used to refer to coordinate systems that are chosen for practical reasons. In such systems the origin in the center of mass of the Earth, of the Earth-Moon system, of the Sun, of the Sun plus the major planets, or of the entire solar system can be selected. However, such selection of "geocentric" or "heliocentric" coordinates has only practical implications and not philosophical or physical ones.
The view of the public
A proportion of the public still believes in the geocentric model. Approximately one in five Americans and Britons believe that the Sun revolves around the Earth, according to surveys in 1999, 2006.[79][80] Approximately one third of Russians believe in the geocentric model, according to a survey in 2011.[81]
See also
- Geocentrism
- Copernican Revolution (metaphor)
- Copernican principle
External links
- Does Heliocentrism Mean That the Sun is Stationary?
- Heliocentric Pantheon
- The Copernican Model: a Sun Centered Solar System
Notes
- ^ Teaching about Evolution and the Nature of Science (National Academy of Sciences, 1998), p.27; also, Don O' Leary, Roman Catholicism and Modern Science: A History (Continuum Books, 2006), p.5.
- ^ Dreyer (1953, pp.135–48); Linton (2004, pp.38–9). The work of Aristarchus's in which he proposed his heliocentric system has not survived. We only know of it now from a brief passage in Archimedes's The Sand Reckoner.
- ^ Debus, Allen G. (1987), Man and nature in the Renaissance, Cambridge University Press, p. 76, ISBN 0-521-29328-6, http://books.google.com/books?id=caJygwa-jiEC, Chapter V, page 76
- ^ In Book 1 section 7 he admits that a model in which the earth revolves with respect to the stars would be simpler but doesn't go as far as considering a heliocentric system.
- ^ Dennis Duke, Ptolemy's Universe
- ^ Boyer, C. A History of Mathematics. Wiley, p. 54.
- ^ Johannes Kepler (1618–21), Epitome of Copernican Astronomy, Book IV, Part 1.2
- ^ Eastwood, B. S. (1992-11-01), "Heraclides and Heliocentrism - Texts Diagrams and Interpretations", Journal for the History of Astronomy 23: 233, Bibcode 1992JHA....23..233E
- ^ Otto E. Neugebauer (1975), A history of ancient mathematical astronomy, Birkhäuser, ISBN 354006995X
- ^ Rufus, W. Carl (1923), "The astronomical system of Copernicus", Popular Astronomy 31: 510–521 [512], Bibcode 1923PA.....31..510R
- ^ Arenarius, I., 4–7
- ^ D.Rawlins, Aristarchus's vast universe: ancient vision, contends that all of Aristarchus's huge astronomical estimates of distance were based upon his gauging the limit of human visual discrimination to be approximately a ten thousandth of a radian which is about right.
- ^ Murdin, Paul, Murdin, Paul, ed., Seleucus of Seleucia (c. 190 BC-?), Adsabs.harvard.edu, doi:10.1888/0333750888, ISBN 0333750888, http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2000eaa..bookE3998, retrieved 2009-08-08
- ^ Index of Ancient Greek Philosophers-Scientists, Ics.forth.gr, http://www.ics.forth.gr/~vsiris/ancient_greeks/hellinistic_period.html, retrieved 2009-08-08
- ^ Bartel, B. L. (1987), "The Heliocentric System in Greek, Persian and Hindu Astronomy", Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 500 (1): 525–545 [527–529], Bibcode 1987NYASA.500..525V, doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb37224.x.
- ^ Shlomo Pines (1986), Studies in Arabic versions of Greek texts and in mediaeval science, 2, Brill Publishers, pp. viii & 201–17, ISBN 9652236268
- ^ Lucio Russo, Flussi e riflussi, Feltrinelli, Milano, 2003, ISBN 88-07-10349-4.
- ^ William Stahl, trans., Martianus Capella and the Seven Liberal Arts, vol. 2, The Marriage of Philology and Mercury, 854, 857, New York: Columbia Univ. Pr, 1977, pp. 332–3
- ^ Eastwood, Bruce S. (2007), Ordering the Heavens: Roman Astronomy and Cosmology in the Carolingian Renaissance, Leiden: Brill, pp. 244–259, ISBN 978-90-04-16186-3
- ^ Eastwood, Bruce S. (1982), "Kepler as Historian of Science: Precursors of Copernican Heliocentrism according to De revolutionibus I, 10", Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society 126: 367–394.
- ^ Nicholas of Cusa, De docta ignorantia, 2.12, p. 103, cited in Koyré (1957), p. 17.
- ^ a b Joseph (2000).
- ^ Thurston (1994).
- ^ Ramasubramanian, K. (1998), "Model of planetary motion in the works of Kerala astronomers", Bulletin of the Astronomical Society of India 26: 11–31 [23–4], Bibcode 1998BASI...26...11R
- ^ K. Ramasubramanian, et al. (1994), p. 788
- ^ Amartya Kumar Dutta (May 2006), "Āryabhata and axial rotation of earth", Resonance (Springer) 11 (5): 58–72 [70–1], doi:10.1007/BF02839373, ISSN 0973-712X
- ^ George G. Joseph (2000), p. 408.
- ^ Ramasubramanian, K.; Srinivas, M. D.; Sriram, M. S. (1994), "Modification of the earlier Indian planetary theory by the Kerala astronomers (c. 1500 AD) and the implied heliocentric picture of planetary motion", Current Science 66: 784–790.
- ^ A. I. Sabra, "Configuring the Universe: Aporetic, Problem Solving, and Kinematic Modeling as Themes of Arabic Astronomy," Perspectives on Science 6.3 (1998): 288–330, at pp. 317–18:
All Islamic astronomers from Thabit ibn Qurra in the ninth century to Ibn al-Shatir in the fourteenth, and all natural philosophers from al-Kindi to Averroes and later, are known to have accepted ... the Greek picture of the world as consisting of two spheres of which one, the celestial sphere ... concentrically envelops the other.
- ^ a b Ragep, F. Jamil (2001a), "Tusi and Copernicus: The Earth's Motion in Context", Science in Context (Cambridge University Press) 14 (1–2): 145–163
- ^ a b Ragep, F. Jamil; Al-Qushji, Ali (2001b), "Freeing Astronomy from Philosophy: An Aspect of Islamic Influence on Science", Osiris, 2nd Series 16 (Science in Theistic Contexts: Cognitive Dimensions): 49–64 & 66–71, Bibcode 2001Osir...16...49R, doi:10.1086/649338
- ^ Adi Setia (2004), "Fakhr Al-Din Al-Razi on Physics and the Nature of the Physical World: A Preliminary Survey", Islam & Science 2, http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m0QYQ/is_2_2/ai_n9532826/, retrieved 2010-03-02
- ^ Qadir (1989), p. 5–10.
- ^ Nicolaus Copernicus, Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy (2004).
- ^ Roshdi Rashed (2007). "The Celestial Kinematics of Ibn al-Haytham", Arabic Sciences and Philosophy 17, p. 7–55. Cambridge University Press.
- ^ E. S. Kennedy, "Al-Bīrūnī's Masudic Canon", Al-Abhath, 24 (1971): 59–81; reprinted in David A. King and Mary Helen Kennedy, ed., Studies in the Islamic Exact Sciences, Beirut, 1983, pp. 573–595.
- ^ G. Wiet, V. Elisseeff, P. Wolff, J. Naudu (1975). History of Mankind, Vol 3: The Great medieval Civilisations, p. 649. George Allen & Unwin Ltd, UNESCO.
- ^ Saliba (1999).
- ^ A. Baker, L. Chapter (2002).
- ^ Saliba (1999):
"What was needed, and was in fact deployed by Copernicus (1473-1543) himself, was the addition of two new mathematical theorems. Both of those theorems were first produced some three centuries before Copernicus and were used by astronomers working in the Islamic world for the express purpose to reform Greek astronomy. [...] Looking at the evidence from the perspective of transmission of science from one culture to another, and in particular the transmission of the two Arabic mathematical theorems to Copernicus, the small fraction of evidence that has been just examined should make it clear that it also gives rise to at least two new problems as well as to many other important issues that should be reconsidered further."
- ^ V. Roberts and E. S. Kennedy (1959), "The Planetary Theory of Ibn al-Shatir", Isis 50: 232-234:
"In all other respects, particularly in the case of Mercury and Venus, the solutions worked out in Copernicus' De revolutionibus for corresponding planets show a remarkable similarity to those of our source."
- ^ Guessoum, N. (June 2008), "Copernicus and Ibn Al-Shatir: does the Copernican revolution have Islamic roots?", The Observatory 128: 231–239 [238], Bibcode 2008Obs...128..231G, "an important underlying question remains to be addressed: since it has become quite clear that Copernicus was indeed influenced by the Maragha school's 'new astronomy', and since there was in Europe up to that point no tradition of criticism toward the Ptolemaic planetary system, how could a classically minded European come up with a theory that would truly revolutionize astronomy and usher in modern science and a new world view?"
- ^ A. I. Sabra (1998). "Configuring the Universe: Aporetic, Problem Solving, and Kinematic Modeling as Themes of Arabic Astronomy", Perspectives on Science 6 (3), p. 288-330:
"It was also Neugebauer who first noted the "identity" between the models of Ibn al-Shatir and of Copernicus for the moon, an observation that led Victor Roberts to subtitle his 1957 article on the solar and lunar models of Ibn al-Shatir "A Pre-Copernican Copernican Model" (Roberts 1957, p. 428, n. 2). And it was Neugebauer who uncovered evidence that argues for a transmission of the couple (in the form it has in Tusi's Memoir) by means of Greek Byzantine manuscripts that reached Italy in the fifteenth century."
- ^ E. S. Kennedy (Autumn 1966), "Late Medieval Planetary Theory", Isis (University of Chicago Press) 57 (3): 365–378 [377], doi:10.1086/350144, JSTOR 228366, "In the face of this array of similarities, the conclusion seems inescapable that, somehow or other, Copernicus was strongly influenced by the work of these people."
- ^ a b Toby E.Huff(1993):The rise of early modern science: Islam, China, and the West[1]
- ^ N.K. Singh, M. Zaki Kirmani,Encyclopaedia of Islamic science and scientists[2]
- ^ Veselovsky, I. N. (1973), "Copernicus and Nasir al-Din al-Tusi", Journal for the History of Astronomy 4: 128–30, Bibcode 1973JHA.....4..128V, http://articles.adsabs.harvard.edu/full/seri/JHA../0004//0000128.000.html.
- ^ Kren, Claudia (1971), "The Rolling Device of Naṣir al-Dīn al-Ṭūsī in the De spera of Nicole Oresme", Isis 62 (4): 490–498, doi:10.1086/350791.
- ^ John Henry, Moving Heaven and Earth (Totem Books, 2001), 87.
- ^ Owen Gingerich, The Book Nobody Read (Heinman, 2004, p. 51)
- ^ Dreyer (1953, p.138); Plutarch (1957, p.55) (on-line copy available). According to a footnote in the latter reference, Diogenes Laertius listed a work of Cleanthes' (apparently now lost) with the title Against Aristarchus (Plutarch, 1957, p.54).
- ^ Dreyer (1953, pp.139ff).
- ^ Rosen (1995, p.159). Rosen disputes the earlier conclusion of another scholar that this was referring specifically to Copernicus's theory. According to Rosen, Calvin had very likely never heard of Copernicus and was referring instead to "the traditional geokinetic cosmology".
- ^ Rosen, Edward (1960), Calvin’s attitude toward Copernicus in Journal of the History of Ideas, volume 21, no. 3, July, pp.431–441. Reprinted in Rosen (1995, pp.161–171).
- ^ Gingerich, Owen (2004), The Book Nobody Read. New York: Walker and Co.
- ^ Hooykaas, R. (1973). Religion and the rise of modern science. Reprint, Edinburgh: Scottish Academic Press, 1977.
- ^ Bye, Dan J. (2007). McGrath vs Russell on Calvin vs Copernicus: a case of the pot calling the kettle black? in The Freethinker, volume 127, no. 6, June, pp.8–10. Available online here.
- ^ Owen Gingerich, The eye of heaven: Ptolemy, Copernicus, Kepler, New York: American Institute of Physics, 1993, 181, ISBN 0-88318-863-5
- ^ Blair, Ann, "Tycho Brahe's critique of Copernicus and the Copernican system", Journal of the History of Ideas, 51, 1990, 364.
- ^ Gingerich, O. & Voelkel, J. R., J. Hist. Astron., Vol. 29, 1998, page 1, 24
- ^ Fantoli, 2003, p. 109
- ^ Arthur Koestler, The Sleepwalkers (Penguin Arkana, 1989 p. 433)
- ^ Arthur Koestler, The Sleepwalkers (Penguin Arkana, 1989 p. 468)
- ^ Arthur Koestler, The Sleepwalkers (Penguin Arkana, 1989 p. 469)
- ^ Arthur Koestler, The Sleepwalkers (Penguin Arkana, 1989 p. 491)
- ^ Heilbronn (1999, p.203)
- ^ a b Weintraub, David A. Is Pluto a Planet, p. 66, Princeton University Press, 2007
- ^ "Kepler's Laws of Planetary Motion: 1609-1666", J. L. Russell, British Journal for the History of Science, Vol. 2, No. 1, June 1964
- ^ Curtis Wilson, "The Newtonian achievement in astronomy", pages 233-274 in R Taton & C Wilson (eds) (1989), The General History of Astronomy, Volume 2A, at page 233
- ^ a b (text quotations from 1729 translation of Newton Principia, Book 3 (1729 vol.2) at pages 232-233).
- ^ "The Pontifical Decrees Against the Doctrine of the Earth's Movement, and the Ultramontane Defence of Them", Rev. William Roberts, 1885, London
- ^ John L.Heilbron, Censorship of Astronomy in Italy after Galileo (in McMullin, Ernan ed., The Church and Galileo, University of Notre Dame Press, Notre Dame, 2005, p. 307, IN. ISBN 0-268-03483-4)
- ^ Noah J. Efron. Jewish Thought and Scientific Discovery in Early Modern Europe. Journal of the History of Ideas, Vol. 58, No. 4 (Oct., 1997), pp. 719-732
- ^ Sefer Elim, Amsterdam, 1629, стр. 304
- ^ a b Copernicus in the Hebraic Literature from the Sixteenth to the Eighteenth Century Journal of the History of Ideas, vol. 38, No. 2 (Apr. - Jun., 1977), pp. 211-226]. (en:André Neher)
- ^ "Shvut Yakov" 3:20 (r. Y. Reisner from Prague 1710-1789)
- ^ Hatam Sopher (1762 - 1839) "Kovetz Tshuvot", 26
- ^ "Igrot Kodesh" v. 7, p.134, letter number 1996
- ^ Steve Crabtree (July 6, 1999). "New Poll Gauges Americans' General Knowledge Levels". Gallup. http://www.gallup.com/poll/3742/new-poll-gauges-americans-general-knowledge-levels.aspx.
- ^ Omar. "Eppure si muove…or does it?". http://orgtheory.wordpress.com/2007/06/06/eppure-si-muoveor-does-it/.
- ^ Alissa de Carbonnel (February 11, 2011). "Third of Russians think sun spins round Earth: poll". Reuters. http://uk.reuters.com/article/2011/02/11/science-us-russia-poll-education-science-idUKTRE71A5B920110211.
References
- Baker, A. and Chapter, L. (2002), "Part 4: The Sciences". In M. M. Sharif, "A History of Muslim Philosophy", Philosophia Islamica.
- Dreyer, J.L.E. (1953), A History of Astronomy from Thales to Kepler, New York, NY: Dover Publications, ISBN 0486600793, http://www.archive.org/details/historyofplaneta00dreyuoft
- Fantoli, Annibale (2003). Galileo — For Copernicanism and the Church, 3rd English edition, tr. George V. Coyne, SJ. Vatican Observatory Publications, Notre Dame, IN. ISBN 88-209-7427-4.
- Heath, T.L. (1913). Aristarchus of Samos, the ancient Copernicus: a history of Greek astronomy to Aristarchus, Oxford, Clarendon. ISBN 0-486-24188-2 (1981 Dover reprint).
- Heilbron, John L. (1999), The Sun in the Church: Cathedrals as Solar Observatories, Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, ISBN 0-674-85433-03, http://books.google.com.au/books?id=mZWy0xPxj3EC&printsec=frontcover
- Joseph, George G. (2000). The Crest of the Peacock: Non-European Roots of Mathematics, 2nd edition. Penguin Books, London. ISBN 0-691-00659-8.
- Koestler, Arthur, (1959) The Sleepwalkers: A History of Man's Changing Vision of the Universe, Penguin Books; 1986 edition: ISBN 0-14-055212-X, 1990 reprint: ISBN 0-14-019246-8
- Koyré, Alexandre (1957). From the Closed World to the Infinite Universe. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins Univ. Pr.
- Linton, Christopher M. (2004), From Eudoxus to Einstein—A History of Mathematical Astronomy, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-521-82750-8
- Plutarch (1957), Plutarch's Moralia in Fifteen Volumes, XII, Loeb Classical Library edition, translated by Harold Cherniss and William C. Helmbold, London: William Heinemann
- Qadir, Asghar (1989). Relativity: An Introduction to the Special Theory. World Scientific. ISBN 9971-5-0612-2.
- Sabra, A. I. (1998), "Configuring the Universe: Aporetic, Problem Solving, and Kinematic Modeling as Themes of Arabic Astronomy", Perspectives on Science 6: 288–330.
- Rosen, Edward (1995), Copernicus and his Successors, London: Hambledon Press, ISBN 1 85285 071 X
- Saliba, George (1999). Whose Science is Arabic Science in Renaissance Europe? Columbia University.
- Taton, René; Wilson, Curtis, eds. (1989), Planetary astronomy from the Renaissance to the rise of astrophysics Part A: Tycho Brahe to Newton, Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0-521-24254-1, http://books.google.com/?id=rkQKU-wfPYMC, retrieved 2009-11-06
- Thurston, Hugh (1994). Early Astronomy. Springer-Verlag, New York. ISBN 0-387-94107-X.
Greek astronomy Astronomers Acoreus · Aglaonike · Agrippa · Anaximander · Andronicus · Apollonius · Aratus · Aristarchus · Aristillus · Attalus · Autolycus · Bion · Callippus · Cleomedes · Cleostratus · Conon · Eratosthenes · Euctemon · Eudoxus · Geminus · Heraclides · Hicetas · Hipparchus · Hippocrates of Chios · Hypsicles · Menelaus · Meton · Oenopides · Philip of Opus · Philolaus · Posidonius · Ptolemy · Pytheas · Seleucus · Sosigenes of Alexandria · Sosigenes the Peripatetic · Strabo · Thales · Theodosius · Theon of Alexandria · Theon of Smyrna · Timocharis
Works Instruments Concepts Callippic cycle · Celestial spheres · Circle of latitude · Counter-Earth · Deferent and epicycle · Equant · Geocentrism · Heliocentrism · Hipparchic cycle · Metonic cycle · Octaeteris · Solstice · Spherical Earth · Sublunary sphere · Zodiac
Influences Influenced Categories:- Ancient Greek astronomy
- History of astronomy
- Obsolete scientific theories
- History of ideas
- Early scientific cosmologies
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.