- Mural instrument
-
 Tycho Brahe's mural quadrant
Tycho Brahe's mural quadrant
 Mural quadrant constructed as a frame mounted on a wall. This instrument was made by John Bird in 1773 and is in the Museum of the History of Science, University of Oxford.
Mural quadrant constructed as a frame mounted on a wall. This instrument was made by John Bird in 1773 and is in the Museum of the History of Science, University of Oxford.
A mural instrument is an angle measuring device mounted on or built into a wall. For astronomical purposes, these walls were oriented so they lie precisely on a meridian. A mural instrument that measured angles from 0 to 90 degrees was called a mural quadrant.
Contents
Construction
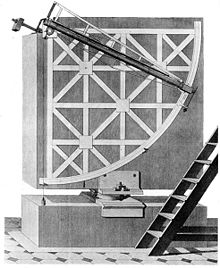 A Bird Mural Quadrant was for many years the main instrument of the Mannheim Observatory, shown here installed
A Bird Mural Quadrant was for many years the main instrument of the Mannheim Observatory, shown here installed
Many older mural quadrants have been constructed by marking directly on the wall surfaces. More recent instruments were made with a frame that was constructed with precision and mounted permanently on the wall.
The arc is marked with divisions, almost always in degrees and fractions of a degree. In the oldest instruments, an indicator is placed at the centre of the arc. An observer can move a device with a second indicator along the arc until the line of sight from the movable device's indicator through the indicator at the centre of the arc aligns with the astronomical object. The angle is then read, yielding the elevation or altitude of the object. In smaller instruments, an alidade could be used. More modern mural instruments would use a telescope with a reticle eyepiece to observe the object.
Many mural quadrants were constructed, giving the observer the ability to measure a full 90° range of elevation. There were also mural sextants that read 60°.
Usage
In order to measure the position of, for example, a star, the observer needs a sidereal clock in addition to the mural instrument. With the clock measuring time, a star of interest is observed with the instrument until it crosses an indicator showing that it is transiting the meridian. At this instant, the time on the clock is recorded as well as the angular elevation of the star. This yields the position in the coordinates of the instrument. If the instrument's arc is not marked relative to the celestial equator, then the elevation is corrected for the difference, resulting in the star's declination. If the sidereal clock is precisely synchronized with the stars, the time yields the right ascension directly[1].
Famous mural instruments
Ulugh Beg's mural sextant, constructed in Samarkand, Uzbekistan during the 15th century.
- A mural sextant was constructed in Ray, Iran, by Abu-Mahmud al-Khujandi in 994.[2]
- Ulugh Beg constructed the "Fakhri Sextant" that had a radius of 40 meters.[3] Seen in the image on the right, the arc was finely constructed with a staircase on either side to provide access for the assistants who performed the measurements.
- Tycho Brahe's mural quadrant in Uraniborg at Hven.
- The mural quadrant at the Greenwich Observatory.
- Ptolemy's mural quadrant at Alexandria. This instrument is also referred to as a plinth.[4]
- The obsolete constellation Quadrans Muralis represents a mural quadrant.
- The mural quadrant at the Mannheimer Observatory.[5] This is another of John Bird's instruments.
References
- ^ Sidereal Time
- ^ O'Connor, John J.; Robertson, Edmund F., "Abu Mahmud Hamid ibn al-Khidr Al-Khujandi", MacTutor History of Mathematics archive, University of St Andrews, http://www-history.mcs.st-andrews.ac.uk/Biographies/Al-Khujandi.html.
- ^ Ulugh Beg, Dictionary of Scientific Biography.
- ^ Hoyle, Fred, Astronomy, A history of man's investigation of the universe, Crescent Books, Inc., London 1962, p 37.
- ^ Mannheimer Observatory quadrant
Greek astronomy Astronomers Acoreus · Aglaonike · Agrippa · Anaximander · Andronicus · Apollonius · Aratus · Aristarchus · Aristillus · Attalus · Autolycus · Bion · Callippus · Cleomedes · Cleostratus · Conon · Eratosthenes · Euctemon · Eudoxus · Geminus · Heraclides · Hicetas · Hipparchus · Hippocrates of Chios · Hypsicles · Menelaus · Meton · Oenopides · Philip of Opus · Philolaus · Posidonius · Ptolemy · Pytheas · Seleucus · Sosigenes of Alexandria · Sosigenes the Peripatetic · Strabo · Thales · Theodosius · Theon of Alexandria · Theon of Smyrna · Timocharis
Works Instruments Antikythera mechanism · Armillary sphere · Astrolabe · Dioptra · Equatorial ring · Gnomon · Mural instrument · Triquetrum
Concepts Influences Influenced Categories:- Ancient Greek astronomy
- Astronomical instruments
- Historical scientific instruments
- Measuring instruments
- History of astronomy
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.

