- Arc (geometry)
-
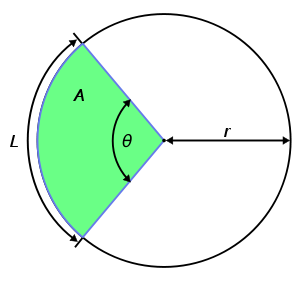 A circular sector is shaded in green. Its curved boundary of length L is a circular arc.
A circular sector is shaded in green. Its curved boundary of length L is a circular arc.
In geometry, an arc is a closed segment of a differentiable curve in the two-dimensional plane; for example, a circular arc is a segment of the circumference of a circle. If the arc is part of a great circle (or great ellipse), it is called a great arc.
Contents
Arc length
The length of an arc of a circle with radius r and subtending an angle
 (measured in radians) with the circle center — i.e., the central angle — equals
(measured in radians) with the circle center — i.e., the central angle — equals  . This is because
. This is becauseSubstituting in the circumference
and solving for arc length, L, in terms of
 yields
yieldsAn angle of α degrees has a size in radians given by
and so the arc length equals
A practical way to determine the length of an arc in a circle is to plot two lines from the arc's endpoints to the center of the circle, measure the angle where the two lines meet the center, then solve for L by cross-multiplying the statement:
- measure of angle/360 = L/Circumference.
For example, if the measure of the angle is 60 degrees and the Circumference is 24", then
- 60/360 = L/24
- 360L=1440
- L = 4".
This is so because the circumference of a circle and the degrees of a circle, of which there are always 360, are directly proportionate.
Arc area
The area between an arc and the center of a circle is:
The area A has the same proportion to the circle area as the angle θ to a full circle:
We can get rid of a π on both sides:
By multiplying both sides by r2, we get the final result:
Using the conversion described above, we find that the area of the sector for a central angle measured in degrees is:
Arc segment area
The area of the shape limited by the arc and a straight line between the two end points is:
To get the area of the arc segment, we need to subtract the area of the triangle made up by the circle's center and the two end points of the arc from the area A. See Circular segment for details.
Arc radius
Using the equality in the intersecting chords theorem (also known as power of a point or secant tangent theorem) it is possible to calculate the radius r of a circle given the height H and the width W of an arc using:
See also
Similar shapes:
External links
- Definition and properties of a circular arc With interactive animation
- A collection of pages defining arcs and their properties, with animated applets Arcs, arc central angle, arc peripheral angle, central angle theorem and others.
- Weisstein, Eric W., "Arc" from MathWorld.
- Radius of an arc or segment With interactive animation
Categories:- Curves
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.











