- Dioptra
-
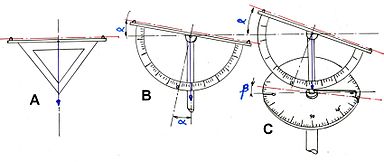
A dioptra (Greek: διόπτρα) is a classical astronomical and surveying instrument, dating from the 3rd century BCE. The dioptra was a sighting tube or, alternatively, a rod with a sight at both ends, attached to a stand. If fitted with protractors, it could be used to measure angles.
Contents
Use
Greek astronomers used the dioptra to measure the positions of stars; both Euclid and Geminus refer to the dioptra in their astronomical works. By the time of Ptolemy (2nd century CE), it was obsolete as an astronomical instrument, having been replaced by the armillary sphere.
It continued in use as an effective surveying tool. Adapted to surveying, the dioptra is similar to the theodolite, or surveyor's transit, which dates to the sixteenth century. It is a more accurate version of the groma.
The dioptra may have been sophisticated enough, for example, to construct a tunnel through two opposite points in a mountain. There is some speculation that it may have been used to build the Eupalinian aqueduct. Called "one of the greatest engineering achievements of ancient times," it is a tunnel 1,036 meters (4,000 ft) long, "excavated through Mount Kastro on the Greek island of Samos, in the 6th century BCE" during the reign of Polycrates. Scholars disagree whether the dioptra was available that early.[1]
An entire book about the construction and surveying usage of the dioptra is credited to Hero of Alexandria (also known as Heron; a brief description of the book is available online; see Lahanas link, below). Hero was "one of history’s most ingenious engineers and applied mathematicians."
The dioptra was used extensively on aqueduct building projects. Screw turns on several different parts of the instrument made it easy to calibrate for very precise measurements
The dioptra was replaced as a surveying instrument by the theodolite.
See also
References
- ^ Apostol, Tom M.. "The Tunnel of Samos". caltech.edu. http://eands.caltech.edu/articles/LXVII1/samos.html. Retrieved 19 June 2011. Also in PDF form: [1]
- Michael Jonathan Taunton Lewis (2001), Surveying Instruments of Greece and Rome, Cambridge University Press, ISBN 0521792975
- Lucio Russo (2004), The Forgotten Revolution: How Science Was Born in 300 BC and Why It Had To Be Reborn, Berlin: Springer. ISBN 3-540-20396-6.
- Evans, J., (1998) The History and Practice of Ancient Astronomy, pages 34-35. Oxford University Press.
External links
- Michael Lahanas, Heron of Alexandria, Inventions, Biography, Science
- Nathan Sidoli (2005), Heron's Dioptra 35 and Analemma Methods: An Astronomical Determination of the Distance between Two Cities, Centaurus, 47(3), 236-258
- Bamber Gascoigne, History of Measurement, historyworld.net
- Tom M. Apostol (2004), The Tunnel of Samos, Engineering and Science, 64(4), 30-40
Greek astronomy Astronomers Acoreus · Aglaonike · Agrippa · Anaximander · Andronicus · Apollonius · Aratus · Aristarchus · Aristillus · Attalus · Autolycus · Bion · Callippus · Cleomedes · Cleostratus · Conon · Eratosthenes · Euctemon · Eudoxus · Geminus · Heraclides · Hicetas · Hipparchus · Hippocrates of Chios · Hypsicles · Menelaus · Meton · Oenopides · Philip of Opus · Philolaus · Posidonius · Ptolemy · Pytheas · Seleucus · Sosigenes of Alexandria · Sosigenes the Peripatetic · Strabo · Thales · Theodosius · Theon of Alexandria · Theon of Smyrna · Timocharis
Works Instruments Antikythera mechanism · Armillary sphere · Astrolabe · Dioptra · Equatorial ring · Gnomon · Mural instrument · Triquetrum
Concepts Influences Influenced 
This history of science article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it.