- Metachondromatosis
-
Metachondromatosis Classification and external resources OMIM 156250 DiseasesDB 32116 Metachondromatosis is an autosomal dominant[1] skeletal disorder affecting the growth of bones, leading to multiple enchondromas and osteochondromas. Affects mainly tubular bones, though can involve the vertebrae.
Genetics
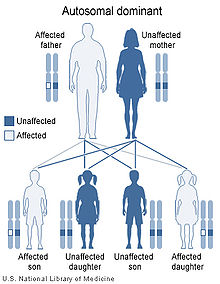
Metachondromatosis is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner.[1] This means that the defective gene responsible for a disorder is located on an autosome, and only one copy of the gene is sufficient to cause the disorder, when inherited from a parent who has the disorder.
It has been associated with PTPN11.[2]
References
- ^ a b Kennedy LA (July 1983). "Metachondromatosis" (PDF). Radiology 148 (1): 117–118. PMID 6602353. http://radiology.rsna.org/content/148/1/117.long.
- ^ Sobreira NL, Cirulli ET, Avramopoulos D, et al. (2010). "Whole-genome sequencing of a single proband together with linkage analysis identifies a Mendelian disease gene". PLoS Genet. 6 (6): e1000991. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1000991. PMC 2887469. PMID 20577567. http://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1000991.
Deficiencies of intracellular signaling peptides and proteins GTP-binding protein regulators GTPase-activating proteinMarinesco–Sjögren syndrome · Aarskog–Scott syndrome · Juvenile primary lateral sclerosis · X-Linked mental retardation 1G protein cAMP/GNAS1: Pseudopseudohypoparathyroidism · Progressive osseous heteroplasia · Pseudohypoparathyroidism · Albright's hereditary osteodystrophy · McCune–Albright syndrome
CGL 2RAS: HRAS (Costello syndrome) · KRAS (Noonan syndrome 3, KRAS Cardiofaciocutaneous syndrome)
RAB: RAB7 (Charcot–Marie–Tooth disease) · RAB23 (Carpenter syndrome) · RAB27 (Griscelli syndrome type 2)
RHO: RAC2 (Neutrophil immunodeficiency syndrome)
ARF: SAR1B (Chylomicron retention disease) ARL13B (Joubert syndrome 8) · ARL6 (Bardet–Biedl syndrome 3)MAP kinase Other kinase/phosphatase RPS6KA3 (Coffin-Lowry syndrome) · CHEK2 (Li-Fraumeni syndrome 2) · IKBKG (Incontinentia pigmenti) · STK11 (Peutz–Jeghers syndrome) · DMPK (Myotonic dystrophy 1) · ATR (Seckel syndrome 1) · GRK1 (Oguchi disease 2) · WNK4/WNK1 (Pseudohypoaldosteronism 2)PTEN (Bannayan–Riley–Ruvalcaba syndrome, Lhermitte–Duclos disease, Cowden syndrome, Proteus-like syndrome) · MTM1 (X-linked myotubular myopathy) · PTPN11 (Noonan syndrome 1, LEOPARD syndrome, Metachondromatosis)Signal transducing adaptor proteins Other NF2 (Neurofibromatosis type II) · NOTCH3 (CADASIL) · PRKAR1A (Carney complex) · PRKAG2 (Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome) · PRKCSH (PRKCSH Polycystic liver disease) · XIAP (XIAP2)see also intracellular signaling peptides and proteins
B structural (perx, skel, cili, mito, nucl, sclr) · DNA/RNA/protein synthesis (drep, trfc, tscr, tltn) · membrane (icha, slcr, atpa, abct, othr) · transduction (iter, csrc, itra), trfkCategories:- Skeletal disorders
- Autosomal dominant disorders
- Rare diseases
- Enzyme defects
- Genetic disorder stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.