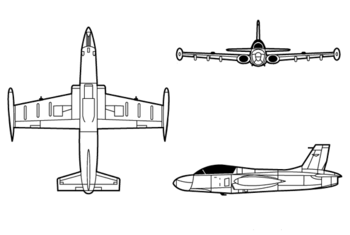
- Aermacchi MB-326
-
MB-326 RAAF Aermacchi MB-326H A7-047, 1980 Role Advanced trainer/Light attack Manufacturer Aermacchi First flight 10 December 1957 Introduction February 1962 Primary users South African Air Force
Brazilian Air Force (retired)
Italian Air Force
Royal Australian Air ForceProduced 1961-? Variants Aermacchi MB-339 The Aermacchi or Macchi MB-326 is a light military jet aircraft designed in Italy. Originally conceived as a two-seat trainer, there have also been single and two-seat light attack versions produced. It is one of the most commercially successful aircraft of its type, being bought by more than 10 countries and produced under licence in Australia, Brazil and South Africa. It set many category records, including an altitude record of 56,807 ft (17,315 m) on 18 March 1966. More than 600 were built.[1]
Contents
Design and development
In the 1950s, before the advent of the turboprop, many countries operated small jet trainers with a similar performance to their full-blown aircraft. Some nations started to develop aircraft like the Fouga Magister, the T-37, the Jet Provost, and the Aero L-29. Italy, still recovering from the war years, could not afford the development of a supersonic interceptor or bomber, and developed light fighters and trainers - a lower-cost solution.
The MB-326 was designed by Ermanno Bazzocchi at Macchi. Bazzocchi considered many configurations, the one chosen was a single-engined design. The airframe was a robust and light structure, metallic, simple and cheap; powered by an efficient engine, the Armstrong Siddeley Viper. This engine was designed as a short-life unit originally destined for target drones, but showed itself to be far more reliable. This airframe and engine combination led, in 1953, to the MB-326 project.
The Italian Air Force was quite interested, and so the MB-326 took part in the contest.
The contest specifications were:
- Max load 7 g at maximum weight
- 5,000 hours lifespan, 50–60 hours between servicing, stall-alert (at 15 km/h (9 mph) more than stall speed)
- Take-off at max load in 800 m (2,625 ft) over a 15 m (50 ft) high obstacle, or 500 m (1,640 ft) at light weight, landing in 450 m (1,480 ft) at minimum weight
- Speed (min-max): 110/130–700 km/h
- Rate-of-climb must be at least 15 m/s (2,950 ft/min) and endurance should be three hours at 3,000 m (9,840 ft).[2]
There were several modifications to the MB-326 project: the horizontal tail surfaces lost their negative dihedral angle, the airbrakes (two in the wings) became one, in the ventral position. In 1956 the AMI approved the project and requested two prototypes (MM.571 and 572) and one airframe for static tests. No weaponry or pressurization was needed, but Bazzocchi introduced them.
The first prototype made its maiden flight on 10 December 1957,[3] flown by chief test-pilot Guido Carestiato, and the second flew the following year.[4] The plane showed very good characteristics, but the modifications affected the weight, which was 400 kg (880 lb) more than the initial estimates. The original Viper 8 engine produced 7.8 kN (1,750 lbf) of thrust, so the Viper 9 was adopted, which had 0.7 kN (147 lbf) more of thrust.
I-MAKI, the prototype, was first demonstrated in France. The second prototype first flew on 22 September 1958. It had a new Viper engine, the '11' model, updated to produce 11.1 kN thrust (1,134 kg, 2,500 lb).
On 15 December 1958, the AMI placed an order for 15 pre-series examples. In 1960, an order for 100 aircraft was placed, establishing Aermacchi's supremacy in jet trainers.
Direct competition came from the Fiat G.80, being more powerful and the first real Italian jet, having flown five years earlier, but it was also heavier, bigger and more expensive. It lost the contest, remaining without a market.
Design
The MB-326 was a low-wing monoplane with an all-metal (light alloy) structure. Powered by a Rolls-Royce Viper non-afterburning turbojet with low air-intakes in the wing roots. Each wing had 22 ribs and two spars. The fuel system had one large tank in the middle-fuselage and two in the wingtips. The aft fuselage was almost entirely dedicated to the engine, from just behind the wings. The cockpit had a tandem configuration, which was chosen to give a better aerodynamic fuselage (slimmer) than the more usual side-by-side arrangement. There was a long, low bubble canopy. The rear of each wing had flaps, and ailerons with a trim surface. 'Wing walls' were added mid-wing to increase the lift characteristics.
Operational history
The MB-326 was one of the last Italian aircraft to set any records, when Guido Carestiano set the C1D group 1 category altitude record of 15,489 m during August 1961.
In the meanwhile, the first machines, after a very long development, finally arrived at the 214° Group's Lecce-Galatina school; temporarily fielded at Brindisi. The type entered service with 43° Flyer course on 22 March 1962. These machines replaced T-6 Texans, and within 130 hours the pilots were as ready as after having 210 hours training in T-6s. This solution was much costlier, but the enthusiasm was great and, with G-91T advanced trainers, there was an "entirely-jet" training course for AMI pilots, and moreover they were all national aircraft. Differing from G.91s that were never convincing as light fighters, the MB-326s immediately scored several export successes.
Eight MB-326Bs were ordered by Tunisia in 1965. These were developed from basic MB-326s with a weapons capability, with the 37th series AMI aircraft being converted (it had civilian markings I-MAKC). The main innovation was its ground attack capability, with six underwing pylons, holding a maximum of 907 kg of stores. In the same year, Ghana ordered nine similar MB-326Fs.
The "A" and "C" models were never realized. The "A" was intended as a light attack aircraft, with two 7.62 mm machine-guns in the nose, but was never built. Later, some MB-326s were called "A", but this only meant that they were fitted with an ADF Marconi AD-370. The "C" version was to have the NASARR radar in the nose, to train F-104 pilots, but it only appeared as a mock-up.
Alitalia ordered four aircraft as trainers in the "D" version; demilitarized and equipped with special instruments to train pilots in preparation for the new jet-liners.
Pilots also provided publicity for the MB-326: Riccardo Peracchi, working for AMI, displayed the MB-326's controllability at many airshows; while Massimo Ralli set many records:
- 8 February 1966, climbing records: 2 min 2 sec to 3,000 m, 3 min 56 sec to 6,000 m, 6 min 39 sec to 9,000 m, and 12,000 m in 10 min 53 sec.
- 18 March 1966, 15,690 m altitude record in horizontal flight, and 17,315 m with a launched climb.
- 18 July 1966, endurance record, with 970 km
- 2 August 1966, speed record over a 3 km straight: 871 km/h
- December 1966: speed of 880.586 km/h over 15–25 km, 831.007 km/h over 100 km, 777.667 km/h over 500 km, and another endurance record at 777.557 km
These successes showed the MB-326's performance, and established it as one of the best in its category. Peracchi displayed its agility, while Ralli concentrated on performance; there were already some customers well-satisfied with this machine.[2]
The Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF) used the MB-326H as a jet trainer. A total of 97 were ordered: 12 were delivered by Macchi, 18 assembled from kits in Australia, and another 67 were built by the Commonwealth Aircraft Corporation and Hawker Aircraft with the designation CA-30. They were essentially similar to the MB-326G but with improved avionics. The RAAF's aerobatic team, The Roulettes, flew the MB-326H from December 1970 until 1989. Although widely liked for its excellent handling and well-suited to its task, the service career of the MB-326 was cut short because of structural fatigue problems. The Australian fleet, for example, had a life of type extension program in the 1980s and were then re-winged in the early 1990s after a fatigue-related crash. Even so the MB-326 was supplemented by new Pilatus PC-9 trainers to reduce flying hours, and the last examples had been withdrawn by 2001.
Other MB-326Gs used the Viper Mk 20 engine which provided 1,524 kg of thrust, and were consequently faster and had an increased payload of 1,814 kg max. Argentina ordered eight, initially as the MB-326K, later called the MB-326GB.
Brazil was the main customer for the MB-326, in 1970 ordering two prototypes and 166 MB-326GCs, called the AT-26 Xavante. It was produced under license by Embraer with a further six for Togo and 10 for Paraguay. Another 17 were built in Italy for Zaire (Force Arienne Zairoise) and 23 for the Zambian Air Force.
The MB-326K (originally known as the MB-336) was the last generation model, fitted with the Viper Mk 600 engine, capable of 1,814 kg thrust to give an even better performance. The first flight took place on 22 August 1970. The two prototypes were I-AMKK and I-KMAK, the MB-326G was converted to this new model.
Dubai bought three in 1974, and a further three in 1978 (MB-326KD), Tunisia eight (MB-326KT), Ghana nine (MB-326KB) and Zaire eight (MB-326KB).
The MB-326L was essentially the MB-326K with two seats. Two MB-326LD were supplied to Dubai and four MB-326LD to Tunisia.
One of the last buyers was, again, AMI, who ordered 12 MB-326E, comprising six MB-326 updated to MB-326G, and six newly produced (MM.54384/389). They had provisions for armament, but the engine was the Viper 11 Mk 200 and not the Viper 20 Mk 540.[2]
The measures to save costs led the MB-326 to be substituted by propeller-driven models, but the Macchi was flexible enough to act as a medium trainer and light attack aircraft. RAAF pilot training in 1985 consisted of 60 hours pre-selection on CAC Winjeels, 150 hours medium and another 75 hours advanced training on MB-326s, before finally progressing to the Mirage IIIOD.
In Italian service, the MB-326 was replaced by the MB-339 between 1981 and 1984, acting after that as fast linkage aircraft, replacing the old T-33s that were slightly faster. Unusually the MB-326 did not see service with the Frecce Tricolori aerobatic team, who kept their faster G-91R PANs (they were later replaced by MB-339s).
The MB.326 failed to impress other NATO airforces, but it did have some success amongst many Third World countries, being used as a front-line machine in local wars.
The MB-326, like its competitors the Cessna T-37 and the BAC Jet Provost, was designed and ordered in the period when the "all-through" jet trainer was a fashionable concept in many air forces. The idea was to provide a single type that could be used for both elementary and advanced training right through to near combat-ready standard. In practice it was soon discovered that the simplicity and economy of scale of operating just one type for all training purposes was far outweighed by the purchase and operating costs of a large all-jet training fleet. Most operators quickly added a cheaper piston-engined type for basic training, and the MB-326 found its primary role as a lead-in trainer to prepare pilots for transition to very high performance fighter aircraft.
The aircraft was important also for two developments: from the MB.326K the MB.326L was produced, this was the direct ancestor of the Aermacchi MB.339. With license-building in Brazil, the MB.326 opened the field to further collaborations, leading to the AMX. Neither the MB.339 nor the AMX were as successful as the MB.326, but this machine was capable of further steps in technology and commerce.
South Africa
South Africa obtained a license to produce the MB-326M (similar to the 'G' model), as the Impala Mk I in 1964 with production starting in 1966.[5] It received 40 Italian-built aircraft followed by about 125 built locally by the Atlas Aircraft Corporation,[6] using them both as trainers and in an armed configuration. Seven examples of the MB-326K were also bought as light attack aircraft, with a further 15 assembled from kits,[7] while around 78 were license-produced and known as the Impala Mk II.[2] Licence production of the single seat version began in 1974.[5] The Impala Mk. II, built in South Africa from an Italian design with a British engine and French guns were highly effective, they also had some Electronic Counter Measures to defend themselves.
South Africa used its Impalas in combat against the Angolans, the Cubans and several militia movements. They typically flew at 550–650 km/h at a height of 15 m to avoid the risk of being shot down or even sighted by AA defenses. One was shot down by a SA-7, another returned with a unexploded missile (SA-7,8 or 9) in its exhaust.[8]
The aircraft had many advantages over high performance jets. Although slower, it could operate from primitive, short airfields and strike within minutes. The South African Air Force (SAAF) used up to 6 x 120 kg or 4 x 250 kg bombs. The main armament consisted of 68 mm SNEB rocket-launchers (four x 6 or two x 18), and two 30 mm guns (with 300 rounds).[9] These guns were the real bonus for the Impala Mk II, helping to give a superior performance compared to the two-seat versions. The latter could carry a pair of 30 mm DEFA guns in under-wing pods. However, the dual capability as trainer-attackers was better appreciated, as was the availability of six hard points and so dual-seat versions were the most produced. Six squadrons were equipped with the Impala Mk. II in the SAAF during the 1970s and 1980s. The situation over Angola and Namibia in 1987 and 1988 was such that the Impalas were withdrawn from the front line, leaving the work to Mirages and Buccaneers.[10]
Impala Mk. IIs were also used as interceptors although it was only opportunistically, not intentionally. In several encounters in 1985 with Mi-8 and Mi-24 helicopters, they shot down a total of six. This happened during a crucial phase of the ground war, when Angolan and Cuban troops were checked in an offensive against UNITA bases. This ended in disaster when the supplies were cut off by UNITA and the SAAF and front line troops ran out of ammunition. Helicopters were being used to supply the besieged troops and the SAAF cut off this link. Two Mi-24s were shot down in the first encounter while escorting Mi-17s.[11] The MiG-21s that escorted them flew too high and did not know what was happening. Two days later the Impala Mk IIs struck again, downing two Mi-24s and two Mi-17s. The attacks on the unsuspecting helicopters were carried out with only two guns per aircraft. The single seat Impala Mk. IIs were also sometimes armed with Matra R550 Magic air-to-air missiles for self defence.[5] The Impala Mk II operated at extreme ranges and had to fly very low, climbing only when helicopters were seen at medium altitude. After each attack they had to return to low level to avoid interception by MiGs.
The Silver Falcons, the SAAF aerobatic team, were equipped with Impala Mk Is.
The flying school for Impalas was Flying Training School at Langebaanweg while operational squadrons were 4, 5, 6, 7 Squadron SAAF and 8 Squadrons while 85 Advanced Flying School also had a small number of Impalas to supplement their Mirage trainers.[5]
Variants
- MB-326 : Two prototypes and 125 production training aircraft for the Italian Air Force.
- MB-326A : Proposed armed version for weapons training, not built.
- MB-326B : Two-seat jet trainer, light attack aircraft for Tunisia. (Eight built).
- MB-326D : Two-seat unarmed jet trainer for Alitalia. (Four built).
- MB-326E : Two-seat armed jet trainer for the Italian Air Force. (Six built).
- MB-326F : Two-seat jet trainer, light attack aircraft for Ghana. (Nine built).
- MB-326G : Two-seat jet trainer, ground-attack aircraft. (Two built).
- MB-326GB : Two-seat jet trainer, ground-attack aircraft. Eight were sold to the Argentine Navy. 17 aircraft were exported to Zaire, and another 23 aircraft to Zambia.
- MB-326GC : Two-seat jet trainer, ground-attack aircraft for the Brazilian Air Force. Built under license in Brazil as the EMBRAER EMB-326. 167 aircraft were built for the Brazilian Air Force. Eleven of the Brazilian aircraft were transferred to the Argentine Navy after the Falklands War. Six aircraft were exported to Togo, and another ten aircraft to Paraguay. Total production, 182.
- AT-26 Xavante : Brazilian Air Force designation of the MB-326GC.
- RT-26 Xavante : A number of AT-26 Xavantes were converted into reconnaissance aircraft.
- MB-326H : Two-seat jet trainer, 87 aircraft were built for the Royal Australian Air Force, and 10 for the Royal Australian Navy. Twelve Italian-built aircraft and 85 built under license in Australia by the Commonwealth Aircraft Corporation with the designation CA-30.
- MB-326K : Single-seat ground-attack aircraft for the South African Air Force. Built under license in South Africa by the Atlas Aircraft Corporation.
- Impala Mk II : South African Air Force designation of the MB-326K.
- MB-326KB : Single-seat ground-attack aircraft for Zaire. (Six built).
- MB-326KD : Single-seat ground-attack aircraft for Dubai. (Three built).
- MB-326KG : Single-seat ground-attack aircraft for Ghana. (Four Built).
- MB-326KT : Single-seat ground-attack aircraft for Tunisia. (Seven built).
- MB-326L : Two-seat advanced jet trainer aircraft.
- MB-326LD : Two-seat advanced jet training aircraft for Dubai. (Two built).
- MB-326LT : Two-seat advanced jet training aircraft for Tunisia. Four built.
- MB-326M : Two-seat jet trainer, ground-attack aircraft for the South African Air Force. Built under license in South Africa by the Atlas Aircraft Corporation.
- Impala Mk I : South African Air Force designation of the MB-326M.
- MB-326RM : Five Italian Air Force MB-326s were converted into ECM aircraft.
Operators
 Argentine Navy MB-326 preserved at Río Grande, Tierra del Fuego
Argentine Navy MB-326 preserved at Río Grande, Tierra del Fuego
- Argentine Navy - The Argentine Naval Aviation received eight MB-326GB plus eleven MB-326GC ex-Brazilian Air Force
- Royal Australian Air Force operated 87 MB-326Hs (RAAF serial A7-001 to -072, -079 to -083) from 1967 to 2001.
- No. 25 Squadron RAAF
- No. 76 Squadron RAAF
- No. 77 Squadron RAAF
- No. 79 Squadron RAAF
- No. 2 Flying Training School RAAF
- No. 2 Operational Conversion Unit RAAF
- No. 5 Operational Training Unit RAAF
- Central Flying School RAAF
- Roulettes
- Telstars
- Aircraft Research and Development Unit
- Fleet Air Arm (RAN) operated ten MB-326Hs from 1970 to 1983.
- No. 724 Squadron RAN
- Brazilian Air Force received 182 MB-326GCs (known as the AT-26 Xavante) and 12 Atlas Impala ex-South African Air Force. All retired in 2010.
- Cameroon Air Force has 8 in service.
- Ghana Air Force received 15 MB.326s.
- Alitalia
- Italian Air Force operated 106 MB-326s, including 15 pre-production versions.
- Paraguayan Air Arm operated ten EMB-326GBs/AT-26 Xavante, all were retired in 2003.
- South African Air Force received 62 MB-326s plus 125 Impala Mk.1s and 73 Mk.2s
- Togolese Air Force received six MB-326GCs.
- Tunisian Air Force received 16 MB-326s.
- United Arab Emirates Air Force bought six aircraft.
- Zaire Air Force received 25 MB-326GBs.
- Zambian Air Force received 23 MB-326GB.
Specifications (MB-326)
Data from Jane's All The World's Aircraft 1969-70 [12]
General characteristics
- Crew: Two
- Payload: 1,814 kg (4,000 lb)
- Length: 10.65m (34 ft 11¼ in)
- Wingspan: 10.56 m (34 ft 8 in)
- Height: 3.72 m (12 ft 2½ in)
- Wing area: 19.0 m² (204.5 ft²)
- Empty weight: 2,237 kg (4,930 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 3,765 kg (8,300 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Bristol Siddeley Viper Mk.11 turbojet, 11.1 kN (2,500 lbf)
Performance
- Never exceed speed: Mach 0.8
- Maximum speed: 806 km/h (436 knots, 501 mph) at 4,575m (15,000 ft)
- Stall speed: 146 km/h (79 knots , 91 mph) (wheels and flaps lowered)
- Range: 1,665 km (900 Nmi, 1,035 miles) with large tip tanks at 11,500 m (38,000 ft)
- Service ceiling: 12,500 m (41,000 ft)
- Rate of climb: 22.3 m/s (4,400 ft/min)
Armament
- Guns: provision for 2 × 12.7 mm Browning machine guns in underwing pods
- Bombs: Up to 2000 lb (900 kg) of weapons on six hardpoints, including gun-pods, bombs, and rockets
Accidents and losses
In Italian Service
- 22 April 1959: First prototype I-MAKI crashed in Egypt; pilot ejected.[13]
Excluding the prototype, 33 Italian Air Force MB-326s were lost in accidents between 1963 and 1992.[14]
South African Air Force service
- On October 2, 1993, an Impala Mark I (Aermacchi MB-326)(no. 489) of the SAAF Silver Falcons aerobatic team crashed after suffering separation of the right wing during a performance at the Lanseria Airshow. The pilot, Captain Charlie Rudnick, ejected but was killed, as the ejection was initiated outside of the design envelope of the ejection seat.[15]
See also
- Related development
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- PZL TS-11 Iskra
- Soko G-2 Galeb
References
- Notes
- ^ Angelucci and Matricardi 1980, pp. 269–271.
- ^ a b c d Jannetti
- ^ Taylor 1969, p. 120.
- ^ Angelucci and Matricardi 1980, p. 269.
- ^ a b c d Potgieter, Herman and Willem Steenkamp. Aircraft of the South African Air Force. London: Jane's, 1981, First edition 1980. ISBN 0-86977-133-7.
- ^ The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft, Issue 1, 1981, p. 20.
- ^ The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft, Issue 2, 1981, p. 34.
- ^ War machines 1985, p. 2119
- ^ War machines 1985
- ^ Fenili
- ^ Cooper, Tom. "Angola: SAAF Bushwacks Six Helicopters." ACIG. Retrieved: 2 January 2010.
- ^ Taylor 1969, pp. 120–121.
- ^ "ASN Wikibase Occurrence # 31989." Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved: 22 February 2011.
- ^ "Chronological Listing of Italian Losses & Ejections." Aviation Safety Network. Retrieved: 22 February 2011.
- ^ "Silver Falcons." silverfalcons.co.za. Retrieved: 22 February 20111.
- Bibliography
- "Aermacchi M.B.326". The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft, London: Orbis, Volume 1, Issue 1, 1981, p. 20.
- "Aermacchi M.B.326K". The Illustrated Encyclopedia of Aircraft, London: Orbis, Volume 1, Issue 2, 1981, p. 34.
- Angelucci, Enzo and Paolo Matricardi. Combat Aircraft 1945-1960. Maidenhead, Berkshire, UK: Sampson Low Guides, 1980. ISBN 562-00136-0.
- Fenili, Vincenzo. "Impala sul Bush." JP4 Magazine, January 1990.
- Jannetti, Fabrizio. "30 anni di '326." Aeronautica & Difesa magazine, Ed. Ai editions, Rome, n.14, December 1987 pp. 38–47.
- Taylor, John W.R., ed. Jane's All The World's Aircraft 1969-70. London: Jane's Yearbooks, 1969.
- War Machines Encyclopaedia (Italian edition printed by De Agostini). London: Aerospace Publishing, 1985, pp. 2117–2119 .
External links
- Specs & Photo at Flugzeuginfo.net
- Serial number history of Australian CAC/MB-326 aircraft
- Warbird Alley: MB-326 page
Aircraft produced by Aermacchi Atlas/Denel aircraft Fixed-wing aircraft Helicopters Commonwealth Aircraft Corporation aircraft CA-1 · CA-2 · CA-3 · CA-4 · CA-5 · CA-6 · CA-7 · CA-8 · CA-9 · CA-10A · CA-11 · CA-12 · CA-13 · CA-14 · CA-15 · CA-16 · CA-17 · CA-18 · CA-19 · CA-20 · (CA-21 no aircraft built) · CA-22 · (CA-23 no aircraft built) · CA-24 · CA-25 · CA-26 · CA-27 · CA-28 · CA-29 · CA-30 · (CA-31 no aircraft built) · CA-32 · CA-33 · CA-34 · CA-35 · CA-36
Embraer aircraft Agricultural: EMB 202 Ipanema
Civil: EMB 110 · EMB 120 · EMB 121 · ERJ 145 family · Legacy 600 · E-Jets · Lineage 1000 · Phenom 100 · Phenom 300 ·
Military: EMB 312 · EMB 314 · AMX · R-99
Built under licence: EMB 326 · EMB 710 · EMB 711 · EMB 712 · EMB 720 · EMB 721 · EMB 810 · EMB 820C
In development/proposed: Legacy 450 · Legacy 500 · KC-390
Not developed: CBA 123
Lists relating to aviation General Aircraft (manufacturers) · Aircraft engines (manufacturers) · Airlines (defunct) · Airports · Civil authorities · Museums · Registration prefixes · Rotorcraft (manufacturers) · TimelineMilitary Accidents/incidents Records Categories:- Macchi aircraft
- Atlas aircraft
- CAC aircraft
- Embraer aircraft
- Italian attack aircraft 1970–1979
- Italian military trainer aircraft 1950–1959
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.