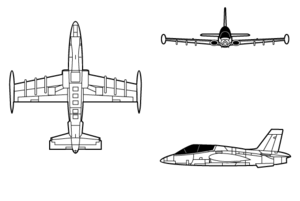
- Aermacchi MB-339
-
MB-339 Role Advanced trainer Manufacturer Alenia Aermacchi First flight 12 August 1976 Primary user Italian Air Force Produced 1978- Number built Over 213 Unit cost $8.3 million Developed from Aermacchi MB-326 The Aermacchi MB-339 is an Italian military trainer and light attack aircraft. It was developed as a replacement for the earlier MB-326.
Contents
Design and development
In September 1972, Aermacchi was awarded a contract to study a replacement for the Italian Air Force)'s MB-326s, comparing seven all-new designs (given the designation MB-338) powered by various engineswith an improved version of the MB-326, designated the MB-339. The MB-339 was considered to meet the Italian Air Forces requirements while being cheaper than the all-new designs which resulted in it being selected to replace both the MB-326 and the Fiat G.91T in Italian service.[1]
The MB-339 is of conventional configuration and all-metal construction, and shares much of the 326's airframe. It has a low, un-swept wing with tip tanks and jet intakes in the roots, tricycle undercarriage, and accommodation for the student and instructor in tandem. The most significant revision was a redesign of the forward fuselage to raise the instructor's seat to allow visibility over and past the student pilot's head. The aircraft was fitted with a larger fin and powerplant for the initial versions was the same Rolls-Royce Viper 632-43, producing 4,000 lbf (17.79 kW), as fitted to the MB-326-K.[2]
The first flight took place on 12 August 1976 and deliveries to the Italian Air Force commenced in 1979.[3] Still in production in 2004 in an enhanced version with a much-modernised cockpit. Over 200 MB-339s have been built, with roughly half of them going to the Italian Air Force.
The Lockheed-Aermacchi MB-339 T-Bird II was a losing contender in the USA's Joint Primary Aircraft Training System (JPATS) aircraft selection. Among the seven to enter, the Raytheon/Pilatus entry won, which became the T-6 Texan II.
According to an article posted on the Italian website 'Il Porto Franci', called 'Armi e finanziamenti nel corno d'Africa', Eritrea paid about $US 50 million for six MB-339 CEs in 1997. This is the original MB-339 with more advanced avionics for the ground attack role, RWR, uprated Viper 680-43 engine, and larger wingtip tanks. It is capable of carrying Sidewinder AAMs, AGM-65 Maverick AGMs, and laser-guided bombs. Unit price of the MB-339C would have to be somewhere around $US 8.3 million in 1997 dollars.
Operational history
Argentina
The Argentine Naval Aviation (Comando de Aviación Naval) was the first foreign user of the forerunner MB-326GB, buying eight in 1969.
In 1980, Comando de la Aviación Naval Argentina (CANA), or Argentine naval air command, ordered ten MB-339As, advanced trainer and light attack aircraft. The MB339 were delivered in 1981 and were operated by the III Escuadra Naval 's 1 Escuadrilla de Ataque.[4] During the Falklands War, late in April 1982, six of them were located at Port Stanley Airport, renamed Base Aérea Militar (BAM) Malvinas.[4] They were the only attack jets to operate from the Falklands, along with four Beech T-34 Mentor piston-engined armament trainer and light attack aircraft, and 24 turboprop FMA IA 58 Pucará light attack aircraft of Grupo 3 de Ataque.[5] Other Airmacchis operated from three mainland bases, at Almirante Zar, Bahia Blanca and Río Grande, Tierra del Fuego naval air station.[6]
On 21 May during a routine reconnaissance flight and flown by Lieutenant Owen Crippa, a MB-339A was the first one to attack the Royal Navy amphibious force. The Aermacchi hit the frigate HMS Argonaut, causing light damage.[7][8] On 27 May, a MB-339A (4-A-114) was shot down by a Blowpipe missile during the Battle for Goose Green, while attempting to attack British ships and landed troops. The Pilot, Teniente (Lt) Miguel, was killed.[9][10] Three MB-339 airframes were captured by the British.[11]
Eritrea
During tensions between Eritrea and Ethiopia in the late 1990's, Eritrea started to rebuild its air force. In 1995-1996, the Eritreans ordered six Aermacchi MB.339FD strike fighters, with which the first combat unit of the ERAF was founded in 1997. They have proved their worth as training aircraft and even during the early fighting in 1998.
Their initial deployment started on 5 June 1998 (the same day in which the ETAF also started its operations). During the same afternoon, the Ethiopians reported two attacks of Eritrean MB.339FDs on the city of Mekelle, the capital of Ethiopian province Tigray. Reportedly, as many as 44 civilians were killed and 135 injured.
However, on 6 June one of the Macchis was shot down north of Mekelle. The pilot ejected and was rescued by a Mi-8 of the ERAF. The Eritrean Macchis were deployed again on the next day during the fighting around Erde Mattios.
On the morning of 12 June 1998, two Eritrean Mi-8 appeared in low level over Addis Pharmaceutical works, in Adigrat, attempting to bomb it. Their weapons, however, fell a few yards from the plant and caused only minor damage. Only a couple of hours later, four MB.339s rocketed and cluster-bombed against several targets in the city as well. According to Ethiopian sources four people died and 30 other were injured during those attacks.
On 5 February 1999 the Ethiopian government claimed that two Eritrean MB.339FDs attacked a fuel depot in Adigrat, some 48 kilometres inside the Ethiopian border, important for the supply of the Ethiopian army with fuel.
Variants
- MB-339X
- Two prototypes
- MB-339A
- Original production variant for Italy. 107 were delivered in three batches 1979–1995 (including MB-339PANs and MB-339RMs.[12] In addition, four delivered to Ghana and five to Dubai.[13]
-
- MB-339PAN
- Variant for Frecce Tricolori aerobatic team., adding smoke generator but removing tip tanks 21 new build or converted from MB-339A.[14]
- MB-339RM
- Radio and radar calibration variant for Italian Air Force. Three built in 1981 but later converted to MB.339A standard.[14]
- MB-339AM
- MB-339A version built for Malaysia. 13 built, with deliveries from 1983.[13]
- MB-339AN
- MB-339A version built for Nigeria. Twelve built from June 1984.[13]
- MB-339AP
- MB-339A version built for Peru. Sixteen built and delivered from November 1981.[13]
- MB-339K Veltro II
- Single-seat dedicated attack version, first flew 30 May 1980.[15] One built.[16]
- MB-339B
- Trainer with more powerful (4,400 lbf (19.57 kN)) Viper 680-43 engine. One example built.[14]
- MB-339C
- Revised trainer version with new, digital avionics.[17]
-
- MB-339CB
- New Zealand trainer and weapons training version of MB-339C, powered by Viper 680-43 engine and equipped with laser rangefinder, radar detection, AIM-9L Sidewinder and AGM-65 Maverick capability. Eighteen built and delivered from March 1991.[12][18][19] - 17 survivors - in storage at RNZAF Base Ohakea, New Zealand
- MB-339CD
- MB-339C for Italy, with modernised flight controls and avionics, but retaining original 4,000 lbf (17.79 kW) Viper 632-43 of MB-339A. 30 built.[20]
- MB-339FD ("Full Digital")
- Export version of the MB-339CD[17]
- MB-339CE
- MB-339C version built for Eritrea powered by Viper 680-43. Six built.[12]
- MB-339CM
- MB-339C version being built for Malaysia.
- MB-339 T-Bird II (Lockheed T-Bird II)
- Version for U.S. JPATS competition, with 4,000 lbf Viper 680-582.[17]
Operators
- Dubai Air Wing operates 7 MB-339A.
- Eritrean Air Force operates 5 MB-339CE.
- Ghana Air Force operates 4 MB-339A
- Italian Air Force operates 72 MB-339A and 30 MB-339CD.
- Royal Malaysian Air Force operated 13 MB-339AM - 8 survivors. An order for 8 MB-339CM replacements was placed in 2006.[21]
- Nigerian Air Force operates 12 MB-339AN.
- Peruvian Air Force operates 14 MB-339AP.
Former operators
- Argentine Naval Aviation 10 originally delivered, widthdraw 1990s
- Royal New Zealand Air Force received 18 MB-339CB used by No. 14 Squadron RNZAF between 1991 and 2002. 17 aircraft are now stored
Specifications (MB-339A)
Data from Jane's All The World's Aircraft 1980-81 [22]
General characteristics
- Crew: two, student and instructor
- Length: 10.97 m (36 ft 0 in)
- Wingspan: 10.86 m (35 ft 7½ in)
- Height: 3.60 m (11 ft 9¾ in)
- Wing area: 19.3 m² (208 ft²)
- Airfoil: NACA 64A-114 (mod) at centreline, NACA 64A-212 (mod) at tip
- Empty weight: 3,075 kg (6,780 lb)
- Loaded weight: 4,400 kg (9,700 lb)
- Max takeoff weight: 5,897 kg (13,000 lb)
- Powerplant: 1 × Rolls-Royce Viper Mk. 632 turbojet, 4,000 lbf (17.8 kN)
Performance
- Never exceed speed: Mach 0.82 (926 km/h, 500 knots, 575 mph)
- Maximum speed: 898 km/h (485 knots, 558 mph) at sea level
- Stall speed: 148.5 km/h (80 knots, 92.5 mph)
- Range: 1,760 km (950 NMI, 1,093 mi)
- Service ceiling: 14,630 m (48,000 ft)
- Rate of climb: 33.5 m/s (6,595 ft/min)
- Wing loading: 228 kg/m² (46.6 lb/ft2)
Armament
See also
- Related development
- Aircraft of comparable role, configuration and era
- BAE Hawk
- Aero L-39 Albatros
- L-159 ALCA
- G-4 Super Galeb
- IAR 99
References
- Notes
- ^ Air International June 1978, p. 276.
- ^ Air International June 1976, pp. 276, 310–311.
- ^ Taylor 1980, p.119.
- ^ a b Chant 2001, p.35.
- ^ Chant 2001, pp.35-36.
- ^ Chant 2001, p.92.
- ^ Chant 2001, p.62.
- ^ Ethell and Price 1983, p.108.
- ^ FREEDMAN, Sir Lawrence, The Official History of the Falklands Campaign (Abingdon, 2005). Volume II, page 732-735
- ^ Chant 2001, pp.66-67.
- ^ "List of Argentine Aircraft Destroyed". http://www.naval-history.net/F64argaircraftlost.htm. Retrieved 2009-November-08.
- ^ a b c Jackson 2003, pp. 276–278.
- ^ a b c d Jackson 2003, p. 278.
- ^ a b c Jackson 2003, p. 276.
- ^ Taylor 1980, pp.777-778.
- ^ Braybrook 1992, p. 143.
- ^ a b c Jackson 2003, p. 277.
- ^ Brayvrook 1992, pp. 143–144.
- ^ Wright 1992, p. 251.
- ^ Jackson 2003, pp. 277–278.
- ^ Air International April 2009, p.7.
- ^ Taylor 1980, pp.119-120.
- Bibliography
- Braybrook, Roy. "Aermacchi MB-339C". Air International, September 1992, Vol. 43, No. 3. pp. 137–144.
- Chant, Christopher. Air War in the Falklands 1982. Oxford, UK, Osprey Combat Aircraft 28, 2001. ISBN 978-1-84176-293-7.
- Ethell, Jeffrey and Alfred Price. Air War South Atlantic.London: Sidgwick & Jackson, 1983. ISBN 0-283-99035-X.
- "Initial Malaysian MB-339CMs Delivered". Air International, April 2009, Vol.76, No. 4. p. 7.
- Jackson, Paul. Jane's All The World's Aircraft 2003–2004. Coulsdon, UK: Jane's Information Group, 2003. ISBN 0 7106 2537 5.
- "Mentor with a pedigree: Aeronautica Macchi's MB-339". Air International, June 1978, Vol. 14 no. 6. pp. 267–276, 310–311.
- Taylor, John W.R. (ed.) Jane's All The World's Aircraft 1980-81. London: Jane's Publishing. ISBN 0-7106-0705-9.
- Wright, Matthew. "Not all black for the winged Kiwis". Air International, May 1992, Vol. 42, No. 5. pp. 249–257.
External links
- Official website
- Aermacchi MB-339 PAN for FlightGear
- http://www.airforce-technology.com/projects/mb339/
- http://web.tiscali.it/aviationgraphic/iaf.html
- http://www.kiwiaircraftimages.com/mb339.html
- Airliners.net
- myaviation.net
- http://www.awti-decimo.com/gallery/thumbnails.php?album=1&page=1
Aircraft produced by Aermacchi Aircraft proposed for the Joint Primary Aircraft Training System Beech/Pilatus PC-9 Mk 2 • Cessna 526 CitationJet • Grumman/SIAI Marchetti S-211A • Lockheed/Aermacchi T-Bird II • Northrop/EMBRAER EMB-312H Super Tucano • Rockwell/RFB Ranger 2000 • Vought/FMA Pampa 2000
Lists relating to aviation General Aircraft (manufacturers) · Aircraft engines (manufacturers) · Airlines (defunct) · Airports · Civil authorities · Museums · Registration prefixes · Rotorcraft (manufacturers) · TimelineMilitary Accidents/incidents Records Categories:- Macchi aircraft
- Falklands War aircraft
- Italian attack aircraft 1980–1989
- Italian military trainer aircraft 1970–1979
- Single-engined jets
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.