- Maze
-
Not to be confused with Maize.For other uses, see Maze (disambiguation).
Part of a series on Puzzles  Types
Types- Guessing game
- Logic puzzle
- Dissection puzzle
- Induction puzzle
- Logic grid puzzle
- Self-reference puzzle
- Mechanical puzzle
- Puzzle video game
- Transport puzzle
- Word puzzle
- Metapuzzle
A maze is a tour puzzle in the form of a complex branching passage through which the solver must find a route. In everyday speech, both maze and labyrinth denote a complex and confusing series of pathways, but technically the maze is distinguished from the labyrinth, as the labyrinth has a single through-route with twists and turns but without branches, and is not designed to be as difficult to navigate.[1] The pathways and walls in a maze or labyrinth are fixed (pre-determined) – puzzles where the walls and paths can change during the game are categorised as tour puzzles. The Cretan labyrinth is the oldest known maze.[2]
Maze construction
Mazes have been built with walls and rooms, with hedges, turf, corn stalks, hay bales, books, paving stones of contrasting colors or designs, bricks and turf,[3] or in fields of crops such as corn or, indeed, maize. Maize mazes can be very large; they are usually only kept for one growing season, so they can be different every year, and are promoted as seasonal tourist attractions. Indoors, Mirror Mazes are another form of maze, where many of the apparent pathways are imaginary routes seen through multiple reflections in mirrors. Another type of maze consists of a set of rooms linked by doors (so a passageway is just another room in this definition). Players enter at one spot, and exit at another, or the idea may be to reach a certain spot in the maze. Mazes can also be printed or drawn on paper to be followed by a pencil or fingertip.
-
Classical labyrinth
Generating mazes
Main article: Maze generation algorithmMaze generation is the act of designing the layout of passages and walls within a maze. There are many different approaches to generating mazes, where various maze generation algorithms exist for building them, either by hand or automatically by computer.
There are two main mechanisms used to generate mazes. "Carving passages" is where one marks out the network of available routes. "Adding walls" is where one lays out a set of obstructions within an open area. Most mazes drawn on paper are where one draws the walls, where the spaces in between the markings compose the passages.
Solving mazes
Main article: Maze solving algorithmMaze solving is the act of finding a route through the maze from the start to finish. Some maze solving methods are designed to be used inside the maze by a traveler with no prior knowledge of the maze, whereas others are designed to be used by a person or computer program that can see the whole maze at once.
The mathematician Leonhard Euler was one of the first to analyze plane mazes mathematically, and in doing so made the first significant contributions to the branch of mathematics known as topology.
Mazes containing no loops are known as "standard", or "perfect" mazes, and are equivalent to a tree in graph theory. Thus many maze solving algorithms are closely related to graph theory. Intuitively, if one pulled and stretched out the paths in the maze in the proper way, the result could be made to resemble a tree.[4]
Mazes in psychology experiments
Mazes are often used in psychology experiments to study spatial navigation and learning. Such experiments typically use rats or mice. Examples are:
- the Barnes maze
- the Morris water maze
- the radial arm maze
- the elevated plus maze
Other types of mazes
- Ball-in-a-maze puzzles
- Dexterity puzzles which involve navigating a ball through a maze or labyrinth.
- Block maze
- A maze where the player must complete or clear the maze pathway by positioning blocks. Blocks may slide into place or be put down. An example is shown below.
- Logic mazes
- See Logic maze. These are like standard mazes except they use rules other than "don't cross the lines" to restrict motion.
- Loops and Traps Maze
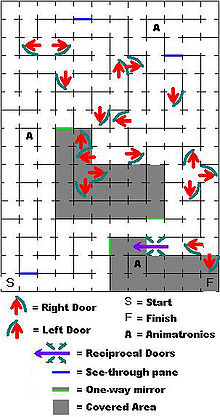
- A maze that features one-way doors. The doors can lead to the correct path or create traps that divert you from the correct path and lead you to the starting point. You may not return through a door which you have entered, so dead ends may be created. The path is a series of loops interrupted by doors. The Halloween Maze in Ridgewood NJ is an example of this type of maze. Through the use of reciprocal doors, the correct path can intersect the incorrect path on a single plane. A graphical variant of this maze type is an arrow maze, shown below.
- Mazes in higher dimensions
- It is possible for a maze to have three or more dimensions. A maze with bridges is three dimensional, and some natural cave systems are three dimensional mazes. The computer game Descent utilized fully three dimensional mazes. Any maze can be topologically mapped onto a three-dimensional maze.[citation needed]
- Number maze
- A maze where numbers are used to determine jumps that form a pathway, allowing for a maze to criss cross itself many times. An example is shown below.
- Picture maze
- A standard maze that forms a picture when solved.
- Turf mazes and Mizmazes
- A pattern like a long rope folded up, without any junctions or crossings.
- Sampling of maze types, also available in a printable view and with a solution key.
Publications about mazes
Numerous mazes of different kinds have been drawn, painted, published in books and periodicals, used in advertising, in software, and sold as art. In the 1970s there occurred a publishing "maze craze" in which numerous books, and some magazines, were commercially available in nationwide outlets and devoted exclusively to mazes of a complexity that was able to challenge adults as well as children (for whom simple maze puzzles have long been provided both before, during, and since the 1970s "craze").
Some of the best-selling books in the 1970s and early 1980s included those produced by Vladimir Koziakin,[5] Rick and Glory Brightfield, Dave Phillips, Larry Evans, and Greg Bright. Koziakin's works were predominantly of the standard two-dimensional "trace a line between the walls" variety. The works of the Brightfields had a similar two-dimensional form but used a variety of graphics-oriented "path obscuring" techniques – although the routing was comparable to or simpler than Koziakin's mazes, the Brightfield's mazes did not allow the various pathway options to be discerned so easily by the roving eye as it glanced about.
Greg Bright's works went beyond the standard published forms of the time by including "weave" mazes in which illustrated pathways can cross over and under each other. Bright's works also offered examples of extremely complex patterns of routing and optical illusions for the solver to work through. What Bright termed "mutually accessible centers" (The Great Maze Book, 1973) also called "braid" mazes, allowed a proliferation of paths flowing in spiral patterns from a central nexus and, rather than relying on "dead ends" to hinder progress, instead relied on an overabundance of pathway choices. Rather than have a single solution to the maze, Bright's routing often offered multiple equally valid routes from start to finish, with no loss of complexity or diminishment of solver difficulties because the result was that it became difficult for a solver to definitively "rule out" a particular pathway as unproductive. Some of Bright's innovative mazes had no "dead ends" – although some clearly had looping sections (or "islands") that would cause careless explorers to keep looping back again and again to pathways they had already travelled.
The books of Larry Evans focused on 3-D structures, often with realistic perspective and architectural themes, and Bernard Meyers (Supermazes No. 1) produced similar illustrations. Both Greg Bright (The Hole Maze Book) and Dave Phillips (The World's Most Difficult Maze) published maze books in which the sides of pages could be crossed over and in which holes could allow the pathways to cross from one page to another, and one side of a page to the other, thus enhancing the 3-D routing capacity of 2-D printed illustrations.
Adrian Fisher is both the most prolific contemporary author on mazes, and also one of the leading maze designers[citation needed]. His book The Amazing Book of Mazes (2006) contains examples and photographs of numerous methods of maze construction, several of which have been pioneered by Fisher; The Art of the Maze (Weidenfeld and Nicholson, 1990) contains a substantial history of the subject, whilst Mazes and Labyrinths (Shire Publications, 2004) is a useful introduction to the subject.
A recent book by Galen Wadzinski (The Ultimate Maze Book) offers formalized rules for more recent innovations that involve single-directional pathways, 3-D simulating illustrations, "key" and "ordered stop" mazes in which items must be collected or visited in particular orders to add to the difficulties of routing (such restrictions on pathway traveling and re-use are important in a printed book in which the limited amount of space on a printed page would otherwise place clear limits on the amount of choices and pathways that can be contained within a single maze). Although these innovations are not all entirely new with Wadzinski, the book marks a significant advancement in published maze puzzles, offering expansions on the traditional puzzles that seem to have been fully informed by various video game innovations and designs, and adds new levels of challenge and complexity in both the design and the goals offered to the puzzle-solver in a printed format.
Mazes open to the public
Africa
- Honeydew Maze, Randburg, Gauteng, South Africa.
- Serendipity Maze, Mouille Point, Cape Town, South Africa. Hedge maze by the sea.[6]
- Walkabout Mazes and Botanical Gardens,[7] Robertson, Western Cape, South Africa. 13870 m² net area Google Maps[8]
Asia
Dubai
(construction was planned but the maze does not seem to exist)
India
- Adham Khan's Tomb, Delhi, India
- A maze inside Bara Imambara is there, which is famous as bhulbhulaiya and is also a popular as tourist place in Lucknow, India
Japan
- Hikimi no Meiro,[10] Masuda, Shimane, Japan
- Kodama no Mori,[11] Kiso, Nagano, Japan
- Kyodai Meiro Palladium,[12] Nikkō, Tochigi, Japan
- Sendai Hi-Land,[13] Sendai, Miyagi, Japan
- Shirahama Energy Land,[14] Shirahama, Wakayama, Japan
South Korea
- Jeju Kimnyung Maze Park, Kimnyong-ri, Jeju, Korea(The first hedge maze in Jeju, designed by Adrian Fisher, 1990; Latitude 33°32'13.34"N Longitude 126°46'21.45"E)
- Mazeland, Pyongdae-ri, Jeju, Korea(World's Largest Whinstone Maze designed by J.K. Ryu, 2005; Latitude 33°29'16.80"N Longitude 126°48'3.70"E)
- Seriworld, Sohgwipo city, Jeju, Korea
- Sulmundae Park, Shinpung-ri, Jeju, Korea(Stone hedge Maze with Sulmundae legend, 2011; Latitude 33°22'3.07"N Longitude 126°49'39.89"E)
Europe
Austria
Inside the labyrinth of Villa Pisani
- Schönbrunn Palace, Austria (small entrance fee, tower at the center to overlook the hedge maze)[15]
Belgium
Germany
- Altjeßnitz, Germany, Sachsen-Anhalt, near Dessau (hedge maze, c.1750) (51°41′35.7″N 12°19′23.9″E / 51.69325°N 12.323306°E)
- Aschaffenburg (Park Schönbusch), Germany, Bavaria (hedge maze, c.1829) (49°57′42″N 9°06′24″E / 49.96155°N 9.1068°E)
- Berlin (Erholungspark Marzahn), Germany (hedge maze)[16]
- Hannover (Herrenhausen Gardens), Germany, Lower Saxony
- Hortus Vitalis – Der Irrgarten,[17] Bad Salzuflen, Germany, North-Rhine-Westphalia (hedge maze)
Greece
- Palace of Knossos
Italy
- Castello di Masino, Caravino, 10010 Torino, Italia [18]
- Porsenna's Maze,[19] Chiusi, Tuscany (see Pliny's Italian labyrinth)
- Villa Pisani, Stra, near Venice
Netherlands
- Drielandenpunt, Vaals (6.500 m2, designed by Adrian Fisher, 1992)
Nordic Countries
- The Labyrinth in Moomin World, Finland
- Labyrinthia, Silkeborg, Denmark[20]
- Labyrinttimaailma (Labyrinth world), Finland
- Nokkakivi amusement park Hedge Maze, Finland
- Samsø Labyrinten (The world's largest permanent maze, 60.000 m2), Denmark,[21][22]
Portugal
- Parque do Arnado,[23] Ponte de Lima, District of Viana do Castelo
- Parque de São Roque,[24] District of Porto[25]
- Reserva Florestal de Recreio do Pinhal da Paz,[26] São Miguel Island, Azores
Spain
- Amaze'n Laberintos, Spain, Majorca, Alcudia, Playa de Muro (wooden maze, 1998)
- Labyrinth in the Way of Santiago – Spain Laberinto del Camino de Santiago – España.
- Parc del Laberint d'Horta, Barcelona, Spain (hedge maze)[27]
UK
- Alnwick Castle Water Gardens Bamboo Maze, Northumberland. Designed by Adrian Fisher
- Blackpool Pleasure Beach Hedge Maze, Lancashire, England. Designed by Adrian Fisher
- Blake House Craft Centre, Braintree, Essex, England (Open July–September)[28][29]
- Blenheim Palace Hedge Maze, Oxfordshire, England. Designed by Minotaur Designs, Adrian Fisher, Randoll Coate and Graham Burgess, 1991[30]
- Carnfunnock Country Park, Northern Ireland. A hedge maze in the shape of Northern Ireland and winner of 1985 Design a Maze competition.[31]
- Castlewellan, Northern Ireland, world's largest permanent hedge maze[32][33]
- Chatsworth House, England (hedge maze)[34]
- The Crystal Palace, England. A hedge maze built into a copse[35]
- Glendurgan Garden, Cornwall. A cherry laurel hedge maze created in 1833.[36]
- Greys Court 'Archbishop's Maze', Oxfordshire, England. Designed by Adrian Fisher, 1981[37]
- Hampton Court Palace, England (hedge maze)[38]
- Hoo Hill Maze, Shefford, Bedfordshire, England[39][40]
- Kentwell Hall, Long Melford, Suffolk, England. Designed Minotaur designs, Adrian Fisher, Randoll Coate and Graham Burgess.
- Leeds Castle, Maidstone, Kent, England. Designed by Minotaur Designs Randoll Coate, Adrian Fisher and Graham Burgess[41]
- Longleat, Wiltshire, England: hedge maze, designed by Greg Bright, 1978, and mirror maze, designed by Adrian Fisher; Labyrinth of Love, Renaissance style Rose garden labyrinth designed by Graham Burgess. Sun and Moon Maze designed by Randoll Coate.
- Murray Star Maze, Scone Palace, Perth, Scotland (hedge maze). Unusual Celtic-weave. Designed by Adrian Fisher[42]
- Noah's Ark Zoo Farm, Bristol, England (longest hedge maze in the world, planted 2003)[43]
- Norwich Cathedral,[44]
- Oak Lane Labyrinth, nr Bury St. Edmunds, Suffolk. Open all year round. Free entry.[45]
- Paulton's Park, Hampshire, England (hedge maze),[46]
- Richings Park Amazing Maize Maze, Richings Park, near Heathrow, England (Open July–September)[47]
- Saffron Walden, Essex, England (hedge maze),[48] (The town also has a historic turf maze)
- St. Catherine's Hill, Hampshire near Winchester, old "Miz-Maze" or "Mizmaze" (unusual square design; path is a narrow groove)[49]
- Symonds Yat, Herefordshire, England[50]
- Traquair House, Innerleithen, Scotland (hedge maze)[51]
- Wonderland, Telford, Shropshire, England[52]
- Worden Park, Leyland, Lancashire, England[53]
North America
 Public maze at Wild Adventures theme park, Valdosta, Georgia. It was removed before the 2010 season.
Public maze at Wild Adventures theme park, Valdosta, Georgia. It was removed before the 2010 season. Maze at Missouri Botanical Garden in St. Louis
Maze at Missouri Botanical Garden in St. Louis
Canada
- Labyrinthe du Hangar 16, Montreal, Canada.[54]
- The Maze on Centre Island, Toronto, Ontario, was a centennial gift to the city by its Dutch-Canadian community in 1967 (Topiary maze, open to public, free, year-round)
- McMaze,[55] St. Andrew's West, Ontario, Canada. Original corn maze designed by Sandy McDonald.
- Saunders Farm, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. The largest collection of full-sized hedge mazes and labyrinths in North America (11).
USA
- Amazing Chicago's Funhouse Maze,[56] Navy Pier, Chicago, Illinois, USA. Designed by Jack Rouse Associates and Adrian Fisher
- America's Largest Corn Maze, Shakopee, Minnesota, USA Sever's Corn Maze[57]
- Black Hills Maze, Rapid City, South Dakota, USA
- Children's maze (made out of packs of hay), Ashland Berry Farm, Ashland, Virginia, USA.
- Davis' Mega Maze, Sterling, Massachusetts USA (3-D adventure corn maze). Designed by Adrian Fisher[58]
- Dole Plantation, Wahiawa, Hawaii, (21°31′29.5″N 158°2′14.9″W / 21.524861°N 158.037472°W) home to the World's Largest Maze.[59]
- The Garden Maze at Luray Caverns, Luray, VA, USA
- Goofy Rooster Corn Maze, Helen, Georgia, U.S.A.[60]
- Magical Mystery Mirror Maze, Mission Beach, San Diego, California, USA. Designed by Adrian Fisher.
- Magnolia Plantation and Gardens (Charleston, South Carolina), USA
- Magowan's Infinite Mirror Maze, Pier 39, San Francisco, California
- Maize Quest Fun Park[61] is the "Largest Collection of People-Sized Mazes in the World" with mazes made of fence, rope, stone, turf, corn, Invisible Dog Fencing, Straw Bales, Tiles, Living Bamboo, and Earthen Mounds. New Park, Pennsylvania, USA
- Mall of Georgia Paving Mazes, Atlanta, Georgia, USA. Designed by Adrian Fisher
- The Maze at the Governor's Palace, Colonial Williamsburg, Virginia, USA
- Maze Mania, Garden City, South Carolina USA (Interchangeable fence Maze appropriate for children and adults)
- Mohonk Mountain House hedge maze, New Paltz, New York
- Monterey Mirror Maze, Monterey, California, USA. Designed by Adrian Fisher.
- Mystery Maze, Wild Adventures theme park, Valdosta, Georgia – manufactured by Amazin' Mazes. Removed before 2010 season.
- Noah's Ark Water Park Mirror Maze, Wisconsin Dells, USA. Designed by Adrian Fisher
- Norton Museum of Art West Palm Beach, Florida. Pavement Maze, Serpent Mound and Turf Labyrinth. Designed by Adrian Fisher.
- Palace of Sweets Mirror Maze, Wildwood, New Jersey, USA. Designed by Adrian Fisher.
- Ridgewood Halloween Maze, Ridgewood, New Jersey, USA (Month of October, Loops and Traps Halloween-themed maze. Designed by Tyler Stewart.) Free attraction.
- Skyline Caverns Mirror Maze, Front Royal, Virginia, USA. Designed by Adrian Fisher.
- Tanglewood Music Center Hedge Maze, Lenox and Stockbridge, Massachusetts[62]
- Trail of Terror, Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA (annual event, 3/4 mile indoor Halloween-themed maze)[63]
Oceania
Australia
- The Maze, Perth, Western Australia[64]
- Ashcombe Maze, Shoreham, Victoria, Australia,[65]
- Mintaro Maze, Mintaro, South Australia,[66]
- A Maze'N Things,[67] Phillip Island (Victoria), Australia[68]
- Tasmazia & The Village of Lower Crackpot, Promised Land, Tasmania
New Zealand
- The Great Maze, The Puzzling World,[69] Wanaka, South Island (1.5 km of passages)
- Tothill's Mazes – Wooden Maze, Corn Maze, Lawn Labyrinth,[70] Christchurch, South Island
South America
Brazil
- Labirinto Verde, Nova Petrópolis, Rio Grande do Sul, (Circular hedge maze built in 1989; Latitude 29°22'32.71"S Longitude 51°06'43.68"W)
See also
References
- ^ Hermann Kern (2000). Through the labyrinth: designs and meanings over 5000 years. Prestel. p. 23. ISBN 9783791321448. http://books.google.com/books?id=pAFsQgAACAAJ. Retrieved 18 June 2011.
- ^ Feature Column from. the AMS. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Lappa Valley Steam Railway – Trevithick Brick Path Maze, Lappa Valley Steam Railway, http://www.lappavalley.co.uk/maze.htm, retrieved 13 June 2010
- ^ Maze to Tree. YouTube (2007-12-23). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Mazes, Vladimir Koziakin (Grosset & Dunlap, 1971) ISBN 0-448-01836-5
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Home. Soekershof. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google.com.au. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Retail Arabia to open French hypermarket Géant in The Gardens Shopping Mall | Nakheel Properties. AMEinfo.com. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ welcome to hikimi town!!. Iwami.or.jp. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ http://kankou.kisomura.com/kodama/g.html[dead link]
- ^ 巨大迷路パラディアム. Kinugawa.ne.jp. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ 仙台ハイランド ホームページ. Hi-land.co.jp. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ ::白浜エネルギーランド:: 移転連絡. Royalpines.co.jp. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Hortus Vitalis – Irrgarten und Erlebniswelt – Ausflugsziel in Bad Salzuflen. Hortus-vitalis.de. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ [1]
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Samsø Labyrinten – verdens største labyrint. Samsolabyrinten.com. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Jardins no Parque do Arnado. Ponte de Lima. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ C.M. Porto. Cm-porto.pt. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Reserva Florestal de Recreio do Pinhal da Paz (São Miguel). Azores.gov.pt. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ maze. Greatmaze.info. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ "Carnfunnock Maze". Larne Borough Council. http://www.larne.gov.uk/template1.asp?parent=588&parent2=646&pid=651&area=6&text=text=1. Retrieved 5 August 2010.
- ^ Records Search Page. Guinness World Records. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Glendurgan Garden. National Trust (2005-11-17). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Hoo Hill Maze. Wuff.me.uk. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ The Maize Maze. Farmmaze.co.uk (2005-07-10). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps (hard to see). Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Home – Wonderland. Wonderlandtelford.net. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Labyrinth Shed 16 | Home. Labyrintheduhangar16.com. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Page Title. Mcmaze.ca. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Amazing Chicago. Amazing Chicago. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Sever's Corn Maze – America's Largest Corn Maze – Shakopee, Minnesota. Severscornmaze.com. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Davis Mega Maze 2010 – Get Lost in the Adventure!. Davisfarmland.com. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ http://www.dole-plantation.com/Maze/maze.aspx[dead link]
- ^ Goofy Rooster Corn Maze Home-newest North Georgia Corn Maze. Goofyrooster.com. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Summer and Fall Family Fun at Maize Quest Fun Park PA (New Park, PA). Mazefunpark.com. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ "Music in the Berkshires: Classical Beyond Tanglewood, Part 3". Hampton Terrace. http://hamptonterrace.com/wp/153/music-in-the-berkshires-classical-beyond-tanglewood-part-3/. Retrieved 3 April 2011.
- ^ http://www.trailofterrorfest.com/home.htm[dead link]
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Amazenthings.com.au. Amazenthings.com.au. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Google Maps. Maps.google.com.au (1970-01-01). Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Puzzling World Wanaka New Zealand, Great Maze, Illusions, Puzzles, Wanaka Attraction, Family Fun NZ. Puzzlingworld.co.nz. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
- ^ Tothill's Mazes » Tothills Mazes. Tothills.com. Retrieved on 2011-06-18.
Further reading
- H. Abelson and A. diSessa, Turtle Geometry: The Computer as a Medium for Exploring Mathematics, MIT Press (1980)
- Adrian Fisher, The Amazing Book of Mazes, Thames & Hudson, London / Harry N Abrams Inc, New York (2006) ISBN 978-0-500-51247-0
- Adrian Fisher and Howard Loxton, Secrets of the Maze, Thames & Hudson, London (1997) / Barron’s Educational Series Inc, New York (1998) ISBN 978-0-500-01811-8
- Adrian Fisher and Jeff Saward, The British Maze Guide, Minotaur Designs, St Albans, UK (1991) – the definitive guide to British Mazes
- Adrian Fisher and Georg Gerster, The Art of the Maze, Weidenfeld & Nicolson, London (1990) ISBN 0-297-83027-9
- John Southcliffe Martineau, "Mazes and Labyrinths: In Great Britain", Wooden Books (2005) ISBN 978-1-9042-6333-3
- W. H. Matthews, Mazes and Labyrinths: Their History and Development (1927). Includes Bibliography. Dover Publications (1970) ISBN 0-486-22614-X
- Jeff Saward, Magical Paths, Mitchell Beazley (2002) ISBN 1-84000-573-4
External links
- Briefing Room CNN's Barry Neild offers escape routes
- Labyrinth Society
- Times Online: Britain's best mazes
Categories:- Mazes
- Garden features
- Puzzles
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.