- Pneumonectomy
-
Pneumonectomy Intervention 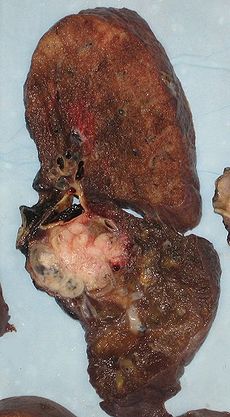
Appearance of the cut surface of a pneumonectomy specimen containing a lung cancer, here a Squamous cell carcinoma (the whitish tumor near the bronchi).ICD-9-CM 32.5 MeSH D011013 A pneumonectomy (or pneumectomy) is a surgical procedure to remove a lung. Removal of just one lobe of the lung is specifically referred to as a lobectomy, and that of a segment of the lung as a wedge resection (or segmentectomy).
Contents
Indications
The most common reason for a pneumonectomy is to remove tumourous tissue arising from lung cancer. In the days prior to the use of antibiotics in tuberculosis treatment, tuberculosis was sometimes treated surgically by pneumonectomy.
The operation will reduce the respiratory capacity of the patient; before conducting a pneumonectomy, the surgeon will evaluate the ability of the patient to function after the lung tissue is removed. After the operation, patients are often given an incentive spirometer to help exercise their remaining lung and to improve breathing function.
A rib or two is sometimes removed to allow the surgeon better access to the lung.
Types
There are two types of pneumonectomy:
- Simple pneumonectomy: removal of just the affected lung
- Extrapleural pneumonectomy (EPP): removal of the affected lung, plus part of the diaphragm, the parietal pleura (lining of the chest) and the pericardium (lining of the heart) on that side.[1] The linings are replaced by Gore-Tex in this radical and painful surgery that is used primarily for treatment of malignant mesothelioma. This technique produces the best long-term survival rates for this serious and fatal disease.[2]
History
Pioneering dates
- 1895: first pneumonectomy in multiple stages by William Macewen on a patient with tuberculosis and emphysema
- 1931: first successful pneumonectomy in two stages by Rudolph Nissen on a patient with crush injury to the thorax
- 1932: first lobectomy, by Harold Brunn
- 1933: first successful single-stage total pneumonectomy by Graham and Singer[3]
- 1939: first segmentectomy, by Churchill and Belsey
References
- ^ http://www.cancer.gov/templates/db_alpha.aspx?CdrID=367446
- ^ http://www.impmeso.org/extra_pleural_pheumonectomy/c30_p24/Mesothelioma_Treatments/Traditional_Treatments/Mesothelioma_Surgery/Pleural_Mesothelioma/Extrapleural_Pneumonectomy.html
- ^ Horn, L; Johnson DH (July 2008). "Evarts A. Graham and the first pneumonectomy for lung cancer". Journal of Clinical Oncology 26 (19): 3268–3275. doi:10.1200/JCO.2008.16.8260. PMID 18591561. http://jco.ascopubs.org/cgi/pdf_extract/26/19/3268.
External links
- Fuentes, P.Pneumonectomy: historical perspective and prospective insight European Journal of Cardio-thoracic Surgery 23 439–445
Respiratory system surgeries and other procedures (ICD-9-CM V3 21-22, 30-34, ICD-10-PCS 0B) Upper RT nose: Rhinoplasty · Septoplasty · Rhinectomy · Rhinomanometry
larynx: Laryngoscopy · Laryngectomy · Laryngotomy (Thyrotomy)Lower RT trachea: Cricothyrotomy · Tracheoesophageal puncture · Tracheotomy
lung: Pneumonectomy · Wedge resection · Lung transplantation · Decortication of lung · Heart-lung transplantChest wall, pleura,
mediastinum, and diaphragmMedical imaging Bronchography · CT pulmonary angiogram · High resolution CT · Spiral CT · Ventilation/perfusion scanCPRs Lung function test Cytology Respiratory therapy/
intubationCategories:- Lung cancer
- Surgical oncology
- Surgical removal procedures
- Oncology stubs
- Surgery stubs
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
