- Languages of Switzerland
-
Languages of Switzerland 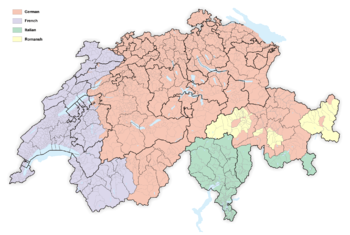
Official language(s) The blue areas represent bodies of water Main immigrant language(s) Albanian, Bosnian, Croatian, English, Macedonian, Portuguese, Serbian, Spanish, Turkish and Ukrainian. Main foreign language(s) English Sign language(s) Swiss Sign Language: Swiss German Sign Language, French Sign Language, Italian Sign Language[1] Common keyboard layout(s) QWERTZ

The four national languages of Switzerland are German, French, Italian, and Romansh.[2] Only three of these languages, however, maintain equal status as official languages at the national level within the Federal Administration of the Swiss Confederation: German, French, and Italian.[3]
Native speakers number about 64 percent (4.6 million) for German (mostly Swiss German dialects, though Swiss Standard German is used in writing and in a few official contexts in speaking), 20 percent (1.5 million) for French (mostly Swiss French, but including some Arpitan dialects), 6.5 percent (0.5 million) for Italian (mostly Swiss Italian, but including Lombard dialects), and less than 0.5 percent (35,000) for Romansh.[4]
The German region (Deutschschweiz) is in the north and center, the French part (Romandie) in the west and the Italian area (Svizzera italiana) in the south. There remains a small Romansh-speaking native population in Graubünden in the east. The cantons of Fribourg, Bern and Valais are officially bilingual; Graubünden is officially trilingual.
Contents
History
The percentage of non-national tongues spoken as a first language in Swiss homes has risen dramatically during the past half century, from less than one percent in 1950 to nine percent in 2000, mostly at the expense of German. The native languages of Swiss residents from 1950 to 2000, in percentages, were as follows:[4]
Year German French Italian Romansh other 2000 63.7 20.4 6.5 0.5 9.0 1990 63.6 19.2 7.6 0.6 8.9 1980 65.0 18.4 9.8 0.8 6.0 1970 64.9 18.1 11.9 0.8 4.3 1960 69.4 18.9 9.5 0.9 1.4 1950 72.1 20.3 5.9 1.0 0.7 National languages and linguistic regions
German
Further information: Swiss German and Swiss Standard German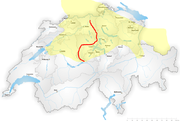 Distribution of High Alemannic dialects. Marked in red is the Brünig-Napf-Reuss line.
Distribution of High Alemannic dialects. Marked in red is the Brünig-Napf-Reuss line.
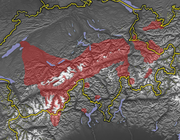 Distribution of Highest Alemannic dialects.
Distribution of Highest Alemannic dialects.
The German-speaking part of Switzerland (German: Deutsche Schweiz, French: Suisse alémanique, Italian: Svizzera tedesca, Romansh: Svizra tudestga) comprises about 65 percent of Switzerland (North Western Switzerland, Eastern Switzerland, Central Switzerland, most of the Swiss plateau and the greater part of the Swiss Alps).
In 17 Swiss cantons, German is the only official language (Aargau, Appenzell Ausserrhoden, Appenzell Innerrhoden, Basel-Stadt, Basel-Landschaft, Glarus, Lucerne, Nidwalden, Obwalden, Schaffhausen, Schwyz, Solothurn, St. Gallen, Thurgau, Uri, Zug, Zurich).[5]
In the cantons of Bern, Fribourg and Valais, French is co-official; in the trilingual canton of Graubünden, more than half of the population speaks German, while the rest speak Romansh or Italian. In each case, all languages are official languages of the respective canton.
While the French-speaking Swiss prefer to call themselves Romands and their part of the country la Romandie, the German-speaking Swiss used to refer to (and, colloquially, still do) the French-speaking Swiss as "Welsche", and to their area as Welschland, which has the same etymology as the English Welsh (see Walha). In Germany Welsch and Welschland refer to Italy; there, the term is antiquated, rarely used, and somewhat disparaging.
The German-speaking Swiss do not feel like a uniform group[citation needed]: the average German-speaking Swiss feels foremost belonging to Solothurn, St. Gallen, or Uri, and sees himself not speaking Swiss German, but the Baseldytsch (dialect of Basel), Bärndütsch (dialect of Bern) or Züridütsch (dialect of Zurich)[citation needed]. The marked subsidiarity of the Swiss federalism, where many political decisions are taken at municipal or cantonal level, supports this attitude.
By the Middle Ages there had developed a marked difference between the rural cantons of the German-speaking part of Switzerland and the city cantons, divided by views about trade and commerce. After the Reformation, all cantons were either Catholic or Protestant and the denominational influences on culture added to the differences. Even today, where all cantons are somewhat denominationally mixed, the different historical denominations can be seen in the mountain villages, where Roman Catholic Central Switzerland abounds with chapels and statues of saints, and the farm houses in the very similar landscape of the Protestant Bernese Oberland show Bible verses carved on the housefronts instead.
French
Main article: Swiss FrenchRomandy (French: Romandie, la Suisse romande, German: Romandie, Welschland, Welschschweiz or Westschweiz,[6]Italian: Svizzera romanda) is the French-speaking part of Switzerland. It covers the area of the cantons of Geneva, Vaud, Neuchâtel, and Jura as well as the French-speaking parts of the cantons of Bern (German-speaking majority), Valais (French-speaking majority), and Fribourg (French-speaking majority). 1.9 million people (or 24.4% of the Swiss population) live in Romandy.[7]
Standard Swiss French and the French of France are the same language, with some differences. For example, like some other regions of the French-speaking world, Swiss people (as well as most Francophone Belgians) use septante (seventy) instead of soixante-dix (literally, "sixty ten") and nonante (ninety) instead of "quatre-vingt-dix" ("four twenties and ten"). In the cantons of Vaud, Valais and Fribourg, speakers use huitante (eighty) instead of the Standard French "quatre-vingts" (four twenties).[8] "Sou" is used throughout Romandy for a 5-centime coin, as is "tune" (or "thune") when referring to a 5-Swiss-franc piece.
Historically, the vernacular language used by inhabitants of most parts of Romandy was Franco-Provençal. Franco-Provençal (also called Arpitan) is a language sometimes considered to be halfway between the langue d'oïl (the historical language of northern France and ancestor of French) and Occitan (the langue d'oc, spoken in southern France). Standard French and Franco-Provençal/Arpitan, linguistically, are distinct and mutual intelligibility is limited. Increasingly, Franco-Provençal/Arpitan is used only by members of the older generations.[citation needed]
The term Romandy does not formally exist in the political system, but is used to distinguish and unify the French-speaking population of Switzerland. The television channel Télévision Suisse Romande (TSR) serves the Romande community across Switzerland, is syndicated to TV5, and CanalSat Romande on October 2.[clarification needed]
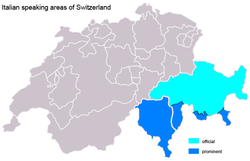
Italian
Main article: Swiss ItalianItalian Switzerland (Italian: Svizzera italiana, Romansh: Svizra taliana, French: Suisse italienne, German: italienische Schweiz) is the Italian-speaking part of Switzerland, which includes the Canton of Ticino and the southern part of Graubünden. Italian is also spoken in the Gondo Valley (leading to the Simplon Pass, on the southern part of the watershed) in Valais.
The linguistic region covers an area approximately 3,500 km² and has a total population of around 350,000 inhabitants,[9] with the number of Italophones residing in Switzerland being 470,000.[4]
The percentage of Italian-speaking Swiss has been rapidly decreasing since the 1970s, after reaching an all-time record of 12 percent of the population during the same decade; however this is entirely because of the reduced number of immigrants from Italy in the country: the percentage of native Italian-speaking Swiss has been steady at 4 percent since the 1950s.[4]
Romansh
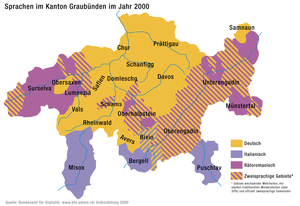 Distribution of Romansh in the canton Graubünden (2000).
Distribution of Romansh in the canton Graubünden (2000). Romansh speakingGerman speakingItalian speakingFurther information: Graubünden
Romansh speakingGerman speakingItalian speakingFurther information: GraubündenOn the cantonal level, Romansh is an official language only in the trilingual canton of Graubünden, where the municipalities in turn are free to specify their own official languages.
Significant communities of Romansh speakers remain in the Surselva, the Oberhalbstein valley, the lower Engadin and the Val Müstair.
Romansh has been recognized as one of four "national languages" by the Swiss Federal Constitution since 1938. It was also declared an "official language" of the Confederation in 1996, meaning that Romansh speakers may use their language for correspondence with the federal government and expect to receive a Romansh response – in Romansh Grischun, because the federal authorities use the standardized language exclusively.
Immigrant languages
The non-official language with the largest group of native speakers are the Serbo-Croatian languages with 103,000 (1.5%) speakers in 2000, followed by Albanian with 95,000 (1.3%), Portuguese with 89,500 (1.2%), Spanish with 77,500 (1.1%), English with 73,000 (1.0%), Macedonian with 61,300[citation needed] and Turkish with 44,500 (0.6%). Speakers of all other non-official languages totaled 173,000. Altogether, roughly 10 percent of the population has a native language other than the four official languages.[4]
See also
- Swiss (people)
- Demographics of Switzerland
- Röstigraben, referring to the asserted difference in mentality between Swiss Germans and the French-speaking Romands
- List of multilingual countries and regions
References
- ^ (Italian) Sguardo su una lingua e una realtà lavorativa - Articolo - VPOD SSP regione Ticino
- ^ "The Federal Constitution of the Swiss Confederation, article 4". http://www.admin.ch/ch/e/rs/101/a4.html. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
- ^ "Diversité des langues et compétences linguistiques en Suisse". http://www.nfp56.ch/f_projekt.cfm?kati=3. Retrieved 2009-04-30.
- ^ a b c d e Lüdi, Georges; Werlen, Iwar (April 2005). "Recensement Fédéral de la Population 2000 — Le Paysage Linguistique en Suisse" (in French, German, Italian) (Portable Document Format). Neuchâtel: Office fédéral de la statistique. http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/fr/index/infothek/lexikon/bienvenue___login/blank/zugang_lexikon.Document.52217.pdf. Retrieved 5 January 2006.
- ^ "The Federal Constitution of the Swiss Confederation, article 1". http://www.admin.ch/ch/e/rs/101/a1.html. Retrieved 2009-05-01.
- ^ "Welsch" is an old German word for "Foreign" and is the same word the Anglo-Saxons used for the original British inhabitants i.e. the people from Wales. It is considered a derogatory term in Switzerland which is not appreciated by the French Swiss unlike the word "Romandie" which derives from "Roman"[citation needed]
- ^ Statistique suisse, Bilan de la population résidante permanente (total) selon les districts et les communes, http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/fr/index/themen/01/02/blank/data/01.Document.67224.xls, retrieved 2010-12-21
- ^ (French) Septante, octante ou huitante, nonante
- ^ (French) Bilan de la population résidante permanente selon les cantons; calculated adding up the inhabitants in Ticino and 11 percent of the inhabitants of Grigioni
External links
- Swiss German
- A quick guide to the Swiss German language
- Characteristics of Swiss German dialects
- (Italian) Differences between the standard Italian language and Swiss Italian
- swiss-linguistics.com Information portal on current linguistic research in Switzerland
- sieps.ch Information Services on Swiss Private Schools and Universities
 Switzerland topics
Switzerland topicsHistory Early History · Old Confederacy · Reformation · Early Modern Switzerland · Napoleonic era · Restauration · During the World Wars · Modern historyLaw Constitution · Civil Code · Law enforcement · Nationality law · Copyright law · Gun politics · Human rights · LGBT rightsPolitics Geography AreasTopicsCantons · Cities · Extreme points · Lakes · Islands · Rivers · Glaciers · Mountains · Mountain passes · CartographyEconomy SIX Swiss Exchange · Berne eXchange · Swiss franc · Banking (list) · Swiss National Bank · Companies · Energy · Science and technology · Taxation · Tourism · Transport · TelecommunicationsMilitary Demographics Culture Symbols Languages of Europe Sovereign
states- Albania
- Andorra
- Armenia
- Austria
- Azerbaijan
- Belarus
- Belgium
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Bulgaria
- Croatia
- Cyprus
- Czech Republic
- Denmark
- Estonia
- Finland
- France
- Georgia
- Germany
- Greece
- Hungary
- Iceland
- Ireland
- Italy
- Kazakhstan
- Latvia
- Liechtenstein
- Lithuania
- Luxembourg
- Macedonia
- Malta
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- Netherlands
- Norway
- Poland
- Portugal
- Romania
- Russia
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Slovakia
- Slovenia
- Spain
- Sweden
- Switzerland
- Turkey
- Ukraine
- United Kingdom
- (England
- Northern Ireland
- Scotland
- Wales)
- Vatican City
States with limited
recognition- Abkhazia
- Kosovo
- Nagorno-Karabakh
- Northern Cyprus
- South Ossetia
- Transnistria
Dependencies
and other territories- Åland
- Faroe Islands
- Gibraltar
- Guernsey
- Jan Mayen
- Jersey
- Isle of Man
- Svalbard
Other entities - European Union
Categories:- Languages of Switzerland
- Regions of Switzerland
- Swiss society
- Geography of Switzerland
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.