- Canton of Uri
-
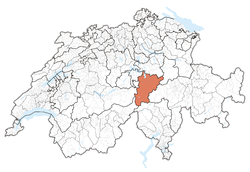
Kanton Uri — Canton of Switzerland — 
Coat of armsCoordinates: 46°47′N 8°37′E / 46.783°N 8.617°ECoordinates: 46°47′N 8°37′E / 46.783°N 8.617°E Capital Altdorf Subdivisions 20 municipalities Government – Executive Regierungsrat (7) – Legislative Landrat (64) Area[1] – Total 1,076.57 km2 (415.7 sq mi) Population (12/2009)[2] – Total 35,335 – Density 32.8/km2 (85/sq mi) Highest point 3,630 m (11,909 ft) - Dammastock Lowest point 434 m (1,424 ft) - Lake Lucerne Joined 1291 Abbreviation UR Languages German Website UR.ch Uri (German:
 Uri (help·info)) is one of the 26 cantons of Switzerland and a founding member of the Swiss Confederation. It is located in Central Switzerland. The canton's territory covers the valley of the Reuss River between Lake Lucerne and the St. Gotthard Pass. German is the primary language spoken in Uri. Uri was the only canton where the children in school had to learn Italian as their first foreign language. But in the school year of 2005/2006 this was changed to English as in most other cantons. The population is about 35,000 of which 3,046 (or 8.7%) are foreigners.[3] The legendary William Tell is said to have hailed from Uri. The historical landmark Rütli lies within the canton of Uri.
Uri (help·info)) is one of the 26 cantons of Switzerland and a founding member of the Swiss Confederation. It is located in Central Switzerland. The canton's territory covers the valley of the Reuss River between Lake Lucerne and the St. Gotthard Pass. German is the primary language spoken in Uri. Uri was the only canton where the children in school had to learn Italian as their first foreign language. But in the school year of 2005/2006 this was changed to English as in most other cantons. The population is about 35,000 of which 3,046 (or 8.7%) are foreigners.[3] The legendary William Tell is said to have hailed from Uri. The historical landmark Rütli lies within the canton of Uri.Contents
History
Uri was first mentioned in 732 as belonging to the abbot of Reichenau. In 853 it was given to the nunnery at Zürich by Louis the German.
It is thought that the name Uri derives from the old German word Aurochs meaning wild ox.[4] The region's traditional coat of arms bears a bull's head.[5]
In 1243 the region had a common seal. By 1274 the powerful Rudolf of Habsburg recognized these privileges. Uri was one of the three original Swiss cantons, having signed the Letter of Alliance (Bundesbrief) in 1291. In 1386 Uri participated in the victory over the Austrians at Sempach. As a result Uri annexed the lands of Urseren in 1410.
The region resisted the Protestant Reformation and remained Roman Catholic. During the Helvetic Republic Uri was part of the canton of Waldstätten. After this, in 1803 as part of the Act of Mediation, Uri regained its independence. All attempts towards religious or constitutional reform were resisted. In 1815 Uri joined the League of Sarnen for this reason. Later on Uri was one of the members of the Sonderbund. The Sonderbund was a separatist Catholic league, but was defeated by the Swiss Confederation which led to the Swiss Federal Constitution.
Geography
The canton is located in the centre of the country on the north side of the Swiss Alps. The lands of the canton are that of the Reuss valley and those of the main river's tributaries. The total area of the canton is 1,077 km2 (416 sq mi). About half of this is considered productive land. Forests cover a significant part of the territory, and glaciers make up 20% of the unproductive land.
The highest elevation in the canton, and in the Urner Alps as a whole, is the Dammastock, at 3,630 m (11,910 ft), north of the Furka Pass. The Glarus and Lepontine Alps ranges are also partially situated in the canton of Uri.
Government
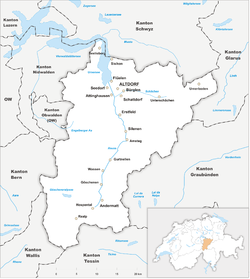
The current constitution dates back to 1888. It was revised in 1929 when the open assembly (Landsgemeinde) was abolished. Uri today comprises 20 self-administered territories: the cantonal capital is Altdorf.
Municipalities
The municipalities of the canton of Uri are: Altdorf, Andermatt, Attinghausen, Bauen, Bürglen, Erstfeld, Flüelen, Göschenen, Gurtnellen, Hospental, Isenthal, Realp, Schattdorf, Seedorf, Seelisberg, Silenen, Sisikon, Spiringen, Unterschächen, Wassen
Demographics
The population is primarily German-speaking and Roman Catholic. As of 2000[update] 86% of the population is Roman Catholic while only 6% are Protestant.[6]
Economy
The cultivated fields of the canton are located in the valley of the Reuss River. There are pastures on the lower mountain slopes. Since most of the terrain is extremely hilly, it is not suitable for cultivation. Hydroelectric power generation is of great importance. Forestry is one of the most important sectors of agriculture. At Altdorf there are cable and rubber factories.
Tourism is an important source of income in the canton of Uri. An excellent network of roads facilitates tourism in remote areas in the mountains.
External links
 Media related to Uri at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Uri at Wikimedia Commons- Official site (German)
- Official statistics
References
- ^ Arealstatistik Standard - Kantonsdaten nach 4 Hauptbereichen
- ^ Swiss Federal Statistical Office, MS Excel document – Bilanz der ständigen Wohnbevölkerung nach Kantonen, Bezirken und Gemeinden (German) accessed 25 August 2010
- ^ Federal Department of Statistics (2008). "Ständige Wohnbevölkerung nach Staatsangehörigkeit, Geschlecht und Kantonen" (Microsoft Excel). http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/de/index/themen/01/02/blank/key/raeumliche_verteilung/kantone__gemeinden.html. Retrieved November 5, 2008.
- ^
- Julius Caesar. “6.28”, Gallic War at Project Gutenberg
- ^ Angst, Walter (1992). A panoply of colors: the cantonal banners of Switzerland and the Swiss national flag. Pelinicus Books. p. 13. ISBN 9993300470. http://books.google.com/books?id=530WAQAAIAAJ&dq=A+Panoply+of+Colours:+The+Cantonal+Banners+of+Switzerland+and+the+Swiss+National+Flag. Retrieved 11 December 2009.
- ^ Federal Department of Statistics (2004). "Wohnbevölkerung nach Religion" (Interactive Map). http://www.bfs.admin.ch/bfs/portal/de/index/themen/01/05/blank/key/religionen.html. Retrieved 2009-01-15.
Three Cantons · Eight Cantons · Thirteen Cantons · coats of arms historical cantons: Unterwalden ·
Unterwalden ·  Basel ·
Basel ·  Appenzell · Baden · Bellinzona · Fricktal · Léman · Linth · Lugano · Oberland · Raetia · Säntis · WaldstättenCategories:
Appenzell · Baden · Bellinzona · Fricktal · Léman · Linth · Lugano · Oberland · Raetia · Säntis · WaldstättenCategories:- Uri
- Cantons of Switzerland
- Imperial valleys
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.