- Developed country
-
A developed country is a country that has a high level of development[clarification needed] according to some criteria. Which criteria, and which countries are classified as being developed, is a contentious issue. According to the International Monetary Fund, advanced economies comprise 65.8% of global nominal GDP and 52.1% of global GDP (PPP) in 2010[1].
Countries not fitting such definitions are classified as developing countries or undeveloped countries.
Contents
Similar terms
Terms similar to developed country include "advanced country", "industrialized country", "'more developed country" (MDC), more economically developed country" (MEDC), "Global North country", "first world country", and "post-industrial country. The term industrialized country may be somewhat ambiguous, as industrialization is an ongoing process that is hard to define. The term MEDC is one used by modern geographers to specifically describe the status of the countries referred to: more economically developed. The first industrialized country was the United Kingdom, followed by Belgium, Germany, United States, France and other Western European countries. According to some economists such as Jeffrey Sachs, however, the current divide between the developed and developing world is largely a phenomenon of the 20th century.[2]
Definition and criteria
Economic criteria have tended to dominate discussions. One such criterion is income per capita; countries with high gross domestic product (GDP) per capita would thus be described as developed countries. Another economic criterion is industrialization; countries in which the tertiary and quaternary sectors of industry dominate would thus be described as developed. More recently another measure, the Human Development Index (HDI), which combines an economic measure, national income, with other measures, indices for life expectancy and education has become prominent. This criterion would define developed countries as those with a very high (HDI) rating. However, many anomalies exist when determining "developed" status by whichever measure is used.[examples needed]
Kofi Annan, former Secretary General of the United Nations, defined a developed country as follows: "A developed country is one that allows all its citizens to enjoy a free and healthy life in a safe environment."[3] But according to the United Nations Statistics Division,
- There is no established convention for the designation of "developed" and "developing" countries or areas in the United Nations system.[4]
And it notes that
- The designations "developed" and "developing" are intended for statistical convenience and do not necessarily express a judgement about the stage reached by a particular country or area in the development process.[5]
The UN also notes
- "In common practice, Japan in Asia, Canada and the United States in northern America, Australia and New Zealand in Oceania, and Europe are considered "developed" regions or areas. In international trade statistics, the Southern African Customs Union is also treated as a developed region and Israel as a developed country; countries emerging from the former Yugoslavia are treated as developing countries; and countries of eastern Europe and of the Commonwealth of Independent States (code 172) in Europe are not included under either developed or developing regions."[4]
Human Development Index (HDI)
The UN HDI is a statistical measure that gauges a country's level of human development. While there is a strong correlation between having a high HDI score and a prosperous economy, the UN points out that the HDI accounts for more than income or productivity. Unlike GDP per capita or per capita income, the HDI takes into account how income is turned "into education and health opportunities and therefore into higher levels of human development."
Since 1990, Norway (2001–2006, 2009–2011), Japan (1990–91 and 1993), Canada (1992 and 1994–2000) and Iceland (2007–08) have had the highest HDI score. The top 47 countries have scores ranging from 0.793 in Barbados to 0.943 in Norway.
Many countries listed by IMF or[6] CIA as "advanced" (as of 2009), possess an HDI over 0.788 (as of 2010). Many countries[7] possessing an HDI of 0.788 and over (as of 2010), are also listed by IMF or CIA as "advanced" (as of 2009). Thus, many "advanced economies" (as of 2009) are characterized by an HDI score of 0.9 or higher (as of 2007).
The latest index was released on 2 November 2011 and covers the period up to 2011. The following are the 47 countries in the top quartile and classified as possessing a "Very high human development".[8]
Rank Country HDI New 2011 Estimates for 2011
[8]Change compared to new 2011 data for 2010[8] New 2011 Estimates for 2011
[8]Change compared to new 2011 data for 2010
[8]1 
 Norway
Norway0.943  0.002
0.0022 
 Australia
Australia0.929  0.002
0.0023 
 Netherlands
Netherlands0.910  0.001
0.0014 
 United States
United States0.910  0.002
0.0025 
 New Zealand
New Zealand0.908 
6 
 Canada
Canada0.908  0.001
0.0017 
 Ireland
Ireland0.908  0.001
0.0018 
 Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein0.905  0.001
0.0019 
 Germany
Germany0.905  0.002
0.00210 
 Sweden
Sweden0.904  0.003
0.00311 
 Switzerland
Switzerland0.903  0.002
0.00212 
 Japan
Japan0.901  0.002
0.00213  (1)
(1) Hong Kong
Hong Kong0.898  0.004
0.00414  (-1)
(-1) Iceland
Iceland0.898  0.002
0.00215 
 South Korea
South Korea0.897  0.003
0.00316 
 Denmark
Denmark0.895  0.002
0.00217 
 Israel
Israel0.888  0.002
0.00218 
 Belgium
Belgium0.886  0.001
0.00119 
 Austria
Austria0.885  0.002
0.00220 
 France
France0.884  0.001
0.00121 
 Slovenia
Slovenia0.884  0.002
0.00222 
 Finland
Finland0.882  0.002
0.00223 
 Spain
Spain0.878  0.002
0.00224 
 Italy
Italy0.874  0.001
0.001Rank Country HDI New 2011 Estimates for 2011
[8]Change compared to new 2011 data for 2010[8] New 2011 Estimates for 2011
[8]Change compared to new 2011 data for 2010
[8]25 
 Luxembourg
Luxembourg0.867  0.002
0.00226 
 Singapore
Singapore0.866  0.002
0.00227 
 Czech Republic
Czech Republic0.865  0.002
0.00228 
 United Kingdom
United Kingdom0.863  0.001
0.00129 
 Greece
Greece0.861  0.001
0.00130 
 United Arab Emirates
United Arab Emirates0.846  0.001
0.00131 
 Cyprus
Cyprus0.840  0.001
0.00132 
 Andorra
Andorra0.838 
33 
 Brunei Darussalam
Brunei Darussalam0.838  0.001
0.00134 
 Estonia
Estonia0.835  0.003
0.00335 
 Slovakia
Slovakia0.834  0.002
0.00236 
 Malta
Malta0.832  0.002
0.00237 
 Qatar
Qatar0.831  0.006
0.00638 
 Hungary
Hungary0.816  0.002
0.00239 
 Poland
Poland0.813  0.002
0.00240  (1)
(1) Lithuania
Lithuania0.810  0.005
0.00541  (-1)
(-1) Portugal
Portugal0.809  0.001
0.00142 
 Bahrain
Bahrain0.806  0.001
0.00143 
 Latvia
Latvia0.805  0.003
0.00344 
 Chile
Chile0.805  0.003
0.00345  (1)
(1) Argentina
Argentina0.797  0.003
0.00346  (-1)
(-1) Croatia
Croatia0.796  0.002
0.00247 
 Barbados
Barbados0.793  0.005
0.005Other lists of developed countries
Only three institutions have produced lists of "developed countries". The three institutions and their lists are the UN list (shown above), the CIA[9] list and the FTSE Group's list, whose list is not included because its association of developed countries with countries with both high incomes and developed markets is not deemed as directly relevant here.[10] However many institutions have created lists which are sometimes referred to when people are discussing developed countries. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) identifies 35 "advanced economies",[11] The OECD, also widely known as the 'developed countries club'[12][13][14] has 34 members. The World Bank identifies 66 "high income countries". The EIU's Quality-of-life survey and a list of countries with welfare states are also included here. The criteria for using all these lists and for countries' inclusion on these lists are often not properly spelt out, and several of these lists are based on old data.
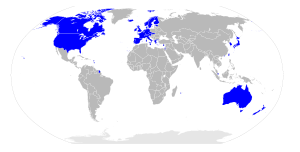
IMF advanced economies
According to the IMF the following 35 economies are classified as "advanced economies":[11]
 Australia
Australia Austria
Austria Belgium
Belgium Canada
Canada Cyprus
Cyprus Czech Republic
Czech Republic Denmark
Denmark Estonia
Estonia Finland
Finland France
France Germany
Germany Greece
Greece Hong Kong
Hong Kong Iceland
Iceland Ireland
Ireland Israel
Israel Italy
Italy Japan
Japan Luxembourg
Luxembourg Malta
Malta Netherlands
Netherlands New Zealand
New Zealand Norway
Norway Portugal
Portugal San Marino[15]
San Marino[15] Singapore
Singapore Slovakia
Slovakia Slovenia
Slovenia South Korea
South Korea Spain
Spain Sweden
Sweden Switzerland
Switzerland Taiwan
Taiwan United Kingdom
United Kingdom United States
United States
The CIA has modified an older version of the IMF's list of Advanced Economies, noting that the IMF's Advanced Economies list "would presumably also cover"[9] some smaller countries. These include:
•  Andorra
Andorra•  Bermuda
Bermuda•  Faroe Islands
Faroe Islands•  Holy See
Holy See•  Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein•  Monaco
MonacoDevelopment Assistance Committee members
There are 24 members — 23 selected OECD member countries and the European Commission—in the Development Assistance Committee,[16] a group of the world's major donor countries that discuss issues surrounding development aid and poverty reduction in developing countries.[17] The following OECD member countries are DAC members:
17 countries in Europe:
 Austria (since 1965)
Austria (since 1965) Belgium (since 1961)
Belgium (since 1961) Denmark (since 1963)
Denmark (since 1963) Finland (since 1975)
Finland (since 1975) France (since 1961)
France (since 1961) Germany (since 1961)
Germany (since 1961) Greece (since 1999)
Greece (since 1999) Ireland (since 1985)
Ireland (since 1985) Italy (since 1961)
Italy (since 1961) Luxembourg (since 1992)
Luxembourg (since 1992) Netherlands (since 1961)
Netherlands (since 1961) Norway (since 1962)
Norway (since 1962) Portugal (since 1961)1
Portugal (since 1961)1 Spain (since 1991)
Spain (since 1991) Sweden (since 1965)
Sweden (since 1965) Switzerland (since 1968)
Switzerland (since 1968) United Kingdom (since 1961)
United Kingdom (since 1961)
2 countries in Asia:
 Japan (since 1961)
Japan (since 1961) South Korea (since 2010)
South Korea (since 2010)
2 countries in North America:
 Canada (since 1961)
Canada (since 1961) United States (since 1961)
United States (since 1961)
2 countries in Oceania:
 Australia (since 1966)
Australia (since 1966) New Zealand (since 1973)
New Zealand (since 1973)
1 Joined the DAC in 1961, withdrew in 1974 and re-joined in 1991.
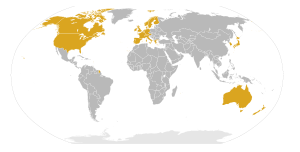
High-income OECD members
There are 31 high-income OECD members.[18] As of 2010, the High-income OECD membership is as follows:
24 countries in Europe:
3 countries in Asia:
2 countries in North America:
2 countries in Oceania:
Economist's quality-of-life survey of 2005
Research about standard of living and quality of life by the Economist Intelligence Unit resulted in a quality-of-life index, covering 111 countries. As of 2005, the top 30 countries are:[19]
Newsweek's Quality of Life Index of 2010
Newsweek published in 2010 the "world's best countries" index, measuring "health, education, economy, and politics" in 100 countries. As of 2010, the top 30 countries in terms of quality of life are:[20]
See also
- Developing country
- Least developed country
References
- ^ IMF GDP data (September 2011)
- ^ Sachs, Jeffrey (2005). The End of Poverty. New York, New York: The Penguin Press. ISBN 1-59420-045-9.
- ^ http://www.unescap.org/unis/press/G_05_00.htm
- ^ a b "Composition of macro geographical (continental) regions, geographical sub-regions, and selected economic and other groupings (footnote C)". United Nations Statistics Division. revised 17 October 2008. http://unstats.un.org/unsd/methods/m49/m49regin.htm#ftnc. Retrieved 2008-12-30.
- ^ http://unstats.un.org/unsd/methods/m49/m49.htm
- ^ The official classification of "advanced economies" is originally made by the International Monetary Fund (IMF). The IMF list doesn't deal with non-IMF members. The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) intends to follow IMF list but adds few economies which aren't dealt with by IMF due to their not being IMF members. By May 2001, the advanced country list of the CIA was more comprehensive than the original IMF list. However, since May 2001, three additional countries (Cyprus, Malta and Slovenia) have been added to the original IMF list, thus leaving the CIA list not updated.
- ^ Namely sovereign states, i.e., excluding Macau: In 2003 the government of Macau calculated its HDI as being 0.909 (the UN does not calculate Macau's HDI); In January 2007, the People's Daily reported (from China Modernization Report 2007): "In 2004... Macau... had reached the level of developed countries". However, Macau is not recognized by any international organisation as a developed/advanced territory, while the UNCTAD organisation (of the UN), as well as the CIA, classify Macau as a "developing" territory. The World Bank classifies Macau as a high income economy (along with developed economies as well as with few developing economies).
- ^ a b c d e f g h i [1]
- ^ a b CIA (2008). "Appendix B. International Organizations and Groups. World Factbook.". https://www.cia.gov/library/publications/the-world-factbook/appendix/appendix-b.html. Retrieved 2008-04-10.
- ^ http://www.ftse.com/Indices/Country_Classification/Downloads/FTSE_Country_Classification_Sept_09_update.pdf The Developed Countries Glossary entry reads: "The following countries are classified by FTSE as developed countries: Australia, Austria, Belgium/Luxembourg, Canada, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hong Kong, Ireland, Israel, Italy, Japan, Netherlands, New Zealand, Norway, Portugal, South Korea, Singapore, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, United Kingdom and the United States."
- ^ a b IMF Advanced Economies List. World Economic Outlook, April 2011, p. 173
- ^ http://www.hungarianquarterly.com/no160/104.shtml
- ^ http://www.indianexpress.com/old/ie/daily/19971214/34850733.html
- ^ http://www.esri.go.jp/en/forum1/minute/minute26-e.html
- ^ [http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2011/01/pdf/text.pdf World Economic Outlook, International Monetary Fund, April 2011, p. 169.
- ^ http://www.oecd.org/document/38/0,3343,en_2649_34603_1893350_1_1_1_1,00.html
- ^ DAC website >> "The DAC in Dates", On the DAC's self-description, see the introductory letter. On other events, refer to the relevant section by date.
- ^ http://data.worldbank.org/about/country-classifications/country-and-lending-groups#OECD_members
- ^ The world in 2005: The Economist Intelligence Unit's quality-of-life index, The Economist. Accessed on line January 8, 2007.
- ^ The world's best countries: 2010 index, Newsweek. Accessed on line August, 15 2010.
External links
- IMF (advanced economies)
- The Economist (quality of life survey)
- The World Factbook (developed countries)
- United Nations Statistics Division (definition)
- United Nations Statistics Division (developed regions)
- World Bank (high-income economies)
Economic classification of countries Developed country · Developing country · Least developed country · High income economy · Newly industrialized country · Heavily Indebted Poor CountriesWorlds Theory GDP Purchasing power parity (PPP)By country (future estimates · per capita [future estimates] · per hour worked, per person employed)GNI per capita Wages Other national accounts Human development Digital divide Lists of countries by GDP rankings Nominal Purchasing power parity (PPP) Per capita · Past to 1 AD (per capita) · Future (per capita) · Per hour · Per person employed · Relative differences between bordering countries per capitaGrowth Gross national income (GNI) Countries by region Africa (nominal · PPP) · Latin America & Caribbean (nominal · PPP) · North America (nominal · PPP) · South America (nominal · PPP) · Arab League · Asia · Asia & Pacific (nominal · nominal per capita · PPP) · Former Soviet Republics · Europe (nominal · nominal per capita · PPP · PPP per capita) · OceaniaSubnational divisions Argentina · Australia · Brazil · Canada · Chile (per capita) · China (per capita · top cities) · Croatia · France · Germany · India · Indonesia · Italy · Japan · Mexico · Pakistan · Russia · South Korea (per capita) · Spain · U.S. (comparison with countries) · OECD
Top country subdivisions by GDP (nominal)Lists of countries by financial rankings · Lists by country · List of international rankings · List of top international rankings by countryLists of countries by quality of life rankings Quality of life Satisfaction with Life · Human Development Index (inequality-adjusted) · Legatum Prosperity Index · Quality-of-life index · Home ownership rate · Happy Planet IndexEnvironment Ecological footprint · Environmental Performance Index · Environmental Sustainability Index · Environmental Vulnerability IndexConsumption/use of Related Categories:- Country classifications
- Human geography
- Economic geography
- Development
- Lists of countries
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.