- Mu Arae
-
Mu Arae Observation data
Epoch J2000.0 Equinox J2000.0Constellation Ara Right ascension 17h 44m 08.7s Declination −51° 50′ 03″ Apparent magnitude (V) +5.12 Characteristics Spectral type G3IV–V U−B color index 0.24 B−V color index 0.7 R−I color index 0.2 Astrometry Radial velocity (Rv) −9.0 km/s Proper motion (μ) RA: −15.06 mas/yr
Dec.: −191.17 mas/yrParallax (π) 64.47 ± 0.31 mas Distance 50.6 ± 0.2 ly
(15.51 ± 0.07 pc)Absolute magnitude (MV) +4.28 Details Mass 1.10 ± 0.01[1] M☉ Radius 1.36 ± 0.01[1] R☉ Luminosity 1.90 ± 0.10[1] L☉ Temperature 5820 ± 40[1] K Metallicity 200 ± 5%[1][note 1] Rotation 31 days Age 6.34 ± 0.40[1] Gyr Other designations Database references SIMBAD data NStED data ARICNS data Extrasolar Planets
Encyclopaediadata Mu Arae (μ Ara, μ Arae), often referred to by its designation in the Henry Draper catalogue HD 160691, is a main sequence G-type star around 50 light-years away from Earth in the constellation of Ara. The star has a planetary system with four known planets, three of them with masses comparable to that of Jupiter. The system's innermost planet was the first "hot Neptune or super-Earth" to be discovered.
Contents
Distance and visibility
According to measurements made by the Hipparcos astrometric satellite, Mu Arae exhibits a parallax of 64.47 milliarcseconds as the Earth moves around the Sun. When combined with the known distance from the Earth to the Sun, this means the star is located at a distance of 50.6 light years (15.51 parsecs).[2][note 2] Seen from Earth it has an apparent magnitude of +5.12 and is visible to the naked eye.
Stellar characteristics
Asteroseismic analysis of the star reveals it is approximately 10% more massive than the Sun and significantly older, at around 6,340 million years. The radius of the star is 36% greater than that of the Sun and it is 90% more luminous. The star contains twice the abundance of iron relative to hydrogen of our Sun and is therefore described as metal-rich. Mu Arae is also more enriched than the Sun in the element helium.[1]
Mu Arae has a listed spectral type of G3IV–V. The G3 part means the star is similar to our Sun (a G2V star). The star may be entering the subgiant stage of its evolution as it starts to run out of hydrogen in its core. This is reflected in its uncertain luminosity class, between IV (the subgiants) and V (main sequence dwarf star stars like the Sun).
Planetary system
Discovery
In 2001, an extrasolar planet was announced by the Anglo-Australian Planet Search team, together with the planet orbiting Epsilon Reticuli. The planet, designated Mu Arae b, was thought to be in a highly eccentric orbit of around 743 days.[3] The discovery was made by analysing variations in the star's radial velocity (measured by observing the Doppler shift of the star's spectral lines) as a result of being pulled around by the planet's gravity. Further observations revealed the presence of a second object in the system (now designated as Mu Arae e), which was published in 2004. At the time, the parameters of this planet were poorly constrained and it was thought to be in an orbit of around 8.2 years with a high eccentricity.[4] Later in 2004, a small inner planet designated Mu Arae c was announced with a mass comparable to that of Uranus in a 9-day orbit. This was the first of the class of planets known as "hot Neptunes" to be discovered. The discovery was made by making high-precision radial velocity measurements with the High Accuracy Radial Velocity Planet Searcher (HARPS) spectrograph.[5]
In 2006, two teams, one led by Krzysztof Goździewski and the other by Francesco Pepe independently announced four-planet models for the radial velocity measurements of the star, with a new planet (Mu Arae d) in a near-circular orbit lasting approximately 311 days.[6][7] The new model gives revised parameters for the previously known planets, with lower eccentricity orbits than in the previous model and including a more robust characterization of the orbit of Mu Arae e. The discovery of the fourth planet made Mu Arae the second known four-planet extrasolar system, after 55 Cancri.
System architecture and habitability
The Mu Arae system consists of an inner Uranus-mass planet in a tight 9-day orbit and three massive planets, probably gas giants, on wide, near-circular orbits, which contrasts with the high-eccentricity orbits typically observed for long-period extrasolar planets. The Uranus-mass planet may be a chthonian planet, the core of a gas giant which has had its outer layers stripped away by stellar radiation.[8] Alternatively it may have formed in the inner regions of the Mu Arae system as a rocky "super-Earth".[5] The inner gas giants "d" and "b" are located close to the 2:1 orbital resonance which causes them to undergo strong interactions. The best-fit solution to the system is actually unstable: simulations suggest the system is destroyed after 78 million years, which is significantly shorter than the estimated age of the star system. More stable solutions, including ones in which the two planets are actually in the resonance (similar to the situation in the Gliese 876 system) can be found which give only a slightly worse fit to the data.[7] Searches for circumstellar discs show no evidence for a debris disc similar to the Kuiper belt around Mu Arae. If Mu Arae does have a Kuiper belt, it is too faint to be detected with current instruments.[9]
The gas giant planet "b" is located in the liquid water habitable zone of Mu Arae. This would prevent an Earth-like planet from forming in the habitable zone, however large moons of the gas giant could potentially support liquid water. On the other hand it is unclear whether such massive moons could actually form around a gas giant planet, thanks to an apparent scaling law between the mass of the planet and its satellite system.[10] In addition, measurements of the star's ultraviolet flux suggest that any potentially habitable planets or moons may not receive enough ultraviolet to trigger the formation of biomolecules.[11] Planet "d" would receive a similar amount of ultraviolet to the Earth and thus lies in the ultraviolet habitable zone, however, it would be too hot for any moons to support surface liquid water.
Planet designations
The established convention for extrasolar planets is that the planets receive lower-case Roman letters starting from "b", in order of discovery. This system is used by the team led by Goździewski.[6] On the other hand, the team led by Pepe have proposed a modification of the designation system, where the planets are designated in order of characterization.[7] Since the parameters of the outermost planet were poorly constrained before the introduction of the 4-planet model of the system, this results in a different order of designations for the planets in the Mu Arae system. Both systems agree on the designation of the 640-day planet as "b". The old system designates the 9-day planet as "d", the 310-day planet as "e" and the outer planet as "c". Since the International Astronomical Union has not defined an official system for designations of extrasolar planets,[12] the issue of which convention is "correct" remains open, however subsequent scientific publications about this system appear to have adopted the Pepe et al. system, as has the system's entry in the Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia.[13][14]
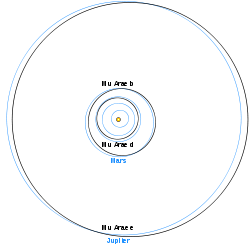
The Mu Arae system[7] Companion
(in order from star)Mass Semimajor axis
(AU)Orbital period
(days)Eccentricity c >0.03321 MJ 0.09094 9.6386 ± 0.0015 0.172 ± 0.04 d >0.5219 MJ 0.921 310.55 ± 0.83 0.0666 ± 0.0122 b >1.676 MJ 1.497 643.25 ± 0.90 0.128 ± 0.017 e >1.814 MJ 5.235 4205.8 ± 758.9 0.0985 ± 0.0627 See also
- 55 Cancri
- Extrasolar planet
- List of extrasolar planets
- PSR 1257+12
Notes
References
- ^ a b c d e f g Soriano, M.; Vauclair, S. (2009). "New seismic analysis of the exoplanet-host star Mu Arae". arXiv:0903.5475 [astro-ph].
- ^ van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "HIP 86796". Hipparcos, the New Reduction. http://webviz.u-strasbg.fr/viz-bin/VizieR-5?-out.add=.&-source=I/311/hip2&recno=86510. Retrieved 2009-04-11.
- ^ Butler et al.; Tinney, C. G.; Marcy, Geoffrey W.; Jones, Hugh R. A.; Penny, Alan J.; Apps, Kevin (2001). "Two New Planets from the Anglo-Australian Planet Search". The Astrophysical Journal 555 (1): 410–417. Bibcode 2001ApJ...555..410B. doi:10.1086/321467. http://www.iop.org/EJ/article/0004-637X/555/1/410/53257.html.
- ^ McCarthy et al.; Butler, R. Paul; Tinney, C. G.; Jones, Hugh R. A.; Marcy, Geoffrey W.; Carter, Brad; Penny, Alan J.; Fischer, Debra A. (2004). "Multiple Companions to HD 154857 and HD 160691". The Astrophysical Journal 617 (1): 575–579. arXiv:astro-ph/0409335. Bibcode 2004ApJ...617..575M. doi:10.1086/425214. http://www.iop.org/EJ/article/0004-637X/617/1/575/60746.html.
- ^ a b Santos et al.; Bouchy, F.; Mayor, M.; Pepe, F.; Queloz, D.; Udry, S.; Lovis, C.; Bazot, M. et al. (2004). "The HARPS survey for southern extra-solar planets II. A 14 Earth-masses exoplanet around μ Arae". Astronomy and Astrophysics 426 (1): L19 – L23. arXiv:astro-ph/0408471. Bibcode 2004A&A...426L..19S. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:200400076.
- ^ a b Gozdziewski, K. et al. (2006). "About the extrasolar multi-planet system around HD160691". arXiv:14, 2006 astro-ph/0608279August 14, 2006.
- ^ a b c d Pepe, F. et al. (2006). "The HARPS search for southern extra-solar planets. IX. μ Ara, a system with four planets". arXiv:18, 2006 astro-ph/0608396August 18, 2006.
- ^ Baraffe, I. et al. (2006). "Birth and fate of hot-Neptune planets". Astronomy and Astrophysics 450 (3): 1221–1229. arXiv:astro-ph/0512091. Bibcode 2006A&A...450.1221B. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20054040.
- ^ Schütz, O. et al. (2004). "A search for circumstellar dust disks with ADONIS". Astronomy and Astrophysics 424 (2): 613–618. arXiv:astro-ph/0408530. Bibcode 2004A&A...424..613S. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20034215.
- ^ Canup, R., Ward, W. (2006). "A common mass scaling for satellite systems of gaseous planets". Nature 441 (7095): 834–839. Bibcode 2006Natur.441..834C. doi:10.1038/nature04860. PMID 16778883.
- ^ Buccino, A. et al. (2006). "Ultraviolet Radiation Constraints around the Circumstellar Habitable Zones". Icarus 183 (2): 491–503. arXiv:astro-ph/0512291. Bibcode 2005astro.ph.12291B. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2006.03.007.
- ^ "Planets Around Other Stars". IAU. http://www.iau.org/PLANETS_AROUND_OTHER_STARS.247.0.html. Retrieved 16 September 2006.
- ^ Short, D.; Windmiller, G.; Orosz, J. A. (2008). "New solutions for the planetary dynamics in HD160691 using a Newtonian model and latest data". MNRAS 386 (1): L43–L46. Bibcode 2008MNRAS.386L..43S. doi:10.1111/j.1745-3933.2008.00457.x.
- ^ "Notes for star HD 160691". Title Extrasolar Planets Encyclopaedia. http://exoplanet.eu/star.php?st=HD+160691. Retrieved 2009-04-11.
External links
- Britt, Robert Roy (2004-08-25). "'Super Earth' Discovered at Nearby Star". Space.com. http://www.space.com/scienceastronomy/super_earth_040825.html. Retrieved 2008-07-17.
- "Fourteen Times the Earth". European Southern Observatory. 2004-08-25. http://www.eso.org/public/outreach/press-rel/pr-2004/pr-22-04.html. Retrieved 2008-07-17.
- "Mu Ara: a system with 4 planets". Geneva Observatory. http://obswww.unige.ch/Exoplanets/hd160691.html. Retrieved 2008-07-17.
- "Mu Arae". SolStation. http://www.solstation.com/stars2/mu-arae.htm. Retrieved 2008-07-17.
- "Mu Arae". Extrasolar Visions. http://www.extrasolar.net/startour.asp?StarCatId=&StarId=128. Retrieved 2008-07-17.
- Image Mu Arae
- Extrasolar Planet Interactions by Rory Barnes & Richard Greenberg, Lunar and Planetary Lab, University of Arizona
The Mu Arae System Stars Planets Star systems within 40–50 light-years from Earth with brightest member's absolute magnitude of +8.5 or brighter. Alpha Ophiuchi «Rasalhague» (46.7 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star)Capella (42.2 ± 0.5 ly; 4 stars)Alpha Cephei «Alderamin» (48.8 ± 0.4 ly; 1 star)Iota Ursae Majoris «Talitha Borealis» (47.7 ± 0.6 ly; 4 stars)Beta Trianguli Australis (40.2 ± 0.3 ly; 2 stars)‡ • Theta Ursae Majoris «Alhaud» (44.0 ± 0.4 ly; 3 stars) • Delta Aquilae «Denebokab» (50.1 ± 0.6 ly; 3 stars)‡36 Ursae Majoris (41.9 ± 0.4 ly; 2 stars) • Upsilon Andromedae (43.9 ± 0.4 ly; 2 stars, 4 planets: planet b • planet c • planet d • planet e) • 10 Tauri (44.8 ± 0.5 ly; 2 stars) • Iota Piscium (45.0 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star) • Alpha Fornacis «Dalim» (46.0 ± 0.4 ly; 2 stars) • Theta Boötis «Asellus Primus» (47.5 ± 0.4 ly; 2 stars) • Psi Capricorni «Yue» (47.9 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star) • Alpha Corvi «Alchiba» (48.2 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star) • Eta Leporis (49.1 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star) • Nu Phoenicis (49.1 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star) • Sigma Boötis «Hemelein Secunda» (50.4 ± 0.6 ly; 2 stars)‡Beta Aquilae «Alshain» (44.7 ± 0.5 ly; 2 stars) • b (31) Aquilae (49.4 ± 0.6 ly; 3 stars)Rho¹ (55) Cancri (40.9 ± 0.4 ly; 2 stars, 5 planets: planet e • planet b • planet c • planet f • planet d) • HR 483 (41.2 ± 0.4 ly; 2 stars) • Lambda Aurigae «Al Hurr» (41.2 ± 0.5 ly; 2 stars) • HR 683 (41.4 ± 0.4 ly; 1 star) • i (44) Boötis (41.6 ± 0.3 ly; 3 stars) • HR 6094 (42.0 ± 0.5 ly; 2 stars, 1 planet: planet b) • HR 6998 (42.4 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star) • 58 Eridani (43.4 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star) • HR 8501 (44.4 ± 0.4 ly; 2 stars) • 18 Scorpii (45.7 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star) • 47 Ursae Majoris (45.9 ± 0.4 ly; 1 star, 3 planets: planet b • planet c • planet d) • 26 Draconis (45.9 ± 0.3 ly; 3 stars) • Pi¹ Ursae Majoris (46.6 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star) • 72 Herculis (46.9 ± 0.4 ly; 1 star) • Nu² Lupi (47.5 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star, 3 planets: planet b • planet c • planet d) • HR 7898 (47.8 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star) • Psi Serpentis (47.9 ± 0.6 ly; 2 stars) • HR 3862 (48.5 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star) • 20 Leonis Minoris «Cor» (48.6 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star) • HD 176051 (48.9 ± 0.4 ly; 2 stars, 1 planet: planet b) • Mu Arae (49.8 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star, 4 planets: planet d • planet e • planet b • planet c)‡ • 51 Pegasi (50.1 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star, 1 planet: planet b «Bellerophon»)‡ • HR 2007 (50.8 ± 0.9 ly; 1 star, 1 planet: planet b)‡HR 4587 (42.1 ± 0.4 ly; 1 star) • Gamma Cephei «Errai» (45.0 ± 0.3 ly; 2 stars, 1 planet: planet b) • Eta Cephei «Al Agemim» (46.8 ± 0.3 ly; 1 star)HR 3384 (39.7 ± 0.3 ly; 1 star)‡ • HR 1925 (39.9 ± 0.4 ly; 1 star)‡ • Gliese 435 (40.8 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star) • HR 3259 (41.0 ± 0.4 ly; 1 star, 3 planets: planet b • planet c • planet d) • Gliese 349 (41.4 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star) • HR 6518 (41.7 ± 0.3 ly; 1 star) • HD 40307 (41.8 ± 0.3 ly; 1 star, 3 planets: planet b • planet c • planet d) • Gliese 428 (42.0 ± 1.0 ly; 2 stars) • Gliese 707 (42.3 ± 0.7 ly; 1 star) • Gliese 204 (42.3 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star) • Gliese 167 (42.7 ± 0.3 ly; 1 star) • Gliese 425 (42.9 ± 1.0 ly; 2 stars) • Gliese 716 (43.1 ± 0.5 ly; 1 star) • Gliese 174 (44.0 ± 0.8 ly; 1 star) • Gliese 656 (44.6 ± 0.6 ly; 1 star) • Gliese 5 (44.7 ± 0.5 ly; 2 stars) • AB Doradus (48.7 ± 0.4 ly; 2 stars)In left column are stellar classes of primary members of star systems. ‡Distance error margin extends out of declared distance interval. Italic are systems possibly located within declared distance interval, but probably not. Bayer Gould 1 G. • 2 G. • 3 G. • 4 G. • 5 G. • 6 G. • 7 G. • 8 G. • 9 G. • 10 G. • 11 G. • 12 G. • 13 G. (η) • 14 G. • 15 G. • 16 G. • 17 G. • 18 G. • 19 G. • 20 G. • 21 G. (ρ¹) • 22 G. • 23 G. (ζ) • 24 G. (ρ²) • 25 G. (ε¹) • 26 G. • 27 G. • 28 G. • 29 G. • 30 G. • 31 G. (ε²) • 32 G. • 33 G. • 34 G. • 35 G. • 36 G. • 37 G. • 38 G. • 39 G. • 40 G. • 41 G. • 42 G. • 43 G. • 44 G. • 45 G. • 46 G. • 47 G. • 48 G. • 49 G. (ι) • 50 G. (γ) • 51 G. (β) • 52 G. • 53 G. (κ) • 54 G. • 55 G. • 56 G. • 57 G. • 58 G. • 59 G. • 60 G. (δ) • 61 G. • 62 G. (α, Choo) • 63 G. • 64 G. • 65 G. • 66 G. • 67 G. (σ) • 68 G. • 69 G. (π) • 70 G. • 71 G. (λ) • 72 G. • 73 G. • 74 G. • 75 G. (μ) • 76 G. • 77 G. (ν¹) • 78 G. (ν²) • 79 G. • 80 G. • 81 G. • 82 G. • 83 G. • 84 G. (θ) • 85Nearby Gliese 674 • Gliese 682 • 41 G.List Categories:- Ara constellation
- Bayer objects
- Durchmusterung objects
- G-type main sequence stars
- G-type subgiants
- Gliese and GJ objects
- Henry Draper Catalogue objects
- HIP objects
- HR objects
- Planetary systems
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.