- Politics of Cornwall
-
NewquayMajor settlements of Cornwall

Cornwall is currently administered as a county of South West England whose politics are influenced by a number of issues that make it distinct from the general political scene in the wider UK, and the political trends of neighbouring counties. Its position on the geographical periphery of the island of Great Britain is also a factor.
Cornwall shares some of the political issues of the other "Celtic nations", in particular Wales, and a notable movement exists seeking greater powers of self-government within the UK, similar to that achieved in Wales. Cornish politics is also defined by its historical relationship between the Liberal Democrats (former Liberal party), and the Conservative Party, the main contenders for political office in Cornwall. There is also marked lack of organised trade unionism, and in many areas, Labour Party support.
Contents
History
Cornwall's politics have partly been dictated by its geography and history. It is a peninsula, relatively distant from London, and its main industries - fishing, farming and various kinds of mining, have been in decline for a long time. Cornwall's GDP still remains low. However, Cornwall is attractive to tourists, and to people seeking to move into the area to live. There are therefore tensions in the housing market between the demands of inward migrants to the area, and the needs of local people.
Historically, Cornwall was a Brythonic speaking area separate from the rest of England until about the 10th century, and retained much of its cultural distinctiveness in later centuries. Religious non-conformism was strong in Cornwall, and the Church of England was less well supported than some areas to the east. This has continued to inform later Cornish politics, in the form of Liberalism, now represented mainly by the Liberal Democrats can be traced to historical associations with Liberalism and non-conformist religion, particularly Methodism, in the 19th century and similarly land ownership and the Conservative party in the same period. The Conservative Party is also fairly strong in Cornwall, but for slightly different reasons. They suffered a particularly bad setback in the 1990s. However they regained three of the six Cornish seats in the 2010 general election. The Labour Party is traditionally much weaker in Cornwall than many other parts of the UK, although it has had some representation locally. This may be partly because there is no major urban centre in Cornwall - Plymouth tends to fulfil that role. Cornwall also traditionally elects a number of independent councillors, and is a centre for the rump Liberal Party in the UK.
The distinctive nature of Cornish politics has led to a significant number of office holders from both the Liberal Democrats and the Conservative Party being supportive of greater Cornish autonomy[citation needed]. However with both parties this has never been official national policy. 1986 saw the death of the charismatic MP David Penhaligon of the (then) Liberal Party. Penhaligon's career looked promising, with some tipping him as a future leader. In a speech he made in support of the Cornish miners at Camborne he said....
“ You need more in an economy than just tourism, icecream and deckchairs. Our mining industry is not a figment of the last decade or the last two decades. It has occupied Cornishmen and it has produced wealth for this century, the previous century and probably the last two thousand years; and what we’re asking the government to do is to recognise the great contribution we have made for the wealth of Britain, and in this time of great trial and tribulation to come to our assistance - that’s what we’re asking our government to do. ” Cornwall's distinctiveness as a national, as opposed to regional, minority has been periodically recognised by major British papers. For example, a Guardian editorial in 1990 pointed to these differences, and warned that they should be constitutionally recognised:
- "Smaller minorities also have equally proud visions of themselves as irreducibly Welsh, Irish, Manx or Cornish. These identities are distinctly national in ways which proud people from Yorkshire, much less proud people from Berkshire will never know. Any new constitutional settlement which ignores these factors will be built on uneven ground." [1]
At a local level the tradition of Independent candidates and councillors is far stronger than most other areas.[citation needed] Mebyon Kernow was formed in 1951, initially as a pressure group. Some of its members and supporters were politicians (councillors and MPs) from the three main British political parties, but later on, it became a party in its own right and members of other parties left. Its most famous supporter of the time was the novelist Daphne du Maurier. One of Mebyon Kernow's main campaigns is for a Cornish Assembly and in 2001 it presented a petition to 10 Downing Street with 50,000 signatures in favour of the Assembly.[2] This was backed up by Cornwall Council's Feb 2003 MORI poll which showed 55% in favour of an elected, fully devolved regional assembly for Cornwall and 13% against.[citation needed] (Previous result 46% in favour in 2002).[3]
Growing dissatisfaction with European Union fishing policy including the Common Fisheries Policy has recently led to a growth of support for United Kingdom Independence Party (UKIP) within fishing ports such as Newlyn. On 26 July 2007 the Conservative party appointed Mark Prisk (Member of Parliament for Hertford and Stortford) "Shadow Minister for Cornwall". This appointment was called "the fictional minister for Cornwall," by a Liberal Democrat MP, as there was no government minister to shadow. [4] The post was not continued following the 2010 election, and no longer exists. This was to put the Duchy's concerns "at the heart of Conservative thinking", according to a party statement. Conservative Party leader David Cameron said he wholeheartedly endorsed the appointment and it would ensure that the voice of Cornwall is heard.[5] However, as the post has been discontinued, this concept remains unproven.
Westminster representation
Following a review by the Boundary Commission for England taking effect at the 2010 general election, Cornwall is divided into six county constituencies to elect MPs to the House of Commons of the United Kingdom.
Before the 2010 boundary changes there were five constituencies in Cornwall. In the 2005 general election, all five seats were won by Liberal Democrats. However, at the 2010 general election Liberal Democrat candidates won three seats and Conservative candidates won three seats.
Current Cornish MPs
- Camborne & Redruth: George Eustice (Conservative)
- North Cornwall: Dan Rogerson (Liberal Democrat)
- South East Cornwall: Sheryll Murray (Conservative)
- St Austell & Newquay: Steve Gilbert (Liberal Democrat)
- St Ives: Andrew George (Liberal Democrat)
- Truro & Falmouth: Sarah Newton (Conservative)
See also 2010 United Kingdom general election result in Cornwall.
Cornwall Council
 Composition of Cornwall County Council following the 2005 elections. Yellow = Liberal Democrats, grey = independents & MK, blue = Conservatives, red = Labour.
Composition of Cornwall County Council following the 2005 elections. Yellow = Liberal Democrats, grey = independents & MK, blue = Conservatives, red = Labour.
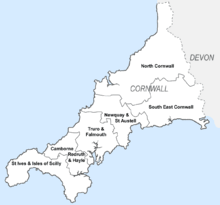
As of 1 April 2009 Cornwall became a unitary authority, with the headquarters of Cornwall Council based in Truro. Before April 2009, Cornwall was a non-metropolitan county that followed the three tier system typical of English shire counties, and had six districts: Penwith, Kerrier, Carrick, Restormel, Caradon and North Cornwall. Cornwall Council provides a wide range of services to more than half a million residents, has an annual budget of more than £1 billion, and is the biggest employer in Cornwall.[6]
The Isles of Scilly, which are part of the ceremonial county of Cornwall, are not part of the Cornwall unitary authority, as they have their own unitary council.
Cornwall Council election results, 4 June 2009
Main article: Cornwall Council election, 2009Elections for the new unitary Cornwall Council were held on 4 June 2009, and 123 members were elected, replacing the previous 82 councillors of Cornwall County Council and also another 249 (some of whom were also county councillors) on the six district councils.[7] At the 2009 elections, the Liberal Democrats lost overall control of Cornwall, with no single party gaining overall control of the new council. Although the Conservatives now have the largest number of elected members, they do not have a majority.[8] The Conservatives received 34% of the vote and won 50 seats, followed by the Liberal Democrats on 28% winning 38 seats, the Independents 23% and 32 seats, and Mebyon Kernow 4% and three seats. The turnout was 41%. Labour, the Green Party, UKIP and the BNP failed to secure any seats in Cornwall.[9][10]
Cornish nationalism
- Main articles: Cornish nationalism, Constitutional status of Cornwall
Two of the major factors in Cornish nationalism are the disputed position of Cornwall as separate constitutional entity within the UK and the rights of the Cornish people as a minority.[11] These issues affect all of those involved in Cornish politics, even those who are at odds with these ideas. Three UK political parties recognise the cause of Cornish self determination, the Liberal Party, the Cornish section of the Green Party of England and Wales and the Communist Party of Britain.
An Gof have also expressed Cornish nationalism, though not in political ways as much as violent ones.
Cornish nationalist and/or regionalist organisations
- Main articles: Mebyon Kernow
The principal political party in the Cornish Nationalist movement is Mebyon Kernow which labels itself as a 'centre-left, green and decentralist party' and has close association with its sister party Plaid Cymru in Wales. Mebyon Kernow's membership is currently calculated at around 1000 members across Cornwall. In 1979, in the first elections to the European Parliament, Mebyon Kernow won almost 10% (over 10,000 votes) of the vote in the Cornwall seat. This reflected a decade of steady growth for the party. MK continues to contest parliamentary seats and also local government seats.
In the 2010 general election, Mebyon Kernow fielded candidates in each of the constituencies in Cornwall. Their best result was in St Austell and Newquay seat where they came fourth with 4.2% of the votes, up 4% from the previous election.
In the other seats contested they came in; North Cornwall: 5th, (last place) 1.1% of votes, -2.1% South Cornwall: 6th (last place) 1.3% of votes, -0.4% Truro and Falmouth: 5th 2.1% of votes, -0.4% Camborne and Redruth: 5th 1.4% of votes +1.4% St Ives 7th (last place) 0.8% of votes, +0.8%
All Mebyon kernow candidates lost their deposits. [12]
In the district elections of 2007 seven Mebyon Kernow district councillors were elected. MK lost one district seat and gained two, a net gain of one. This gave them seven of the 249 seats (2.8% of seats) up for election. Mebyon Kernow got around 5 percent of the total vote in these district elections, putting the party in third position behind the Liberal Democrats and the Conservative Party and ahead of Labour in several seats including Kerrier, Restormel, North Cornwall and Caradon.[13]
Several former Cornish MPs were also members of Mebyon Kernow, including Peter Bessell (Liberal Party), John Pardoe (Liberal Party), David Mudd (Conservative), David Penhaligon (Liberal Party) and currently Andrew George (Liberal Democrats).[14]
The Cornish Nationalist Party was founded as a splinter group from Mebyon Kernow in the 1970s following a split over the ideological path of the Cornish National Movement, the members of the Cornish Nationalist party favouring a more 'right of centre approach' to attracting support. Initially led by Dr James Whetter, the Cornish Nationalist Party are not currently a registered political party under the Registration of Political Parties Act 1998 and therefore cannot stand for local or Westminster elections.
In addition to political parties, other independent organisations promote the autonomy movement. The Cornish Stannary Parliament is a human rights pressure group which claims to be a revival of the mediaeval Stannary Parliaments, local legislative organisations in the mining regions. It was established in 1974 and had campaigned since then against the government of the United Kingdom's position on the constitutional status of Cornwall. Other groups include TGG (Tyr-Gwyr-Gweryn), Cornwall 2000, Cornish Solidarity who are constitutional and Cornish human rights groups and the Cornish Constitutional Convention which campaigns for a Cornish Assembly.
Seneth an Stenegow Kernow (Cornish Stannary Parliament)
The Cornish Stannary Parliament (Seneth an Stenegow Kernow) are another pressure group but do not stand in elections at present. The Cornish Stannary Parliament is the original governing body of Cornwall's historic tin mining community. Today it plays a key role in ensuring that the people, land and heritage of Cornwall are treated fairly in the eyes of a UK legal system that some consider to be failing in its capacity to recognise Cornwall's distinct constitutional position.[15]
Other issues and lobby groups
Within Cornwall there are a growing number of pressure groups/lobbying groups devoted to Cornish issues other than the national question. Local environmental issues feature prominently, notably the Surfers against Sewage group, formed in this region, heavily dependent on the tourist industry. The Campaign for Nuclear Disarmament (CND) has a local presence, with a branch in Penzance.[16] Some east Cornwall CND activists are members of the Plymouth branch. There is a Cornish branch of Greenpeace.[17] Amnesty International have a local branch.
See also
Other Cornish politicians
- Doris Ansari (Chairman Cornwall County Council) [18]
- List of all Cornwall County Councillors
- Dick Cole - (leader of Mebyon Kernow)
- Paul Tyler - (Liberal Democrats) Life peer
- Mark Prisk - former Shadow Minister for Cornwall & MP (was a new position with no government opposite number)
Elections and results
- Truro by-election, 1987
- 2001 United Kingdom general election result in Cornwall
- 2005 United Kingdom general election result in Cornwall
- 2010 United Kingdom general election result in Cornwall
- Cornwall local elections
- Cornwall Council election, 2009
Parliamentary representation from Cornwall
Further information: Parliamentary representation from Cornwall- St Ives (UK Parliament constituency)
- Camborne and Redruth (UK Parliament constituency)
- Truro and Falmouth (UK Parliament constituency)
- St Austell and Newquay (UK Parliament constituency)
- North Cornwall (UK Parliament constituency)
- South East Cornwall (UK Parliament constituency)
Historic Cornish Parliamentary constituencies
- Bodmin (UK Parliament constituency)
- Bossiney (UK Parliament constituency)
- Callington (UK Parliament constituency)
- Camelford (UK Parliament constituency)
- Cornwall (UK Parliament constituency)
- East Cornwall (UK Parliament constituency)
- West Cornwall (UK Parliament constituency)
- East Looe (UK Parliament constituency)
- East Looe and West Looe (UK Parliament constituency)
- Falmouth and Camborne (UK Parliament constituency)
- Fowey (UK Parliament constituency)
- Grampound (UK Parliament constituency)
- Helston (UK Parliament constituency)
- Launceston (UK Parliament constituency)
- Liskeard (UK Parliament constituency)
- Lostwithiel (UK Parliament constituency)
- Mitchell (UK Parliament constituency)
- Newport (Cornwall) (UK Parliament constituency)
- Penryn (UK Parliament constituency)
- Penryn and Falmouth (UK Parliament constituency)
- St Austell (UK Parliament constituency)
- St Germans (UK Parliament constituency)
- St Mawes (UK Parliament constituency)
- Saltash (UK Parliament constituency)
- Tregony (UK Parliament constituency)
- Truro (UK Parliament constituency)
- Truro and St Austell (UK Parliament constituency)
- West Looe (UK Parliament constituency)
Constitutional status of Cornwall
- Revived Cornish Stannary Parliament
- Cornwall (territorial duchy)
- Duchy of Cornwall
- Duke of Cornwall
- Royal Commission on the Constitution (United Kingdom)
- Constitutional status of Cornwall
- Stannary Courts and Parliaments
- Cornwall Commonwealth Games Association
- Cornish self-government movement
- Mebyon Kernow
- Celtic League (political organisation)
- Cornish Assembly
- Cornish Nationalist Party
- Fry an Spyrys
References
- ^ The Guardian, editorial, 8th May 1990
- ^ 50,000 Assembly petition presented to 10 Downing Street
- ^ Give Cornwall what it wants.
- ^ http://www.newstatesman.com/uk-politics/2009/03/conservative-party-local-mps
- ^ Mark Prisk appointed Tory Shadow Minister for Cornwall
- ^ Cornwall Council 2009 elections
- ^ Cornwall Council June 2009 Electoral divisions
- ^ Lib Dems lose control of Cornwall in June 2009 Cornwall Council elections
- ^ Cornwall Council election results 5 June 2009
- ^ BBC Cornwall 2009 Cornwall Council election results
- ^ Cornish demand recognition on the 2011 Census
- ^ [1]
- ^ BBC - 2007 Local Election results
- ^ Mebyon Kernow
- ^ Cornish Stannary Parliament
- ^ CND - Local Group Contacts
- ^ Greenpeace Active Supporters
- ^ Members: Details
External links
- Cornwall County Council
- The Cornish Stannary Parliament
- Mebyon Kernow
- Tories to appoint Cornwall Minister
- TGG (Tyr Gwyr Gweryn)
- You Tube - Mark Prisk
Geography of Cornwall Unitary authorities Major settlements Bodmin • Bude • Callington • Camborne • Camelford • Falmouth • Fowey • Hayle • Helston • Launceston • Liskeard • Looe • Lostwithiel • Marazion • Newlyn • Newquay • Padstow • Par • Penryn • Penzance • Porthleven • Redruth • Saltash • St Austell • St Blazey • St Columb Major • St Ives • St Just-in-Penwith • St Mawes • Stratton • Torpoint • Truro • Wadebridge
See also: Civil parishes in CornwallRivers Topics History • Status debate • Flag • Culture • Places • People • The Duchy • Diocese • Politics • Hundreds/shires • Places of interest • full list...Celtic nations and their cultures Nations Languages Peoples Culture Music Sport Bando · Cammag · Cnapan · Cornish hurling · Cornish wrestling · Curling · Gaelic football · Gaelic handball · Golf · Gouren · Rounders · Highland games · Hurling · Road bowls · ShintyPolitical parties in the United Kingdom House of Commons (650): Conservatives (307) · Labour (258, including 28 Labour Co-operative)* · Liberal Democrats (57) · DUP (8) · SNP (6) · Sinn Féin† (5) · Plaid Cymru (3) · SDLP (3) · Greens (E&W) (1) · Alliance (1) · Independent (1)House of Lords (789): Labour (243) · Conservatives (218) · crossbenchers (182) · Liberal Democrats (92) · Lords Spiritual (26) · DUP (4) · UUP (4) · UKIP (2) · Plaid Cymru (1) · Conservative Independent (1) · Independent Labour (1) · non-affiliated (16)Scottish Parliament (129): SNP (69) · Scottish Labour (37) · Scottish Conservatives (15) · Scottish Liberal Democrats (5) · Scottish Greens (2) · Independent (1)National Assembly for Wales (60): Northern Ireland Assembly (108): DUP (38) · Sinn Féin (29) · UUP (16) · SDLP (14) · Alliance (8) · Greens (NI) (1) · Traditional Unionist Voice (1) · Independent (1)London Assembly (25): European Parliament
(72 of 736):Conservatives (ECR, 25, including 1 UCUNF)‡ · Labour (PES, 13) · UKIP (EFD, 13) · Liberal Democrats (ELDR, 11) · BNP (Non-Inscrit, 2) · Greens (E&W) (EGP, 2) · SNP (EFA, 2) · Plaid Cymru (EFA, 1) · Sinn Féin (EUL-NGL, 1) · DUP (Non-Inscrit, 1)Other national and regional parties: Christian Peoples Alliance · Christian · Communist Party of Britain · English Democrats · Independent Working Class Association · IKHH · Liberal · Mebyon Kernow · National Front · Official Monster Raving Loony · Progressive Unionist · Respect · Scottish Socialist · Social Democratic · Socialist Labour · Socialist · Socialist Workers · Solidarity · Workers' Party of IrelandNotes: *Co-operative Party candidates stand jointly with the Labour Party as “Labour and Co-operative Party” candidates. †Although Sinn Féin have five elected members and have offices at Westminster, they are abstentionist and therefore do not take their seats. ‡Some Ulster Unionist Party candidates stand jointly with the Conservative Party as "Ulster Conservatives and Unionists – New Force" candidates.Portal:Politics - List of political parties by representation - Politics of the United KingdomCategories:
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.