- Tolperisone
-
Tolperisone 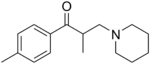
Systematic (IUPAC) name 2-methyl-1-(4-methylphenyl)-3-(1-piperidyl)propan-1-one Clinical data AHFS/Drugs.com International Drug Names Pregnancy cat. ? Legal status ? Identifiers CAS number 728-88-1 
ATC code M03BX04 PubChem CID 5511 UNII F5EOM0LD8E 
KEGG D08617 
Chemical data Formula C16H23NO Mol. mass 245.36 g/mol SMILES eMolecules & PubChem  (what is this?) (verify)
(what is this?) (verify)Tolperisone, a piperidine derivative, is a centrally-acting muscle relaxant. Trade names include Biocalm,Muscodol, Mydeton, Mydocalm, Myolax, Myoxan and Viveo.
Contents
Clinical use
Typically, tolperisone is indicated in the treatment of acute muscle spasms in back pain and spasticity in neurological diseases.
Manufacturer claims
Tolperisone is currently marketed in Europe as a centrally-acting muscle relaxant, which reportedly has special advantages over other drugs of its class, in that it reportedly does not cause drowsiness or lethargy, according to some manufacturers.[1]
Besides claiming "tolperisone has an excellent efficacy and safety profile", these manufacturers also state[1] tolperisone has the unique property of mediating muscle relaxation "without concomitant sedation" and it does not cause incoordination, weakness, mental confusion or withdrawal phenomena, in contrast to other muscle relaxants.
== Indications ==
Tolperisone is reportedly used in the typical treatment of the following conditions:
- Pathologically increased tone of the cross-striated muscle caused by neurological diseases (damage of the pyramidal tract, multiple sclerosis, myelopathy, encephalomyelitis)
- Spastic paralysis and other encephalopathies manifested with muscular dystonia
- Spondylosis
- Spondylarthrosis
- Cervical and lumbar syndromes
- Arthrosis of the large joints
- Obliterating atherosclerosis of the extremity vessels
- Diabetic angiopathy
- Thromboangiitis obliterans
- Raynaud's syndrome'Bold text
Contraindications and cautions
Manufacturers report that tolperisone should not be used in the following conditions:
- Myasthenia
- Children under 1 years of age
- Pregnancy
- Breastfeeding
Side effects and adverse reactions
Some people using tolperisone have reported[2] the following reactions:
- In hypersensitivity: muscle weakness, headache, arterial hypotension, nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia.
- Skin allergic reactions: skin rash, hives, Quincke's edema, anaphylactic shock.
The side effects and reactions listed above may not include all effects reported by the drug's manufacturer.
Interactions
Tolperisone is believed to have few interactions with other medicines, but this does not rule out any interactions that may not have been reported to caregivers thus far.
Some manufacturers have stated tolperisone may enhance the effects of other neuromuscular blocking agents.
Dosage
 A blister package of Mydocalm 50mg tablets intended for distribution in the Slovak Republic
A blister package of Mydocalm 50mg tablets intended for distribution in the Slovak Republic
According to various sources, the typical oral adult dose for tolperisone is 150-450 mg in a 24-hour period, divided into two or three portions. It is highly advised that dosage information be confirmed by information provided from the manufacturer and prescriber.
More detailed dosage information[3] is as follows:
Adults over 12 years old:
- Oral: 50-150 mg every 8 hours
- IM: 100 mg every 12 hours.
- IV: 100 mg over 24 hours.
Pediatric dosage (minimum weight of 20 kg, minimum age 6 years):
- Oral dosage: 1.0 mg/kg every 8 hours.
Neonatal dosage (minimum weight of 3 kg)
- 2.5 mg/kg every 8 hours.
Also see
- Tolperisone at Drug Info Systems (www.druginfosys.com)
- Papers and safety and efficacy studies of tolperisone at BioInfo
- Tolperisone at Sanochemia Austria
External links
- Hofer D, Lohberger B, Steinecker B, Schmidt K, Quasthoff S, Schreibmayer W (2006). "A comparative study of the action of tolperisone on seven different voltage dependent sodium channel isoforms". Eur J Pharmacol 538 (1–3): 5–14. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2006.03.034. PMID 16650844.
- Kocsis P, Farkas S, Fodor L, Bielik N, Thán M, Kolok S, Gere A, Csejtei M, Tarnawa I (2005). "Tolperisone-type drugs inhibit spinal reflexes via blockade of voltage-gated sodium and calcium channels". J Pharmacol Exp Ther 315 (3): 1237–46. doi:10.1124/jpet.105.089805. PMID 16126840.
- Ribi C, Vermeulen C, Hauser C (2003). "Anaphylactic reactions to tolperisone (Mydocalm)". Swiss Med Wkly 133 (25–26): 369–71. PMID 12947534.
Footnotes
Skeletal muscle relaxants (M03) Peripherally acting
(primarily antinicotinic,
NMJ block)Curare alkaloidsultra-short duration: Gantacurium
short duration: Mivacurium • Chandonium
intermediate duration: Atracurium • Cisatracurium • Fazadinium • Rocuronium • Vecuronium
long duration: Doxacurium • Dimethyltubocurarine • Pancuronium • Pipecuronium • Laudexium • Gallamine
unsorted: Hexafluronium (Hexafluorenium)Choline derivatives: Suxamethonium (Succinylcholine)
Polyalkylene derivatives: HexamethoniumCentrally acting Carbamic acid estersBenzodiazepinesAnticholinergics (Antimuscarinics)OtherBaclofen • Chlormezanone • Chlorphenesin • Chlorzoxazone • Donepezil • Eperisone • Flopropione • Mephenesin • Mephenoxalone • Metaxalone • Phenyramidol • Pridinol • Promoxolane • Quinine • Thiocolchicoside • Tizanidine • Tolperisone • TrazodoneDirectly acting Categories:- Piperidines
- Muscle relaxants
- Aromatic ketones
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
